Difference between revisions of "LRM for Continuous Globalization"
(→Introduction) |
(→Installation Components) |
||
| (12 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
= Introduction = |
= Introduction = |
||
| − | The [[Terms_and_Definitions|Lingoport Resource Manager]], or LRM, is designed to be deployed on a [[Terms_and_Definitions|Continuous Globalization]] system. It automates the tasks for tracking, checking, sending, receiving, and pushing/checking resource |
+ | The [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportResourceManager|Lingoport Resource Manager]], or LRM, is designed to be deployed on a [[Terms_and_Definitions#ContinuousGlobalization|Continuous Globalization]] system. It automates the tasks for tracking, checking, sending, receiving, and pushing/checking [[Terms_and_Definitions#resourcefiles|resource files]] to a [[Terms_and_Definitions#repository|repository]], and provides an accurate translation status from the Dashboard's code perspective. |
It integrates seamlessly with translation products, such as Lingotek. |
It integrates seamlessly with translation products, such as Lingotek. |
||
= Target User= |
= Target User= |
||
| − | The results are presented via the Dashboard for any registered users, such as development team members, development management, i18n specialists, L10n management, translators, QA, etc. |
+ | The results are presented via the [[Terms_and_Definitions#Dashboard|Dashboard]] for any registered users, such as development team members, development management, i18n specialists, L10n management, translators, QA, etc. |
| − | The typical LRM <code>actor</code> is a Jenkins system which automates the different tasks and pushes the results to the Dashboard. |
+ | The typical [[Terms_and_Definitions#LRM|LRM]] <code>actor</code> is a [[Terms_and_Definitions#Jenkins|Jenkins]] system which automates the different tasks and pushes the results to the Dashboard. |
= Typical Deployment = |
= Typical Deployment = |
||
| − | LRM is installed on the Continuous Globalization system, with a database to track the actions and the status of the resource bundles. |
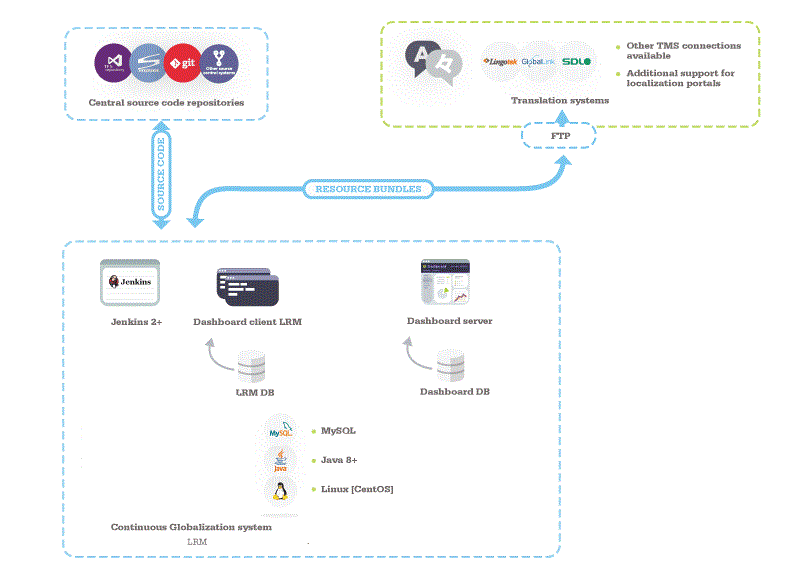
+ | [[Terms_and_Definitions#LRM|LRM]] is installed on the [[Terms_and_Definitions#ContinuousGlobalization|Continuous Globalization]] system, with a database to track the actions and the status of the resource bundles. |
The LRM project has been on-boarded on the Continuous Globalization system. |
The LRM project has been on-boarded on the Continuous Globalization system. |
||
[[File:LRM for CI2.gif]] |
[[File:LRM for CI2.gif]] |
||
| − | <b>Note</b>: the Continuous Globalization system needs to be a Linux machine, preferably |
+ | <b>Note</b>: the Continuous Globalization system needs to be a Linux machine, preferably CentOS. |
= Typical Workflow= |
= Typical Workflow= |
||
| − | Jenkins uses LRM via scripts to: |
+ | [[Terms_and_Definitions#Jenkins|Jenkins]] uses [[Terms_and_Definitions#LRM|LRM]] via scripts to: |
| − | * Get the code from a repository |
+ | * Get the code from a [[Terms_and_Definitions#repository|repository]] |
| − | * Establish the status of the translation for all resource |
+ | * Establish the status of the translation for all [[Terms_and_Definitions#resourcefiles|resource files]] |
| − | * Push prep kits to translation products if necessary and if the critical checks pass. |
+ | * Push [[Terms_and_Definitions#prepkit|prep kits]] to translation products if necessary and if the critical checks pass. |
* Pull translated files from the translation products if necessary |
* Pull translated files from the translation products if necessary |
||
* Check the translated files and push them to the repository at the right location if the critical checks pass |
* Check the translated files and push them to the repository at the right location if the critical checks pass |
||
* Notify the configured recipients of the actions taken |
* Notify the configured recipients of the actions taken |
||
| + | |||
| + | = Installation Components = |
||
| + | |||
| + | * The '''Dashboard System''' and '''Continuous Globalization system''' is shown on different machines, although they could be one machine. The Build Server transfers [[Terms_and_Definitions#resourcefiles|resource files]] to and from the [[Terms_and_Definitions#TMS|Translation Management System]]. |
||
| + | * The '''Developer Machine''' is not shown in this diagram. The developer will push source code to the repositories and may not have any Lingoport Software on their machine. |
||
| + | * There is no '''Globalyzer Server''' or Globalyzer clients in this scenario. |
||
= Installation Notes = |
= Installation Notes = |
||
Latest revision as of 19:02, 30 December 2016
Contents
Introduction
The Lingoport Resource Manager, or LRM, is designed to be deployed on a Continuous Globalization system. It automates the tasks for tracking, checking, sending, receiving, and pushing/checking resource files to a repository, and provides an accurate translation status from the Dashboard's code perspective.
It integrates seamlessly with translation products, such as Lingotek.
Target User
The results are presented via the Dashboard for any registered users, such as development team members, development management, i18n specialists, L10n management, translators, QA, etc.
The typical LRM actor is a Jenkins system which automates the different tasks and pushes the results to the Dashboard.
Typical Deployment
LRM is installed on the Continuous Globalization system, with a database to track the actions and the status of the resource bundles. The LRM project has been on-boarded on the Continuous Globalization system.
Note: the Continuous Globalization system needs to be a Linux machine, preferably CentOS.
Typical Workflow
Jenkins uses LRM via scripts to:
- Get the code from a repository
- Establish the status of the translation for all resource files
- Push prep kits to translation products if necessary and if the critical checks pass.
- Pull translated files from the translation products if necessary
- Check the translated files and push them to the repository at the right location if the critical checks pass
- Notify the configured recipients of the actions taken
Installation Components
- The Dashboard System and Continuous Globalization system is shown on different machines, although they could be one machine. The Build Server transfers resource files to and from the Translation Management System.
- The Developer Machine is not shown in this diagram. The developer will push source code to the repositories and may not have any Lingoport Software on their machine.
- There is no Globalyzer Server or Globalyzer clients in this scenario.
Installation Notes
Setting up LRM requires more in-depth installation and configuration than setting up the client side of Globalyzer. Please refer to this section for Installation and Configuration .