Difference between revisions of "Command Center Installation"
(→Run InstallCommmandCenter.sh) |
(→Installation Files) |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
== Credentials == |
== Credentials == |
||
(internal, LDAP, SSO) |
(internal, LDAP, SSO) |
||
| − | |||
| − | == Installation Files == |
||
| − | Please contact ''support (at) lingoport (dot) com'' in order to get files which will be used for the installation or the update of your Command Center instance: |
||
| − | * <code>command-center-config.sh</code> : for your specific configuration |
||
| − | * <code>InstallCommandCenter.sh</code> : for new installations: This will drop any data in the database and start cleanly |
||
| − | * <code>UpdateCommandCenter.sh</code> : for updates to an existing system |
||
= Installation = |
= Installation = |
||
Revision as of 17:22, 17 January 2023
Contents
Pre-Requisites
Before installing or updating Command Center, please verify this section is complete.
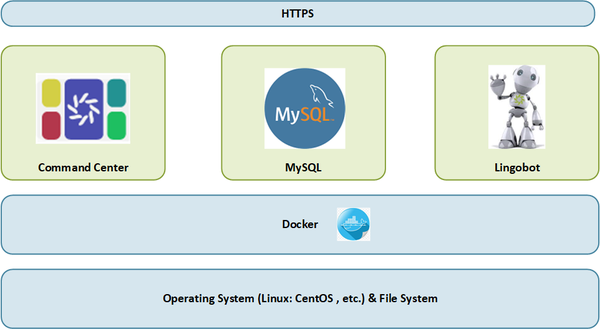
Intro
Diagram
Hardware
Docker Pre-Requisite
Docker is a platform that allows you to easily develop, test, and deploy applications as containers. This section will walk you through the process of installing Docker on a Linux system.
On the system (most likely a VM) dedicated to Command Center, make sure you have the latest version of docker up and running. The following steps may help.
A user with sudo privileges is required to run most commands.
Uninstall old docker versions
This is an optional step in case your docker version is out of date:
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
Install docker using the repository
sudo yum install -y yum-utils
sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
Start Docker.
Start docker using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl start docker
Enable the Docker service to start automatically on system boot by running the following command:
$ sudo systemctl enable docker
Verify that Docker Engine is installed correctly
Run the hello-world image.
$ sudo docker run hello-world
This command will run a test container and display a message indicating that the installation is working properly.
Firewall
Credentials
(internal, LDAP, SSO)
Installation
Create the database conf file
The following is provided for a CentOS system:
Uses the centos user as default user for docker
/home/centos/mysql/conf.d/mysql.cnf
[client] default-character-set = utf8mb4
[mysql] default-character-set = utf8mb4
Install Command Center
New Installation
Copy install/update/uninstall and install.conf file to your home directory (/home/centos)
[TEMPORARY-TO BE REWRITTEN ]
You can find files at https://github.com/Lingoport/Command-Center/tree/liliDev/docker
install.conf InstallCommmandCenter.sh UninstallCommmandCenter.sh UpdateCommmandCenter.sh
Set up install.conf
You need to provide your serverURL, your Docker Hub username and token, and MYSQL root password you want to use
Run InstallCommmandCenter.sh
./InstallCommmandCenter.sh
To check the running container status
docker ps
Note: Docker image version is not the Command Center version, check latest docker image version at https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/lingoport/command-center_dev/general
You should see at least an MySQL and a Command Center container running.
Log in to the URL based on the command-center-config.sh settings, so something like:
https://commandcenter.mycompany.io/
You should now be able to install the licenses and create projects.
Update
Licenses
Start and Stop System
Verify Installation
Installation / Update (Docker)