Difference between revisions of "Machine Learning"
(→Work Flow) |
(→Work Flow) |
||
| Line 43: | Line 43: | ||
[[File:mark_prediction_as_false_bigger.png|800px]] |
[[File:mark_prediction_as_false_bigger.png|800px]] |
||
| − | After marking the prediction of several issues as false, please select <b>Machine Learning->GO!</b>, and wait for the predicting process to finish. |
+ | After marking the prediction of several issues as false, please select <b>Machine Learning->GO!</b>, and wait for the predicting process to finish. |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Machine_learning_go.png|800px]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | Possible prediction values for each issue are: |
||
| + | |||
* <code>-</code>: Issue has not been marked by a user and Machine Learning hasn't been invoked yet |
* <code>-</code>: Issue has not been marked by a user and Machine Learning hasn't been invoked yet |
||
* <code>N</code>: Projects that ran before 6.1 are marked as N if Machine Learning is not applied. It corredsponds to another version of "-" |
* <code>N</code>: Projects that ran before 6.1 are marked as N if Machine Learning is not applied. It corredsponds to another version of "-" |
||
Revision as of 21:26, 7 June 2018
Contents
Upcoming in Globalyzer 6.1
This new feature is under development and will be available starting with Globalyzer 6.1
Machine Learning Overview
Machine Learning prediction is a Globalyzer Workbench and Globalyzer Lite feature that helps users more quickly identify the real issues in their source code. We suggest applying Machine Learning as a follow-up step to scanning with [[Terms_and_DefinitionsRule Sets. It helps to determine which candidate issues using Rule Sets are indeed i18n issues.
Installation
Prerequisites: Java 8, Python 3.6.x and H2O.ai 3.x
1. Download Python version 3.6+ from website https://www.python.org/downloads/
2. Install python and add python to PATH environment variable
3. Go to this link http://h2o-release.s3.amazonaws.com/h2o/rel-wheeler/4/index.html and make navigate to the "INSTALL IN PYTHON" tab. The instructions there are also shown below.
Install dependencies (prepending with `sudo` if needed): pip install requests pip install tabulate pip install scikit-learn pip install colorama pip install future
At the command line, copy and paste these commands one line at a time:
pip uninstall h2o pip install http://h2o-release.s3.amazonaws.com/h2o/rel-wheeler/4/Python/h2o-3.16.0.4-py2.py3-none-any.whl
Success if response messages have "Successfully installed h2o-3.16.0.4"
Test1: From the command line type in "python -V", It is successful success if it replies with a python version like "Python 3.6.2". If the python version is 2.x then there is a problem, possibly with paths that needs to be addresssed.
Test2: On the command line, go into python. In python:
> import h2o > h2o.init()
This should complete without errors.
Work Flow
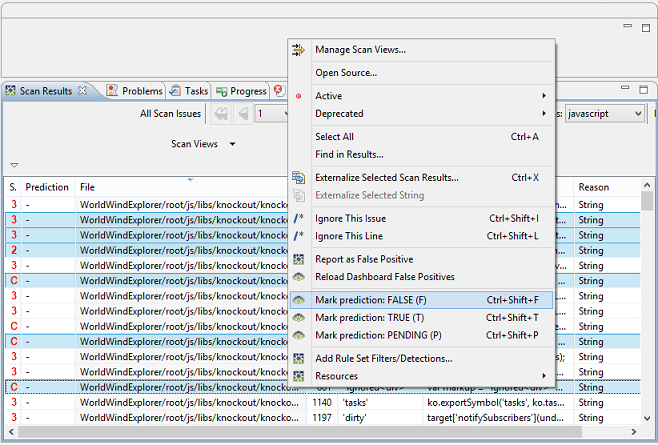
To use Machine Learning, first create a Globalyzer project with scans in the Globalyzer Workbench. At the Scan Results view, right mouse click on some issues that you determine are not real issues, and choose Mark prediction: FALSE (F) from the menu. Please mark the prediction of several issues as false before applying Machine Learning.
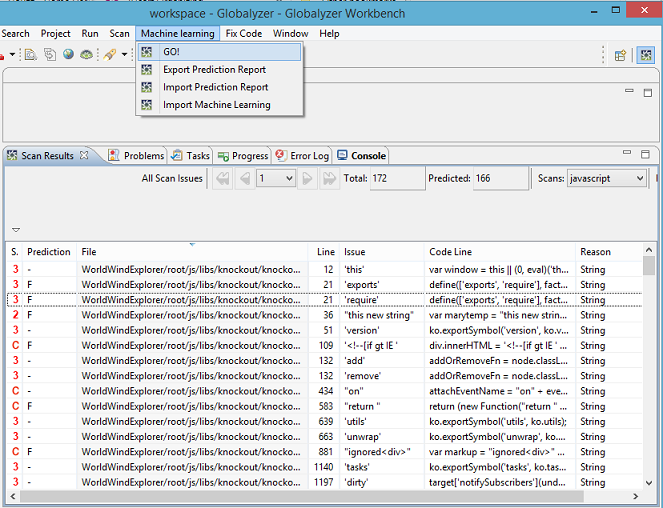
After marking the prediction of several issues as false, please select Machine Learning->GO!, and wait for the predicting process to finish.
Possible prediction values for each issue are:
-: Issue has not been marked by a user and Machine Learning hasn't been invoked yetN: Projects that ran before 6.1 are marked as N if Machine Learning is not applied. It corredsponds to another version of "-"Negative: filtered issues are predicted asNegativeand used to train Machine Learning.T: Marked by a user (or detected by a rule) as a real issue to train Machine LearningF: Marked by a user as a false issue to train Machine Learning
ML True: Machine learning prediction that the issue is a true issue, i.e. the issue should be refactored.ML False: Machine Learning prediction that the issue is a false issue and can be ignoredML NULL: Machine Learning cannot make a prediction, so must be considered a true issue
If you find that issues predicted as ML False are indeed issues, please right mouse click on the issue and select Mark prediction: TRUE(T); the next time you run GO!, Machine Learning will learn your correction. If you are not satisfied with the prediction results, please continue marking more issues as F or T, and rerun Machine Learning.
Once you are satisfied with the prediction results, the issues with a prediction value of T, ML True, or ML NULL are the true issues that need to be addressed. The issues with a prediction value of F or ML False can be ignored. The suggested way to view the predicted active issues is to select Scan Views->All Predicted Active.
Tips:
- View all issues, including filtered issues: One way to understand some of the Machine Learning results is to show all issues, including filtered ones. When an issue is predicted as
ML False, it is easier to see why when it is surrounded by filtered issues with the same type of patterns.
- Scan->Search in Scan Results:
- Search on the Prediction column for issues which are
ML False. From the Search panel, you can right click on the items to change the prediction with Globalyzer->Mark Prediction: TRUE (or FALSE). - Search on the Prediction column for issues which are
ML NULLandML True: This will help you see which issues are predicted as true issues.
- Search on the Prediction column for issues which are
- Sorting: In the Scan Results, a few sorts can be useful:
- Sort on Issue: Lots of similar issues should be treated the same, either
ForT. By sorting on issues, you may see a pattern to use as a category for Machine Learning - Sort on File: A sequence of lines may have patterns which can be used to categorize issues quickly. Use multi-selection to accelerate the
TorFcategorization. - Sort on Prediction: Instead of 'Searching', sorting on the Prediction columns can also help you see better some of the potential categories some issues fall into.
- Sort on Issue: Lots of similar issues should be treated the same, either
Globalyzer Lite
To use Machine Learning when running Globalyzer Lite, you need to first run the Workbench and invoke Machine Learning as described above on the desired scans in the project. Then, when you export the project to Lite, choose to export Machine Learning for those scans. This generates special Machine Learning files in the project/lingoport directory, and sets flags in the generated project definition file (PDF) to use Machine Learning.
When Lite runs a PDF with scans using Machine Learning, it first scans the source using rules in the rule sets, and then invokes Machine Learning processing. The generated XML report will include Machine Learning prediction information, which will be read by the Dashboard. The Dashboard will only display Active issues with a prediction value of -, T, ML True, or ML NULL. Active issues with a prediction value of F or ML False will not be displayed on the Dashboard.
Continuous Integration System
When using Machine Learning in our Continuous Integration System, make sure everything in the project/lingoport directory is pushed to your repository. This ensures that everything downstream will work as intended.
Machine Learning FAQ
1. If I change the status of an issue, will Machine Learning work?
Yes, it will work. When you change the status of an issue, the prediction of the issue will be set by default. For example, if you move an issue to ToDo, the prediction will be marked as True; if you move an issue to Ignore/Invalid, the prediction will be marked as False. You may still manually mark the prediction of any issue, overriding the default. Then, when Machine Learning is invoked, it will use the True and False values as input to make predictions on the remaining Active issues.
2. In Scan Results, what is the meaning of the Predicted count?
With the introduction of Machine Learning, Scan Results has a new count display, called Predicted. This is the number of Active issues with a prediction value of -, T, ML True, or ML NULL. This is the number of Active issues that will appear on the Dashboard. Note that Active issues with a prediction value of F or ML False will not be displayed on the Dashboard.
3. How does Machine Learning work?
We use h2o.ai to analyze the issue, the issue code line, and the issue reason. Based on filtered issues and your marked false issues, Machine Learning will try to find similar Active issues and set their prediction to ML False. Machine Learning prediction may be different per invocation; you won't have the exact same results every time. In addition, Machine Learning needs input to learn from, so if you only mark one issue as False, Machine Learning may not be able to find other similar issues.
4. What kind of Machine Learning algorithm does Globalyzer use?
Globalyzer uses the Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM) algorithm. Gradient Boosting Machine (for Regression and Classification) is a forward learning ensemble method. The guiding heuristic is that good predictive results can be obtained through increasingly refined approximations. H2O’s GBM sequentially builds regression trees on all the features of the dataset in a fully distributed way - each tree is built in parallel. More details: http://docs.h2o.ai/h2o/latest-stable/h2o-docs/data-science/gbm.html
5. What is H2O.ai? Do I have to install it?
H2O is an open source, in-memory, distributed, fast, and scalable machine learning and predictive analytics platform that allows you to build machine learning models on big data and provides easy productionalization of those models in an enterprise environment. And yes, to use Machine Learning, you must install H2O.ai to your system. It's an in-memory platform so you don't need to worry about the security of your code and data.