Difference between revisions of "Introduction"
(→Command Center) |
|||
| (120 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | + | = Lingoport - Overview = |
|
| − | Lingoport provides products and services which help our clients meet [ |
+ | Lingoport provides products and services which help our clients continuously meet [https://lingoport.com/what-is-i18n/ internationalization] and ongoing localization challenges relating to software development and active globalization. |
| + | For more information about internationalization: https://lingoport.com/what-is-i18n/ |
||
| − | === Services === |
||
| − | Software [http://www.lingoport.com/software-internationalization-services/ internationalization (i18n) consulting services] are far ranging, including i18n assessments, requirements, project planning, architecture, small and large scale implementation efforts, testing, documentation, training and more. We have over a decade of successful implementation experience on wide ranging technologies and application domains. Lingoport products are incorporated into our services engagements, making for repeatable and scalable results. We can support internationalization during your concurrent development efforts and help you meet release date demands. |
||
| + | The Lingoport Products help software engineering teams with the [[Terms_and_Definitions#globalization|globalization]] tasks: |
||
| − | === Products === |
||
| + | * Automatically find and manage [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] issues and [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] changes in your source code and [[Terms_and_Definitions#repository|repositories]] for a wide variety of programming languages. |
||
| − | '''[[About Globalyzer | Globalyzer]]''' – Supports individuals and entire development teams in finding, fixing and maintaining internationalization issues in code in a broad list of programming languages (More information at [http://lingoport.com/globalyzer Lingoport.com/Globalyzer]). |
||
| + | * Integrate with [[Terms_and_Definitions#TMS|translation management systems]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] vendors for rapid [[Terms_and_Definitions#globalization|globalization]] development, testing and deployment. |
||
| − | |||
| + | * Verify translations in an efficient, process-driven manner. |
||
| − | '''[[LRM_FAQ | Lingoport Resource Manager]]''' – Provides simplified resource file management, verification and translation updating, helping development and localization teams keep up with initial and ongoing application interface resources, their translation and automated re-insertion into product builds (More information at [http://lingoport.com/lrm Lingoport.com/LRM]). |
||
| + | * Works behind your firewall keeping your source code secure. |
||
| − | |||
| − | '''Dashboard''' – Displays information provided from Globalyzer and/or Lingoport Resource Manager, showing key metrics and drill downs to individual issues and violations (More information at [http://lingoport.com/dashboard Lingoport.com/Dashboard]) |
||
===Contact Information:=== |
===Contact Information:=== |
||
Phone: +1 303-444-8020 |
Phone: +1 303-444-8020 |
||
| − | Email: info |
+ | Email: info at Lingoport.com |
Lingoport, Inc. |
Lingoport, Inc. |
||
| − | =Overview= |
||
| − | The [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportSuite|Lingoport Suite]] encompasses |
||
| − | [[Terms_and_Definitions#Globalyzer|Globalyzer]], the [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportResourceManager|Lingoport Resource Manager]], and the [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportDashboard|Lingoport Dashboard]]. Together the suite enables continuous tracking and updates to the [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] status of software products. |
||
| + | == Services == |
||
| − | The Lingoport Suite helps Software Engineering teams with the [[Terms_and_Definitions#globalization|globalization]] tasks: |
||
| + | Lingoport has been providing software [http://www.lingoport.com/software-internationalization-services/ internationalization (i18n) consulting services] since the company's inception in 2001. |
||
| − | * Automatically find and manage [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] issues and [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] changes in your source code and [[Terms_and_Definitions#repository|repositories]] for a wide variety of programming languages. |
||
| − | * Integrate with [[Terms_and_Definitions#TMS|translation management systems]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] vendors for rapid [[Terms_and_Definitions#globalization|globalization]] development, testing and deployment. |
||
| − | * Works behind your firewall keeping your source code secure |
||
| + | These services include: |
||
| − | The suite is composed of three integrated components to create & maintain software |
||
| + | * '''I18n Analysis''' - plan for new i18n projects, or gap analysis for mitigating i18n issues. A Lingoport architect and supporting team members clarify i18n business, technical and resource requirements based on market requirements, development discussions, programming technologies and Globalyzer scanning results. |
||
| − | for any language or cultural format in every release increment. |
||
| + | * '''I18n Implementation''' - Lingoport provides i18n development teams that can work in a hybrid approach, collaborating with client teams, as well as in turnkey fashion. |
||
| − | * '''Globalyzer''': Identify internationalization (i18n) issues that inhibit [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] and global user experience during development: Catch up on [[Terms_and_Definitions#i18n|i18n]] technical debt. |
||
| + | * '''General i18n Consulting and Custom Projects''' - Sometimes specific problem solving or i18n bug fixing is needed. Lingoport can fulfill that resource need, working in coordination with your teams. |
||
| − | * '''LRM (Lingoport Resource Manager)''': Make localization proactive. Detect & manage changes to [[Terms_and_Definitions#resourcefiles|resource files]] in your source code. Streamline translation jobs. Automate localization updates between development and translation. |
||
| + | * '''Process Customization''' - Any Lingoport product purchase includes consulting time to customize and optimize the Lingoport product suite for the customer. |
||
| − | * '''Dashboard''': The hub of our suite. See it all, drill down, create notifications and manage the process. Bridge gaps between localization & development. Increase visibility and track globalization metrics. |
||
| − | = |
+ | == Lingoport Products == |
| + | [[File:Lingoport Products Overview.JPG|700px|center]] |
||
| − | <br> |
||
| − | If your [[Terms_and_Definitions#continuousglobalizationsystem|Continuous Globalization System]] is installed using the [[Terms_and_Definitions#StackInstaller|Stack Installer]], these products and applications will be installed via that method. These are minimum versions and anything higher is acceptable. |
||
| + | The Lingoport products support the continuous globalization process, from the code repository to the translation vendors and back. |
||
| − | == Supported Versions == |
||
| − | Lingoport supports the current version and the one before that: |
||
| + | '''[[About Globalyzer | Globalyzer]]''' – Supports individuals and entire development teams in finding, fixing and maintaining internationalization issues in code in a broad list of programming languages. (More information at [http://lingoport.com/globalyzer Lingoport.com/Globalyzer]). |
||
| − | {| border="1" class="wikitable" style="width=50%" |
||
| − | !Date |
||
| − | !Suite |
||
| − | !Globalyzer |
||
| − | !LRM |
||
| − | !InContext QA |
||
| − | !Dashboard |
||
| − | !LingoBot |
||
| − | !LingoBot CLI |
||
| − | !JDK |
||
| − | !MySQL |
||
| − | !Linux |
||
| − | !Jenkins |
||
| − | !Tomcat* |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | !2018-12-18 |
||
| − | |1.23.24 |
||
| − | |6.2 |
||
| − | |4.1 |
||
| − | |1.0 |
||
| − | |5.6.7 |
||
| − | |2.2 |
||
| − | |1.1.0 |
||
| − | |1.8** |
||
| − | |5.6 |
||
| − | |CentOS 7 |
||
| − | |2.156+ |
||
| − | |8.x |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | !2018-08-08 |
||
| − | |1.21.14 |
||
| − | |6.1.1 |
||
| − | |4.0 |
||
| − | |<b>1.0</b> |
||
| − | |5.6.6 |
||
| − | |2.1 |
||
| − | |1.0.1 |
||
| − | |1.8** |
||
| − | |5.6 |
||
| − | |CentOS 7 |
||
| − | |2.131+ |
||
| − | |8.x |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | |} |
||
| + | '''[[About Localyzer | Localyzer]]''' – Provides simplified resource file management, verification and translation updating. Localyzer helps development and localization teams keep up with initial and ongoing application interface resources, their translation and automated re-insertion into product builds. (More information at [https://lingoport.com/software-internationalization-products/localyzer-localization-automation/ Lingoport.com/Localyzer]). |
||
| − | === Historical Versions === |
||
| + | * '''Machine Translation''' - Lingoport Supports several popular machine translation vendors as part of the continuous globalization and localization process. |
||
| + | ** [https://aws.amazon.com/translate/ AWS Translate] |
||
| + | ** [https://www.systransoft.com/systran/translation-technology/neural-machine-translation-nmt/ Systran] |
||
| + | ** [https://cloud.google.com/translate Google Translate] |
||
| + | ** [https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/translator/ Microsoft Translator] |
||
| + | * '''Translation Management Systems(TMS)''': Lingoport Localyzer is integrated with leading TMS platforms for a fully automated process from code repository to translator and back. |
||
| + | '''[[LocalyzerQA | LocalyzerQA]]''' - A simplified way to perform linguistic review and verify and correct translation issues as part of the continuous globalization process. |
||
| − | {| border="1" class="wikitable" style="width=50%" |
||
| − | !Date |
||
| − | !Suite |
||
| − | !Globalyzer |
||
| − | !LRM |
||
| − | !InContext QA |
||
| − | !Dashboard |
||
| − | !LingoBot |
||
| − | !LingoBot CLI |
||
| − | !JDK |
||
| − | !MySQL |
||
| − | !Linux |
||
| − | !Jenkins |
||
| − | !Tomcat* |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | !2018-05-17 |
||
| − | |1.17.25 |
||
| − | |6.1 |
||
| − | |3.4.1 |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |5.6.5 |
||
| − | |2.0 |
||
| − | |<b>1.0.1</b> |
||
| − | |1.8** |
||
| − | |5.6 |
||
| − | |CentOS 7 |
||
| − | |2.73 |
||
| − | |8.x |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | !2017-12-12 |
||
| − | |1.15.4 |
||
| − | |6.0 |
||
| − | |3.4 |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |5.6.4 |
||
| − | |1.2 |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |1.8** |
||
| − | |5.6 |
||
| − | |CentOS 7 |
||
| − | |2.73 |
||
| − | |7.x |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | !2017-09-22 |
||
| − | |1.14 |
||
| − | |6.0 |
||
| − | |3.3 |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |5.6.3 |
||
| − | |<b>1.0</b> |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |1.8 |
||
| − | |5.6 |
||
| − | |CentOS 7 |
||
| − | |2.73 |
||
| − | |7.x |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | |- |
||
| + | '''Express Suite'''- uses the Lingoport software suite and integrates core capabilities with GitHub to bring developers instant access to languages, all integrated with the way they already work. Linguistic review is done in context, for accuracy and application specific terminology. |
||
| − | !2017-05-01 |
||
| + | * [[Globalyzer i18n Express |Globalyzer i18n Express]]- Globalyzer i18n Express is a GitHub application which scans the added and modified files checked in on a GitHub commit, looking for i18n issues. The committed files are scanned with default rule sets. Files checked in will be scanned and a summary will be added as a comment to the commit in GitHub. |
||
| − | |1.8 |
||
| + | * [[Localyzer Express |Localyzer Express]] - Localyzer Express is a GitHub application which allows for a near immediate machine translation of standard application resource files. Resource files are used by internationalized applications to display user facing strings (such as user interface labels) in different locales (languages, country, variant). As an example, messages.properties, an English resource file, can be translated in French and Japanese, respectively messages_fr.properties and messages_ja.properties. |
||
| − | |5.3 |
||
| + | * [[LocalyzerQA | LocalyzerQA]] - A simplified way to perform linguistic review in a running application and verify and correct translation issues as part of the continuous globalization process. When paired with [[Localyzer Express |Localyzer Express]], it allows for an ''always-on'' machine translation followed by linguistic review in the context of the running application. |
||
| − | |3.2 |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |5.6.2 |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |1.8 |
||
| − | |5.6 |
||
| − | |CentOS 7 |
||
| − | |2.19 |
||
| − | |7.x |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | |- |
||
| + | == Command Center == |
||
| − | !2017-02-01 |
||
| − | |1.8 |
||
| − | |5.3 |
||
| − | |3.1 |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |5.6.1 |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |1.8 |
||
| − | |5.6 |
||
| − | |CentOS 7 |
||
| − | |2.19 |
||
| − | |7.x |
||
| − | |- |
||
| + | [[File:IntroductionSignIn.jpg|600px|center]] |
||
| − | !2016-12-15 |
||
| − | |1.7 |
||
| − | |5.2 |
||
| − | |3.1 |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |5.6.1 |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |N/A |
||
| − | |1.8 |
||
| − | |5.6 |
||
| − | |CentOS 7 |
||
| − | |2.19 |
||
| − | |7.x |
||
| − | |} |
||
| − | ''Updated December 2018'' |
||
| + | '''Command Center''' is the hub of the Lingoport products. See it all, drill down, create notifications and manage the process. Bridge gaps between localization & development. Increase visibility and track globalization metrics. |
||
| − | <nowiki>*</nowiki>Tomcat is required only for the [[Terms_and_Definitions#GlobalyzerServer|Globalyzer Server]]. If a customer chooses to use Lingoport's hosted Globalyzer Server for user administration and rule set creation, the Tomcat requirement is not applicable. |
||
| + | With Command Center, Globalyzer and Localyzer projects can be created and managed together with their data source repositories and the translation management systems. It has been designed to make it easy to manage globalization and localization within an organization by administrators, managers, developers and translators. |
||
| − | <nowiki>**</nowiki>At this time only Java 1.8 is supported. Java 1.9 is <b>not supported</b>, but will be in future releases. |
||
| + | [[File:CCProjects.jpg|600px|center]] |
||
| − | === Continuous Globalization System Hardware Requirements === |
||
| + | ==== Additional Specialized Applications ==== |
||
| − | Many of the Lingoport Suite components are installed on the [[Terms_and_Definitions#continuousglobalizationsystem|Continuous Globalization System]]. This includes [[Terms_and_Definitions#LRM|LRM]], [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportDashboardServer|Dashboard Server]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportDashboardClient|Dashboard Client]], [[Terms_and_Definitions#Jenkins|Jenkins]], MySQL, and [[Terms_and_Definitions#GlobalyzerClient|Globalyzer Client]]. |
||
| + | In addition to the product suite, Lingoport has several integrated components to create and maintain software |
||
| + | for any language or cultural format in every release increment : |
||
| + | * '''IDE (Integrated Development Environment) Integration''': Developers can identify and fix globalization and localization issues in real time. |
||
| − | {| border="1" class="wikitable" style="width=50%" |
||
| + | * '''LingoBot''' : Slack and Microsoft Teams system integration |
||
| − | ! Element |
||
| + | Together with the products and assorted specialized applications, Lingoport enables continuous tracking and updates to the [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] status of software products. |
||
| − | ! Recommended Minimum |
||
| + | =The Continuous Globalization Process = |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | ! CPU |
||
| − | | 4 |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | ! Memory |
||
| − | | 16 GB |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | ! Disk |
||
| − | | 500 GB |
||
| − | |} |
||
| + | * The process starts with the code repository. Developers check in code. |
||
| − | The [[Terms_and_Definitions#GlobalyzerServer|Globalyzer Server]] may be hosted by Lingoport, reside on another server, or be installed on the same system. Other Linux and Windows machines may have Globalyzer clients installed. |
||
| + | * Command Center is where both Globalyzer and Localyzer application work side by side |
||
| + | ** Globalyzer reports the globalization issues to be corrected in the code. |
||
| + | ** Localyzer is used to: |
||
| + | *** set up the locales to translate to |
||
| + | *** identify the resource file types |
||
| + | *** set up the translation vendor, the TMS (translation management system), or the machine translation engine. |
||
| + | * Globalyzer can be used to create the resource files and push them to the code repository. |
||
| + | * Globalyzer and Localyzer analyses are executed from Command Center. The resource files are identified and what needs to be sent to be translated. If a translation vendor is machine translation, then the Localyzer job automatically does the translation, and pushes the translated files back to the code repository. |
||
| + | * The Command Center Localyzer page has a button to send identified files to the translation vendor. Localyzer automatically checks for returned files, imports them and push the files back to the repository. |
||
| + | * During the Linguistic Review process, LingoportQA uses a special locale with identifier keys that can be used to indicate which terms need to be corrected. LingoportQA submits the change. |
||
| + | ** For machine translation Localyzer projects, the code is fixed and the new strings is pushed to the repo. |
||
| + | ** For TMS projects, an additional approval step is done, the files are imported and pushed to the repo. |
||
| − | =Lingoport |
+ | =Lingoport Product Details= |
==Globalyzer== |
==Globalyzer== |
||
| + | Scans code and detects internationalization (i18n) issues |
||
| + | |||
| + | * Connects to the Globalyzer server and logs in. (This might not happen if local rule sets are used) |
||
| + | * Downloads rule sets from server, or uses local rulesets. |
||
| + | * Uses rule set to scan code. |
||
| + | * Displays the i18n issues. |
||
| + | * Can run on developer machines in an Integrated Development Environment |
||
| + | * Runs on the Continuous Globalization System - these results are displayed on Lingoport Dashboard |
||
| + | |||
Lingoport's Globalyzer scans source code for [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] issues. It uses sets of regular expression based rules [[Terms_and_Definitions#ruleset|('rule sets')]] on tokens found by lexers/parsers to detect these issues and to filter false positives. These rule sets are synced and stored on a single server, and may be downloaded onto numerous client applications which perform the source code scans. Please note that the rule sets are only lists of regular expressions, and do not contain any code. |
Lingoport's Globalyzer scans source code for [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] issues. It uses sets of regular expression based rules [[Terms_and_Definitions#ruleset|('rule sets')]] on tokens found by lexers/parsers to detect these issues and to filter false positives. These rule sets are synced and stored on a single server, and may be downloaded onto numerous client applications which perform the source code scans. Please note that the rule sets are only lists of regular expressions, and do not contain any code. |
||
| − | Client applications include a desktop client ([[Terms_and_Definitions#GlobalyzerWorkbench|"Globalyzer Workbench"]]), |
+ | Client applications include an [[Terms_and_Definitions#IDE|IDE]] tool ([[Terms_and_Definitions#GlobalyzerIDE|"Globalyzer in IDE"]]), a desktop client ([[Terms_and_Definitions#GlobalyzerWorkbench|"Globalyzer Workbench"]]), command line clients ([[Terms_and_Definitions#GlobalyzerCommandLine|"Globalyzer CLI"]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#GlobalyzerLite|"Globalyzer Lite"]]), and an [[Terms_and_Definitions#GlobalyzerAPI|API]] that may be used to construct custom programs including Globalyzer code scanning functionality. Client applications may produce scan results in XML, CSV, HTML and Excel formats. Results are also consumed by the Lingoport Dashboard to be analyzed and displayed. The desktop client may also be used to view the results directly. It may be used to scan files that developers are working on, and will display the scan results in the IDEs console output window. |
<b>Globalyzer Server</b> - allows development teams around the world to share and collaborate together using high powered [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] [[Terms_and_Definitions#ruleset|rule sets]] during scanning of code. Development Teams can set up their own server, or use Lingoport's Globalyzer Server to set up users and rule sets. |
<b>Globalyzer Server</b> - allows development teams around the world to share and collaborate together using high powered [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] [[Terms_and_Definitions#ruleset|rule sets]] during scanning of code. Development Teams can set up their own server, or use Lingoport's Globalyzer Server to set up users and rule sets. |
||
| + | <b>Globalyzer Clients</b> |
||
| − | <b>Globalyzer Workbench</b> - provides a fully functional code analysis and editing environment for finding, fixing, testing and reporting on internationalization issues in a wide variety of programming languages. Globalyzer Workbench runs as a stand-alone desktop editor in an Eclipse Environment. |
||
| + | *<b>Globalyzer Lite in IDE</b> - It is ideal for [[Terms_and_Definitions#scan|scanning]] code for internationalization issues on the fly and generating corresponding reports. It does not require an external database. Globalyzer Lite parses and executes Globalyzer Lite Project Definition XML files. Globalyzer Lite in IDE can be incorporated into developers' IDE platforms for a true continuous improvement and development system. |
||
| + | *<b>Globalyzer Workbench</b> - provides a fully functional code analysis and editing environment for finding, fixing, testing and reporting on internationalization issues in a wide variety of programming languages. Globalyzer Workbench runs as a stand-alone desktop editor in an Eclipse Environment. |
||
| + | ** Creates the Project Definition XML files. |
||
| + | ** Sets up the Machine Learning environment. |
||
| + | ** Updates Rule Sets on the server and exports them to the local clients. |
||
| + | ** Creates the resource files to be used by Localyzer . |
||
| + | *<b>Globalyzer Command Line</b> - create automated [[Terms_and_Definitions#scan|Globalyzer scans]] as part of your [[Terms_and_Definitions#ContinuousIntegration|continuous integration]] so that you can report and track internationalization issues over time. There is also a Globalyzer Ant Client, Maven Client and XSL Client. |
||
| − | <b>Globalyzer Lite</b> - ideal for [[Terms_and_Definitions#scan|scanning]] code for internationalization issues on the fly and generating corresponding reports. It does not require an external database, therefore multiple instances of Globalyzer Lite can be run concurrently. Globalyzer Lite parses and executes Globalyzer Lite Project Definition XML files. This bypasses the need to create [[Terms_and_Definitions#Globalyzerprojects|projects]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#scan|scans]] using Globalyzer Workbench. |
||
| − | <b>Globalyzer |
+ | *<b>Globalyzer API</b> - allows you to create [[Terms_and_Definitions#Globalyzerprojects|Globalyzer projects]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#scan|scans]], execute scans, and generate reports from a Java program. |
| + | ==Localyzer (formerly LRM) == |
||
| − | <b>Globalyzer API</b> - allows you to create [[Terms_and_Definitions#Globalyzerprojects|Globalyzer projects]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#scan|scans]], execute scans, and generate reports from a Java program. |
||
| + | Localyzer manages [[Terms_and_Definitions#resourcefiles|resource files]], which contain application text as key-value pairs (the keys are used in the application to retrieve the associated text). Resource files are typically translated across languages as part of the [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] process. Localyzer is used to determine the translation status of these resource files using a MySQL database. It also automates the process of sending text out to [[Terms_and_Definitions#translationvendor|translation vendors]] when changes are made to be base (usually English) application text. |
||
| + | Localyzer also performs various checks regarding the resource files. These checks include confirmation of file integrity, detection of duplicate or missing keys, and numerous other validations. When a translation vendor returns translated text for these resource files, Localyzer will detect the new content and perform its validations. If the validations pass then Localyzer will merge the new translations into appropriate resource files and check these in to source control. The check-in is typically done on a dedicated localization branch. |
||
| − | ==Lingoport Resource Manager (LRM) == |
||
| − | The Lingoport Resource Manager (LRM) manages [[Terms_and_Definitions#resourcefiles|resource files]], which contain application text as key-value pairs (the keys are used in the application to retrieve the associated text). Resource files are typically translated across languages as part of the [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] process. LRM is used to determine the translation status of these resource files. It also automates the process of sending text out to [[Terms_and_Definitions#translationvendor|translation vendors]] when changes are made to be base (usually English) application text. LRM is often used in [[Terms_and_Definitions#Jenkins|Jenkins]] scripts to automate translation. |
||
| + | ==InContext Translation == |
||
| − | LRM also performs various checks regarding the resource files. These checks include confirmation of file integrity, detection of duplicate or missing keys, and numerous other validations. When a translation vendor returns translated text for these resource files, LRM will detect the new content and perform its validations. If the validations pass then LRM will merge the new translations into appropriate resource files and check these in to source control. The check-in is typically done on a dedicated localization branch. |
||
| + | Used by translators, resource files are instrumented as they are sent to [[Terms_and_Definitions#TMS|translation management systems]] so that they can see the string in the application and its context in order to translate more effectively. |
||
| + | ==InContext QA== |
||
| − | <b>LRM Server</b> - this term is used interchangeably with <b>LRM</b>. |
||
| + | The translation reviewer can easily select instrumented resources in an application, identify poor translations, and give suggestions for making improvements. InContext QA greatly improves the translation quality assurance process and can be a vital part of the continuous improvement environment. |
||
| − | |||
| − | <b>LRM Database</b> - the MySQL database used by LRM to manage resource files and translation status. The database is created when LRM Server is installed. |
||
==Lingoport Dashboard== |
==Lingoport Dashboard== |
||
| − | The Lingoport Dashboard displays the [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] status of software projects. |
+ | The Lingoport Dashboard displays the [[Terms_and_Definitions#internationalization|internationalization]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#localization|localization]] status of software projects. The Lingoport Dashboard scans source code and reads in XML reports generated by Globalyzer and Localyzer. It then sends the information to the web server built on the [[Terms_and_Definitions#SonarQube|SonarQube]] platform and displays the information in an easy to digest fashion. This information includes all detected internationalization issues, which may be viewed in source code - with the affected line(s) highlighted. The translation status, translation history, and current translation efforts for projects are also displayed. |
| − | |||
| − | <b>Dashboard Server</b> - displays the results of Globalyzer scans and/or the Lingoport Resource Manager (LRM) status in a web browser. |
||
| − | |||
| − | <b>Dashboard Client</b> - analyzes source code with Globalyzer and/or with LRM and uploads the report information to the Dashboard Server for display. |
||
| − | |||
| − | ==Stack Installer== |
||
| − | The Lingoport Stack Installer and the Stack Updater are automated tools to install, or update, and configure the [[Terms_and_Definitions#continuousglobalizationsystem|Continuous Globalization System]] and the [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportDashboard|Lingoport Dashboard Server]] and [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportDashboardClient|Client]]. They install and configure prerequisite software programs and then install, or update, [[Terms_and_Definitions#LRM|LRM]], [[Terms_and_Definitions#GlobalyzerClient|Globalyzer client]], and [[Terms_and_Definitions#LingoportDashboard|Lingoport Dashboard]]. |
||
| − | |||
| − | =An Example of the Lingoport Suite= |
||
| − | |||
| − | ==The Lingoport Dashboard== |
||
| − | |||
| − | [[File:dashboard_home.jpg|700px]] |
||
| − | |||
| − | Here is an example of the Lingoport Dashboard. This is the Dashboard Home page which shows several Lingoport Projects defined. For the project '''CET.NOAAWeather''', there are '''144 Globalyzer Issues''', it is '''97.7%''' complete. The project uses LRM and is '''93.0%''' completely translated. |
||
| − | |||
| − | If '''CET.NOAAWeather''' is selected, we open a more detailed overview of the Lingoport Suite functions. |
||
| − | |||
| − | ==Lingoport Overview== |
||
| − | [[File:dashboard_overview2.jpg|700px]] |
||
| − | |||
| − | Notice at the top of this screen that it says that it is the '''Lingoport Overview'''. This shows the summary of the Globalyzer Scan and the Resource Manager (LRM) status. |
||
| − | |||
| − | This shows that the Globalyzer Scan looked at '''110 files''' in '''22 directories''' for a total of '''8027 lines'''. |
||
| − | |||
| − | The Globalyzer Issues that were identified were '''Concatenations''' and '''Locale Sensitive Methods'''. |
||
| − | |||
| − | The Resource Manager (LRM) shows '''1 Base Resource File''' to be translated into '''4 Target Locales''' and it is '''93% Complete'''. |
||
| − | |||
| − | From the Dashboards pulldown under the CET.NOAAWeather project name, I can get more detail about the Globalyzer and LRM status. |
||
| − | |||
| − | ==Resource Manager== |
||
| − | |||
| − | [[File:dashboard_lrm.jpg|700px]] |
||
| − | |||
| − | This screen shows the details for the '''Resource Manager''' (LRM) status for project '''CET.NOAAWeather'''. |
||
| − | |||
| − | Notice the '''Resource Manager Completion Report''' in the lower right side. This shows the 4 locales and each of them are '''93%''' completely translated. There is '''1 file''' with '''4 keys''' and '''14 words''' that need to be translated for each locale. |
||
| − | |||
| − | The '''Next Prep Kit Content''', there are no new files to send to translation. This indicates that the base resource file has not changed since the last kit. |
||
| − | |||
| − | In '''Prep Kit Due Dates''', there are two prep kits (number '''3''' and '''4''') that are outstanding. The prep kits are at the translation vendor and they are '''2 days late''' returning. |
||
| − | |||
| − | ==Globalyzer== |
||
| − | |||
| − | [[File:dashboard_globalyzer2.jpg|700px]] |
||
| − | The Globalyzer screen shows more of the details of the Globalyzer Scans. For this example, looking at the '''Globalyzer Scans''' at the bottom left of the screen, we see that only one scan was done. It was a scan named '''java''' based on the Rule Set named '''java05182016''' which found '''144 issues''' in '''6154 lines''' and '''65 files'''. |
||
| + | == Services used by Lingoport products == |
||
| − | These issues are identified as '''Major''', '''Critical''' or '''Minor''' in the '''Globalyzer Issues''' pie chart. |
||
| + | To check on services used by the Lingoport processes: |
||
| + | *incontext-server.service |
||
| + | *lingoport-lingobot.service |
||
| + | *localyzerqa-server.service |
||
| − | If '''Issues''' is selected under '''CET.NOAAWeather''', more detail of the identified issues can be seen. |
||
| + | As the sudo user, these can be checked with the command: |
||
| − | ==Issues== |
||
| + | sudo systemctl status <service name> |
||
| − | [[File:dashboard_issue.jpg|700px]] |
||
| + | The services can be started with: |
||
| − | The Issues page shows all the selected issues. In this case, it is showing '''160''' issues, all of the Globalyzer (144) and LRM (16) issues. |
||
| + | sudo systemctl start <service name> |
||
| + | The services can be stopped with: |
||
| − | For the issue at the top of the screen, the file '''ImageTask.java''' has a '''Locale Sensitive Method''' issue with the use of the '''java.lang.String''' method '''toLowerCase'''. Selecting the file will show the issue in the code. |
||
| + | sudo systemctl stop <service name> |
||
Latest revision as of 19:15, 19 March 2024
Lingoport - Overview
Lingoport provides products and services which help our clients continuously meet internationalization and ongoing localization challenges relating to software development and active globalization.
For more information about internationalization: https://lingoport.com/what-is-i18n/
The Lingoport Products help software engineering teams with the globalization tasks:
- Automatically find and manage internationalization issues and localization changes in your source code and repositories for a wide variety of programming languages.
- Integrate with translation management systems and localization vendors for rapid globalization development, testing and deployment.
- Verify translations in an efficient, process-driven manner.
- Works behind your firewall keeping your source code secure.
Contact Information:
Phone: +1 303-444-8020
Email: info at Lingoport.com
Lingoport, Inc.
Services
Lingoport has been providing software internationalization (i18n) consulting services since the company's inception in 2001.
These services include:
- I18n Analysis - plan for new i18n projects, or gap analysis for mitigating i18n issues. A Lingoport architect and supporting team members clarify i18n business, technical and resource requirements based on market requirements, development discussions, programming technologies and Globalyzer scanning results.
- I18n Implementation - Lingoport provides i18n development teams that can work in a hybrid approach, collaborating with client teams, as well as in turnkey fashion.
- General i18n Consulting and Custom Projects - Sometimes specific problem solving or i18n bug fixing is needed. Lingoport can fulfill that resource need, working in coordination with your teams.
- Process Customization - Any Lingoport product purchase includes consulting time to customize and optimize the Lingoport product suite for the customer.
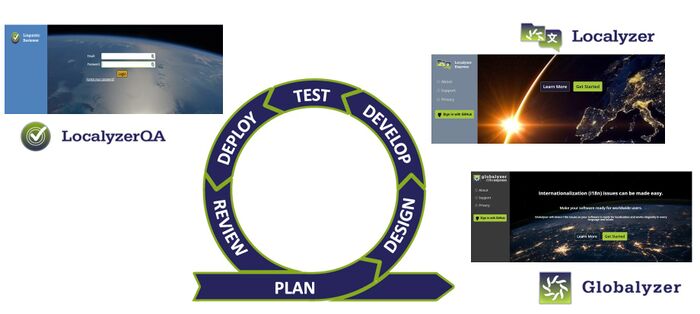
Lingoport Products
The Lingoport products support the continuous globalization process, from the code repository to the translation vendors and back.
Globalyzer – Supports individuals and entire development teams in finding, fixing and maintaining internationalization issues in code in a broad list of programming languages. (More information at Lingoport.com/Globalyzer).
Localyzer – Provides simplified resource file management, verification and translation updating. Localyzer helps development and localization teams keep up with initial and ongoing application interface resources, their translation and automated re-insertion into product builds. (More information at Lingoport.com/Localyzer).
- Machine Translation - Lingoport Supports several popular machine translation vendors as part of the continuous globalization and localization process.
- Translation Management Systems(TMS): Lingoport Localyzer is integrated with leading TMS platforms for a fully automated process from code repository to translator and back.
LocalyzerQA - A simplified way to perform linguistic review and verify and correct translation issues as part of the continuous globalization process.
Express Suite- uses the Lingoport software suite and integrates core capabilities with GitHub to bring developers instant access to languages, all integrated with the way they already work. Linguistic review is done in context, for accuracy and application specific terminology.
- Globalyzer i18n Express- Globalyzer i18n Express is a GitHub application which scans the added and modified files checked in on a GitHub commit, looking for i18n issues. The committed files are scanned with default rule sets. Files checked in will be scanned and a summary will be added as a comment to the commit in GitHub.
- Localyzer Express - Localyzer Express is a GitHub application which allows for a near immediate machine translation of standard application resource files. Resource files are used by internationalized applications to display user facing strings (such as user interface labels) in different locales (languages, country, variant). As an example, messages.properties, an English resource file, can be translated in French and Japanese, respectively messages_fr.properties and messages_ja.properties.
- LocalyzerQA - A simplified way to perform linguistic review in a running application and verify and correct translation issues as part of the continuous globalization process. When paired with Localyzer Express, it allows for an always-on machine translation followed by linguistic review in the context of the running application.
Command Center
Command Center is the hub of the Lingoport products. See it all, drill down, create notifications and manage the process. Bridge gaps between localization & development. Increase visibility and track globalization metrics.
With Command Center, Globalyzer and Localyzer projects can be created and managed together with their data source repositories and the translation management systems. It has been designed to make it easy to manage globalization and localization within an organization by administrators, managers, developers and translators.
Additional Specialized Applications
In addition to the product suite, Lingoport has several integrated components to create and maintain software for any language or cultural format in every release increment :
- IDE (Integrated Development Environment) Integration: Developers can identify and fix globalization and localization issues in real time.
- LingoBot : Slack and Microsoft Teams system integration
Together with the products and assorted specialized applications, Lingoport enables continuous tracking and updates to the internationalization and localization status of software products.
The Continuous Globalization Process
- The process starts with the code repository. Developers check in code.
- Command Center is where both Globalyzer and Localyzer application work side by side
- Globalyzer reports the globalization issues to be corrected in the code.
- Localyzer is used to:
- set up the locales to translate to
- identify the resource file types
- set up the translation vendor, the TMS (translation management system), or the machine translation engine.
- Globalyzer can be used to create the resource files and push them to the code repository.
- Globalyzer and Localyzer analyses are executed from Command Center. The resource files are identified and what needs to be sent to be translated. If a translation vendor is machine translation, then the Localyzer job automatically does the translation, and pushes the translated files back to the code repository.
- The Command Center Localyzer page has a button to send identified files to the translation vendor. Localyzer automatically checks for returned files, imports them and push the files back to the repository.
- During the Linguistic Review process, LingoportQA uses a special locale with identifier keys that can be used to indicate which terms need to be corrected. LingoportQA submits the change.
- For machine translation Localyzer projects, the code is fixed and the new strings is pushed to the repo.
- For TMS projects, an additional approval step is done, the files are imported and pushed to the repo.
Lingoport Product Details
Globalyzer
Scans code and detects internationalization (i18n) issues
- Connects to the Globalyzer server and logs in. (This might not happen if local rule sets are used)
- Downloads rule sets from server, or uses local rulesets.
- Uses rule set to scan code.
- Displays the i18n issues.
- Can run on developer machines in an Integrated Development Environment
- Runs on the Continuous Globalization System - these results are displayed on Lingoport Dashboard
Lingoport's Globalyzer scans source code for internationalization issues. It uses sets of regular expression based rules ('rule sets') on tokens found by lexers/parsers to detect these issues and to filter false positives. These rule sets are synced and stored on a single server, and may be downloaded onto numerous client applications which perform the source code scans. Please note that the rule sets are only lists of regular expressions, and do not contain any code.
Client applications include an IDE tool ("Globalyzer in IDE"), a desktop client ("Globalyzer Workbench"), command line clients ("Globalyzer CLI" and "Globalyzer Lite"), and an API that may be used to construct custom programs including Globalyzer code scanning functionality. Client applications may produce scan results in XML, CSV, HTML and Excel formats. Results are also consumed by the Lingoport Dashboard to be analyzed and displayed. The desktop client may also be used to view the results directly. It may be used to scan files that developers are working on, and will display the scan results in the IDEs console output window.
Globalyzer Server - allows development teams around the world to share and collaborate together using high powered internationalization rule sets during scanning of code. Development Teams can set up their own server, or use Lingoport's Globalyzer Server to set up users and rule sets.
Globalyzer Clients
- Globalyzer Lite in IDE - It is ideal for scanning code for internationalization issues on the fly and generating corresponding reports. It does not require an external database. Globalyzer Lite parses and executes Globalyzer Lite Project Definition XML files. Globalyzer Lite in IDE can be incorporated into developers' IDE platforms for a true continuous improvement and development system.
- Globalyzer Workbench - provides a fully functional code analysis and editing environment for finding, fixing, testing and reporting on internationalization issues in a wide variety of programming languages. Globalyzer Workbench runs as a stand-alone desktop editor in an Eclipse Environment.
- Creates the Project Definition XML files.
- Sets up the Machine Learning environment.
- Updates Rule Sets on the server and exports them to the local clients.
- Creates the resource files to be used by Localyzer .
- Globalyzer Command Line - create automated Globalyzer scans as part of your continuous integration so that you can report and track internationalization issues over time. There is also a Globalyzer Ant Client, Maven Client and XSL Client.
- Globalyzer API - allows you to create Globalyzer projects and scans, execute scans, and generate reports from a Java program.
Localyzer (formerly LRM)
Localyzer manages resource files, which contain application text as key-value pairs (the keys are used in the application to retrieve the associated text). Resource files are typically translated across languages as part of the localization process. Localyzer is used to determine the translation status of these resource files using a MySQL database. It also automates the process of sending text out to translation vendors when changes are made to be base (usually English) application text.
Localyzer also performs various checks regarding the resource files. These checks include confirmation of file integrity, detection of duplicate or missing keys, and numerous other validations. When a translation vendor returns translated text for these resource files, Localyzer will detect the new content and perform its validations. If the validations pass then Localyzer will merge the new translations into appropriate resource files and check these in to source control. The check-in is typically done on a dedicated localization branch.
InContext Translation
Used by translators, resource files are instrumented as they are sent to translation management systems so that they can see the string in the application and its context in order to translate more effectively.
InContext QA
The translation reviewer can easily select instrumented resources in an application, identify poor translations, and give suggestions for making improvements. InContext QA greatly improves the translation quality assurance process and can be a vital part of the continuous improvement environment.
Lingoport Dashboard
The Lingoport Dashboard displays the internationalization and localization status of software projects. The Lingoport Dashboard scans source code and reads in XML reports generated by Globalyzer and Localyzer. It then sends the information to the web server built on the SonarQube platform and displays the information in an easy to digest fashion. This information includes all detected internationalization issues, which may be viewed in source code - with the affected line(s) highlighted. The translation status, translation history, and current translation efforts for projects are also displayed.
Services used by Lingoport products
To check on services used by the Lingoport processes:
- incontext-server.service
- lingoport-lingobot.service
- localyzerqa-server.service
As the sudo user, these can be checked with the command:
sudo systemctl status <service name>
The services can be started with:
sudo systemctl start <service name>
The services can be stopped with:
sudo systemctl stop <service name>