Difference between revisions of "Deployment Scenarios"
(→Resource Manager Process) |
(→Internal to company network) |
||
| (49 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Setting up the [[Terms_and_Definitions#continuousglobalizationsystem|Lingoport Continuous Globalization System]] at a customer site can be done in many ways, as shown in the different deployment scenarios. The following is meant to show some of the flow and the necessary access to the system. |
Setting up the [[Terms_and_Definitions#continuousglobalizationsystem|Lingoport Continuous Globalization System]] at a customer site can be done in many ways, as shown in the different deployment scenarios. The following is meant to show some of the flow and the necessary access to the system. |
||
| + | [[File:Deployment - Wiki.gif|500px]] |
||
| − | *The Customer's systems are shown in Light Blue; <b>CentOS</b> for the main system where [[Terms_and_Definitions#Jenkins |Jenkins]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#Dashboard|Dashboard]] reside. |
||
| − | *Access from outside the Customer's system are shown in Light Green. |
||
| + | The green box is the '''Continuous Globalization System'''. It is a Linux (CentOS or RedHat) operating system that has the following installed: |
||
| − | [[Image:Deployment and Security.gif]] |
||
| + | * Jenkins |
||
| − | |||
| − | The large blue box is the '''Lingoport Server'''. It is a Linux (CentOS or RedHat) operating system that has the following installed: |
||
| − | * Jenkins (running on port 8080) |
||
* Java |
* Java |
||
* MySQL |
* MySQL |
||
* Globalyzer clients |
* Globalyzer clients |
||
| − | * Lingoport Dashboard Server |
+ | * Lingoport Dashboard Server and Database |
* Lingoport Dashboard Client |
* Lingoport Dashboard Client |
||
| − | * |
+ | * Localyzer Server and Database |
| + | * InContext Server |
||
* SMTP mail server account |
* SMTP mail server account |
||
| − | The |
+ | The Globalyzer Server is either a hosted Lingoport server or another onsite server. |
==A typical workflow== |
==A typical workflow== |
||
| Line 26: | Line 24: | ||
# Jenkins tools determine if the resource files need to be sent to, or imported from, the translation vendor. This may be done via an FTP connection. |
# Jenkins tools determine if the resource files need to be sent to, or imported from, the translation vendor. This may be done via an FTP connection. |
||
# Emails are sent to designated recipients about the status of the translation upload or import. |
# Emails are sent to designated recipients about the status of the translation upload or import. |
||
| − | # Lingoport Dashboard updates the status using the results of the Globalyzer scans and |
+ | # Lingoport Dashboard updates the status using the results of the Globalyzer scans and Localyzer resource reports. |
== External Access and Ports == |
== External Access and Ports == |
||
| + | |||
| − | * Ability to install/update programs via 'yum'. |
||
| + | === External Access === |
||
| − | * [[Terms_and_Definitions#Jenkins|Jenkins]] is accessed via port 8080 within Customer's firewall for Linux system |
||
| + | |||
| − | * [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportDashboard|Lingoport Dashboard]] is accessed via port 9000 within Customer's firewall for Linux system |
||
| + | * Must have the ability to install/update programs via 'yum' |
||
| − | * The [[Terms_and_Definitions#translationvendor|Translation Vendor]] may be accessed by different means, for instance port 21 for FTP or port 22 for SFTP. |
||
| + | * Access to epel yum package repository: https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm |
||
| − | * Download does not have to be directly to the target machine. It can be downloaded by another machine and then transferred. |
||
| + | * Access to https://globalyzer.com. |
||
| − | * Access for the Lingoport (or internal) installation team can be done in many ways, such as SSH for Telnet or Putty. |
||
| + | ** May purchase an Enterprise License to deploy an on-site Globalyzer server. |
||
| − | * Linux system must be able to access https://globalyzer.com. |
||
| + | ** If using local rulesets for Globalyzer, access is still needed to https://globalyzer.com to manage and store rulesets. |
||
| + | * Access to the Jenkins update center |
||
| + | * Access to the SonarQube update center |
||
| + | |||
| + | === Ports === |
||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Internal to company network ===== |
||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" class="wikitable" style="text-align:left; width=50%;" |
||
| + | !Services!!Ports!!Inbound (session)!!Outbound (session)!!Notes |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |SSH (for system config/maintenance)|| 22 || Y || N || System configuration and maintenance |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |[[Terms_and_Definitions#Jenkins|Jenkins]] & [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportDashboard|Lingoport Dashboard]]: HTTP(S) Access || 80 (HTTP) and/or 443 (HTTPS) || Y || N || HTTPS requires configuration of certificate. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Automation (Bot) support || 5001 || Y || Y || Optional. May also place directly on 443 if a second DNS + HTTPS provided |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |[[Terms_and_Definitions#translationvendor|Translation Vendor]] interactions: FTP/FTPS/SFTP (MemoQ, etc.) || 21 (FTP) or 443 (FTPS) or 22 (SFTP - recommended) || (FTP/S only) || Y || FTP/FTPS also require data ports (> 1024). Recommend SFTP if possible. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |[[Terms_and_Definitions#translationvendor|Translation Vendor]] interactions: XTM and Memsource || 80 (HTTP) optional. 443 (HTTPS) required. || (Some cases) || Y || May need to be external if XTM/Memsource not installed on premise. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |SMTP/SMTPS || 25 or 465 or 587 || N || Y || Depends on corporate mail setup. |
||
| + | |} |
||
| + | |||
| + | ==== External access ==== |
||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" class="wikitable" style="text-align:left; width=50%;" |
||
| + | !Services!!Ports!!Inbound!!Outbound!!Notes |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Lingoport SSH access || 22 || Y || N || Optional. Recommended for ease of upgrades and maintenance. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |HTTP & HTTPS access to required sites (above) || 80 and 443 || N || Y || See [[Deployment_Scenarios#External Access]] |
||
| + | |} |
||
| + | |||
| + | == Content == |
||
| + | |||
| + | * Lingoport Installers and Updaters available on Lingoport SFTP site (lingoport.net). Or may be sent in a custom fashion by special request. Download does not have to be directly to the target machine. It can be downloaded by another machine and then transferred. |
||
| + | * Lingoport requests SSH access to the Lingoport Server. This allows Lingoport to best debug and troubleshoot problems. If this is not possible, Lingoport can guide a customer through the setup using a videoconferencing program such as WebEx or GoToMeeting. |
||
==Optional Access== |
==Optional Access== |
||
| Line 64: | Line 100: | ||
* The Globalyzer clients also run on the Lingoport Server (light-blue box at bottom of graphic) and the results are displayed on the [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportDashboard|Lingoport Dashboard]] (see data flow) |
* The Globalyzer clients also run on the Lingoport Server (light-blue box at bottom of graphic) and the results are displayed on the [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportDashboard|Lingoport Dashboard]] (see data flow) |
||
| − | == |
+ | ==Localyzer (formerly LRM) == |
| − | + | Localyzer manages translation [[Terms_and_Definitions#resourcefiles|resource files]]. |
|
| − | * |
+ | * Localyzer detects problems in resource files (duplicate or missing keys, parameter mismatch in text for different languages, etc.) |
| − | * |
+ | * Localyzer also detects changes to resource files and sends relevant changes out to the [[Terms_and_Definitions#translationvendor|translation vendor]] for translation into other languages. |
| − | * |
+ | * Localyzer automatically retrieves translations from translations vendors and checks those changes into the code source control repository. |
| − | * |
+ | * Localyzer runs on the Lingoport Server (light-blue box at bottom of graphic). |
==Lingoport Dashboard== |
==Lingoport Dashboard== |
||
| − | The Lingoport Dashboard displays [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] status using Globalyzer and |
+ | The Lingoport Dashboard, a web application, displays [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] status using Globalyzer and Localyzer reports. |
* Displays overview and detail views of Globalyzer scan results and Resource Manager translation status. |
* Displays overview and detail views of Globalyzer scan results and Resource Manager translation status. |
||
* Users can view Globalyzer and Resource Manager issues in context within the source code. |
* Users can view Globalyzer and Resource Manager issues in context within the source code. |
||
* Lingoport Dashboard runs on the Lingoport Server (light-blue box at bottom of graphic). |
* Lingoport Dashboard runs on the Lingoport Server (light-blue box at bottom of graphic). |
||
| + | |||
| + | ===Lingoport Dashboard Client=== |
||
| + | The Lingoport Dashboard client runs the scripts which analyzes the projects and creates the XML files that get pushed to the server. |
||
| + | |||
| + | ===Lingoport Dashboard Server=== |
||
| + | The Lingoport Dashboard server displays the results of the Globalyzer Scans and Localyzer reports in a web application. |
||
==Jenkins (not a Lingoport program)== |
==Jenkins (not a Lingoport program)== |
||
| − | Jenkins is used to automate running of Globalyzer Client, Resource Manager and updating of the Lingoport Dashboard |
+ | Jenkins is used to automate running of Globalyzer Client, Resource Manager and updating of the Lingoport Dashboard. |
* Several tools created by Lingoport are used to run automation and analysis scripts from the Jenkins interface for the Lingoport Dashboard. |
* Several tools created by Lingoport are used to run automation and analysis scripts from the Jenkins interface for the Lingoport Dashboard. |
||
* Jenkins runs on the Lingoport Server (light-blue box at bottom of graphic) |
* Jenkins runs on the Lingoport Server (light-blue box at bottom of graphic) |
||
=Data Flow= |
=Data Flow= |
||
| − | |||
| − | ==Lingoport Access== |
||
| − | Lingoport requests SSH access to the Lingoport Server. This allows Lingoport to best debug and troubleshoot problems. |
||
| − | If this is not possible, Lingoport can guide a customer through the setup using a videoconferencing program such as WebEx or GoToMeeting. |
||
== Globalyzer Process == |
== Globalyzer Process == |
||
| Line 96: | Line 134: | ||
==Resource Manager Process == |
==Resource Manager Process == |
||
| − | Sends to-be-translated resource files updates to translation vendor, typically over SFTP. Resource file updates received from translation vendor, also typically over SFTP. Updates are checked for consistency (various in-depth checks), and then committed to source control -- if the checks pass. |
||
| − | [[File:Lingoport_Resource_Manager_Prep-Kit_Process_Diagram.png|700px]] |
+ | <!-- [[File:Lingoport_Resource_Manager_Prep-Kit_Process_Diagram.png|700px]] --> |
| − | |||
| − | * Emails are sent to a list of email contacts defined in a configuration file. |
||
| − | ** Notifications for sent / received resource files |
||
| − | ** Error notifications |
||
| − | ** Translation status weekly email |
||
| − | * Stores data in MySQL database |
||
| − | * Run on Linux system (light-blue box at bottom of graphic) |
||
| − | * Generates XML reports that will be read by the Lingoport Dashboard. |
||
*[[Terms_and_Definitions#ResourceFiles|Resource Files]] and Bundles are pulled from the Source Control Repository to the [[Terms_and_Definitions#LRMServer|LRM Server]]. |
*[[Terms_and_Definitions#ResourceFiles|Resource Files]] and Bundles are pulled from the Source Control Repository to the [[Terms_and_Definitions#LRMServer|LRM Server]]. |
||
| − | * |
+ | * Localyzer determines if there are problems with the resource files or if there are new keys to be translated. |
| − | * If there are keys to be translated, a [[Terms_and_Definitions#prepkit|Prep Kit]] is created to track the translation. |
+ | * If there are keys to be translated, a [[Terms_and_Definitions#prepkit|Prep Kit]] is created using MySQL to track the translation. |
| − | * The prep kit files (one per translation locale) |
+ | * The prep kit files (one per translation locale) are sent to the translation vendor via SFTP and success or failure emails are sent to designated recipients. |
| − | * When the prep kits have been translated, |
+ | * When the prep kits have been translated, Localyzer downloads and imports the files and sends status emails. |
| − | * |
+ | * Localyzer pushes the new resource files into the source code repository. |
| − | * The Lingoport Dashboard updates |
+ | * The Lingoport Dashboard updates its status using the Localyzer reports. |
| − | |||
| − | ==Lingoport Dashboard== |
||
| − | Internal within customer network. XML Reports generated by Globalyzer and Resource Manager are uploaded via the Dashboard Client to the Dashboard Server. Dashboard Client sends code information to Dashboard Server. |
||
| − | |||
| − | * Resource Manager and Globalyzer are run on a server internal to Customer's network. Each generates an XML report. |
||
| − | * Dashboard Client reads both source code and these XML reports. |
||
| − | * Dashboard Client processes this data, and sends it to the Dashboard Server. |
||
| − | * Data sent over HTTP/HTTPS. |
||
| − | * Most often, the Dashboard Client and Dashboard Server are hosted on the same machine (light-blue box at bottom of graphic), so network communication is internal to this machine. |
||
| − | * Requires a either a username/password or a user token, which will be stored in configuration files. |
||
| − | * Stores data in MySQL database. |
||
| − | * Dashboard Server is a web application, hosted on port 9000 by default. |
||
| − | |||
| − | ==Jenkins (not a Lingoport program)== |
||
| − | Used to automate running of Globalyzer Client, Resource Manager and updating of the Lingoport Dashboard |
||
| − | |||
| − | * Various security options available, username/password is most common. LDAP is another option. |
||
| − | * Run on Linux system (light-blue box at bottom of graphic) |
||
| − | * Web application, hosted on port 8080 by default. |
||
= Additional Deployments Scenarios = |
= Additional Deployments Scenarios = |
||
Latest revision as of 18:28, 2 November 2021
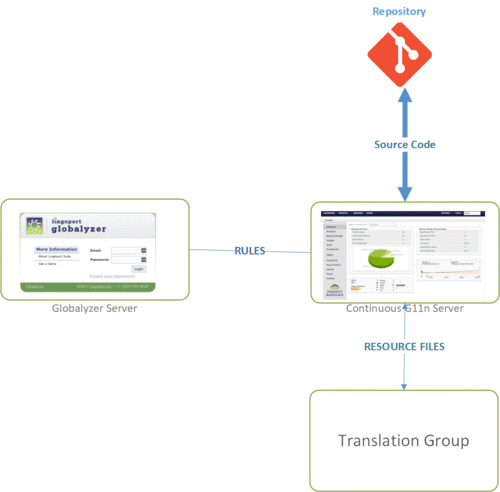
The Lingoport Suite is composed of Globalyzer, LRM (Resource Manager) and the Lingoport Dashboard. A number of other products are used with the Suite. You may need some of the components for a set of users and other components for Continuous Globalization.
Contents
Typical Deployment and Ports
Setting up the Lingoport Continuous Globalization System at a customer site can be done in many ways, as shown in the different deployment scenarios. The following is meant to show some of the flow and the necessary access to the system.
The green box is the Continuous Globalization System. It is a Linux (CentOS or RedHat) operating system that has the following installed:
- Jenkins
- Java
- MySQL
- Globalyzer clients
- Lingoport Dashboard Server and Database
- Lingoport Dashboard Client
- Localyzer Server and Database
- InContext Server
- SMTP mail server account
The Globalyzer Server is either a hosted Lingoport server or another onsite server.
A typical workflow
- Code is committed to a central source code repository (Git, Subversion, etc) by developers.
- Jenkins tools pull the source code from the code repository and scan using Rule Sets stored on the Globalyzer Server or analyze the resource files.
- Jenkins tools determine if the resource files need to be sent to, or imported from, the translation vendor. This may be done via an FTP connection.
- Emails are sent to designated recipients about the status of the translation upload or import.
- Lingoport Dashboard updates the status using the results of the Globalyzer scans and Localyzer resource reports.
External Access and Ports
External Access
- Must have the ability to install/update programs via 'yum'
- Access to epel yum package repository: https://dl.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/epel-release-latest-7.noarch.rpm
- Access to https://globalyzer.com.
- May purchase an Enterprise License to deploy an on-site Globalyzer server.
- If using local rulesets for Globalyzer, access is still needed to https://globalyzer.com to manage and store rulesets.
- Access to the Jenkins update center
- Access to the SonarQube update center
Ports
Internal to company network
| Services | Ports | Inbound (session) | Outbound (session) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSH (for system config/maintenance) | 22 | Y | N | System configuration and maintenance |
| Jenkins & Lingoport Dashboard: HTTP(S) Access | 80 (HTTP) and/or 443 (HTTPS) | Y | N | HTTPS requires configuration of certificate. |
| Automation (Bot) support | 5001 | Y | Y | Optional. May also place directly on 443 if a second DNS + HTTPS provided |
| Translation Vendor interactions: FTP/FTPS/SFTP (MemoQ, etc.) | 21 (FTP) or 443 (FTPS) or 22 (SFTP - recommended) | (FTP/S only) | Y | FTP/FTPS also require data ports (> 1024). Recommend SFTP if possible. |
| Translation Vendor interactions: XTM and Memsource | 80 (HTTP) optional. 443 (HTTPS) required. | (Some cases) | Y | May need to be external if XTM/Memsource not installed on premise. |
| SMTP/SMTPS | 25 or 465 or 587 | N | Y | Depends on corporate mail setup. |
External access
| Services | Ports | Inbound | Outbound | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lingoport SSH access | 22 | Y | N | Optional. Recommended for ease of upgrades and maintenance. |
| HTTP & HTTPS access to required sites (above) | 80 and 443 | N | Y | See Deployment_Scenarios#External Access |
Content
- Lingoport Installers and Updaters available on Lingoport SFTP site (lingoport.net). Or may be sent in a custom fashion by special request. Download does not have to be directly to the target machine. It can be downloaded by another machine and then transferred.
- Lingoport requests SSH access to the Lingoport Server. This allows Lingoport to best debug and troubleshoot problems. If this is not possible, Lingoport can guide a customer through the setup using a videoconferencing program such as WebEx or GoToMeeting.
Optional Access
You may want to update either Jenkins or the underlying Dashboard platform to the latest version. If so, you may want to update the continuous globalization system directly or to download the files on one system and copy them over to the continuous globalization system. The URL for updates are:
- https://updates.jenkins-ci.org
- https://update.sonarsource.org
- https://repo.mysql.com
- http://pkg.jenkins-ci.org/redhat-stable/jenkins.repo
- https://jenkins-ci.org/redhat/jenkins-ci.org.key
Furthermore, email notification emails require an SMTP account. The SMTP server access may be internal to your Company or external depending on your email services (e.g. smtp.gmail.com for Google).
Installation Components
Globalyzer
Globalyzer scans code and detect internationalization (i18n) issues.
Globalyzer Server
The Globalyzer Server stores regular expression (regex) scanning rules called Rule Sets that are used to identify issues in source code.
- Stores regex pattern based 'rule sets' used to detect i18n issues and filter out false positives and Globalyzer accounts.
- The Globalyzer Server does not store any code or customer information.
Globalyzer Clients
The Globalyzer clients display i18n issues found by the Globalyzer scan.
- The Globalyzer clients connect to the Globalyzer Server. The clients log in and download rule sets from the Globalylzer server to scan code. No code is sent to the Globalyzer server, although the Globalyzer clients may push rule set modifications.
- The Globalyzer clients run on developer machines.
- The Globalyzer clients also run on the Lingoport Server (light-blue box at bottom of graphic) and the results are displayed on the Lingoport Dashboard (see data flow)
Localyzer (formerly LRM)
Localyzer manages translation resource files.
- Localyzer detects problems in resource files (duplicate or missing keys, parameter mismatch in text for different languages, etc.)
- Localyzer also detects changes to resource files and sends relevant changes out to the translation vendor for translation into other languages.
- Localyzer automatically retrieves translations from translations vendors and checks those changes into the code source control repository.
- Localyzer runs on the Lingoport Server (light-blue box at bottom of graphic).
Lingoport Dashboard
The Lingoport Dashboard, a web application, displays internationalization and localization status using Globalyzer and Localyzer reports.
- Displays overview and detail views of Globalyzer scan results and Resource Manager translation status.
- Users can view Globalyzer and Resource Manager issues in context within the source code.
- Lingoport Dashboard runs on the Lingoport Server (light-blue box at bottom of graphic).
Lingoport Dashboard Client
The Lingoport Dashboard client runs the scripts which analyzes the projects and creates the XML files that get pushed to the server.
Lingoport Dashboard Server
The Lingoport Dashboard server displays the results of the Globalyzer Scans and Localyzer reports in a web application.
Jenkins (not a Lingoport program)
Jenkins is used to automate running of Globalyzer Client, Resource Manager and updating of the Lingoport Dashboard.
- Several tools created by Lingoport are used to run automation and analysis scripts from the Jenkins interface for the Lingoport Dashboard.
- Jenkins runs on the Lingoport Server (light-blue box at bottom of graphic)
Data Flow
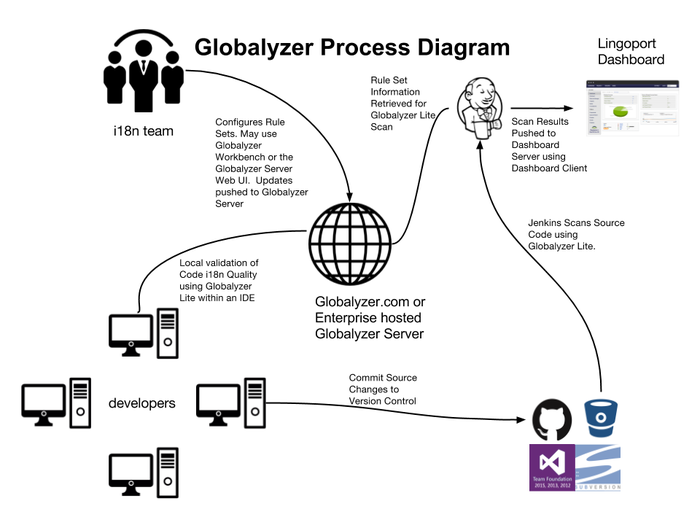
Globalyzer Process
- The internationalization team creates and configures rule sets on the Globalyzer Server. Rule sets are based on the coding languages used.
- Developers can use the Globalyzer Lite client with the rule sets to validate their code locally before committing to a repository.
- A Jenkins tool scans the code using the rule sets, creates XML reports, and pushes the results to the Lingoport Dashboard Server using the Lingoport Dashboard Client.
Resource Manager Process
- Resource Files and Bundles are pulled from the Source Control Repository to the LRM Server.
- Localyzer determines if there are problems with the resource files or if there are new keys to be translated.
- If there are keys to be translated, a Prep Kit is created using MySQL to track the translation.
- The prep kit files (one per translation locale) are sent to the translation vendor via SFTP and success or failure emails are sent to designated recipients.
- When the prep kits have been translated, Localyzer downloads and imports the files and sends status emails.
- Localyzer pushes the new resource files into the source code repository.
- The Lingoport Dashboard updates its status using the Localyzer reports.
Additional Deployments Scenarios
In the Additional Deployments section, we illustrate some possible deployments:
- Team Members
- i18n specialists
- Developers
- Other Continuous Globalization Deployments