Difference between revisions of "Globalyzer 5 Java Rules"
(→User Interface) |
(→User Interface) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
* '''Class or Variable Type(s)''': This is a pattern which would match the class name. It could be something like <code>java.sql.Connection</code> |
* '''Class or Variable Type(s)''': This is a pattern which would match the class name. It could be something like <code>java.sql.Connection</code> |
||
* '''Description''': The description or the reason for this filter could be something like "java.sql.Connection prepareStatement do not need to be externalized into a resource bundle for i18n purposes" |
* '''Description''': The description or the reason for this filter could be something like "java.sql.Connection prepareStatement do not need to be externalized into a resource bundle for i18n purposes" |
||
| − | * '''Help''': The link to a more verbose help page which may indicate the context and the reason for the filter. |
+ | * '''Help Page''': The link to a more verbose help page which may indicate the context and the reason for the filter. |
= Type of Rules = |
= Type of Rules = |
||
Revision as of 15:44, 27 October 2015
Contents
Introduction
User Interface
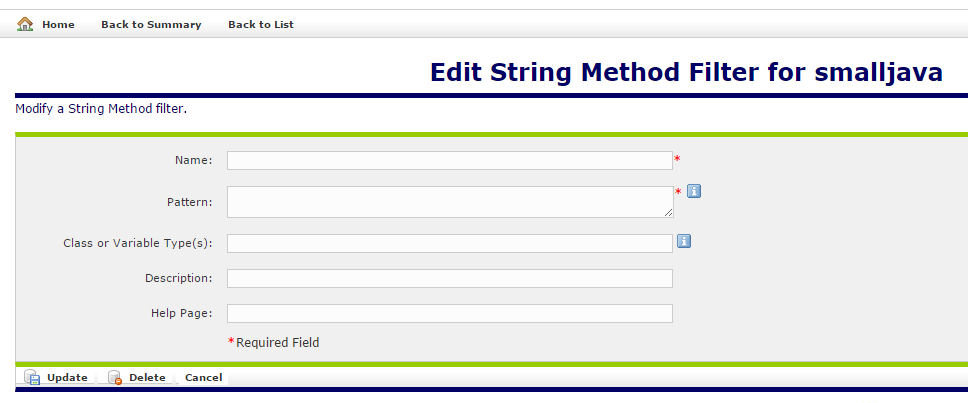
The Globalyzer 5 Java Rules allow for class names to be specified as part of the rule. The following UI shows how to configure a new String Method Filter for the smalljava rule set.
- Name: That the name of the rule. It could be something like
SQL Connection prepareStatement - Pattern: That is the pattern which would match the method name. It could be something as simple as
prepareStatement - Class or Variable Type(s): This is a pattern which would match the class name. It could be something like
java.sql.Connection - Description: The description or the reason for this filter could be something like "java.sql.Connection prepareStatement do not need to be externalized into a resource bundle for i18n purposes"
- Help Page: The link to a more verbose help page which may indicate the context and the reason for the filter.
Type of Rules
Example
Code Snippet
import company.util.Dbg; // A fully qualified class name
import company.project.*; // Label is in the company.project package.
[...]
Dbg dbg = Dbg.getInstance();
Label lbl = new Label();
[...]
dbg.setText("{0}: {1} action taken.");
[...]
label.setText("Menu");
This snippet of code does have strings.
The class company.project.Dbg is a debug class and the text method puts the String parameter into a database for support purposes. That string is not visible to the end user. In that instance, the setText method on a variable of type company.project.Dbg should be filtered.
The variable lbl of class company.project.Label represents a text area in the User Interface and the setText method passes a user visible string. The string Menu passed to this setText method should be flagged: It needs to be externalized out of the code into a resource bundle.