Difference between revisions of "Pull Requests"
(→Configuring Pull Requests) |
(→Verify the Lingoport Dashboard Plugin) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
= Configuring Pull Requests = |
= Configuring Pull Requests = |
||
== Verify the Lingoport Dashboard Plugin == |
== Verify the Lingoport Dashboard Plugin == |
||
| − | The Pull Requests rely on the GitHub plugin. If your system was installed using the Stack Installer, this plugin should have been included |
+ | The Pull Requests rely on the Dashboard GitHub plugin. If your system was installed using the Stack Installer, this plugin should have been included |
<ol> |
<ol> |
||
<li> Go to the Lingoport Dashboard and log in as Administrator. |
<li> Go to the Lingoport Dashboard and log in as Administrator. |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
<li> With '''Installed''' selected, search for '''GitHub'''. You should find a plugin with the description: "Provide some integration between GitHub and SonarQube" |
<li> With '''Installed''' selected, search for '''GitHub'''. You should find a plugin with the description: "Provide some integration between GitHub and SonarQube" |
||
</ol> |
</ol> |
||
| − | If you do not find the Plugin installed, select '''Available''', search for 'GitHub' again and Install it. |
+ | If you do not find the Plugin installed, select '''Available''', search for 'GitHub' again and Install it. |
== Set up Nodes on Jenkins == |
== Set up Nodes on Jenkins == |
||
Revision as of 17:11, 1 February 2018
The Lingoport Suite offers two options for Pull Requests from your repository. The Pull Request can be done on your Lingoport Server or there is a distributed option that uses the Master/Agent capability of Jenkins to distribute the work among several nodes.
To use the Distributed Pull Request option, please install the Node Installer optional software.
Contents
GitHub and Git Pull Requests
GitHub is a Web-based Git repository hosting service. It offers all of the distributed revision control and source code management (SCM) functionality of Git as well as adding its own features.
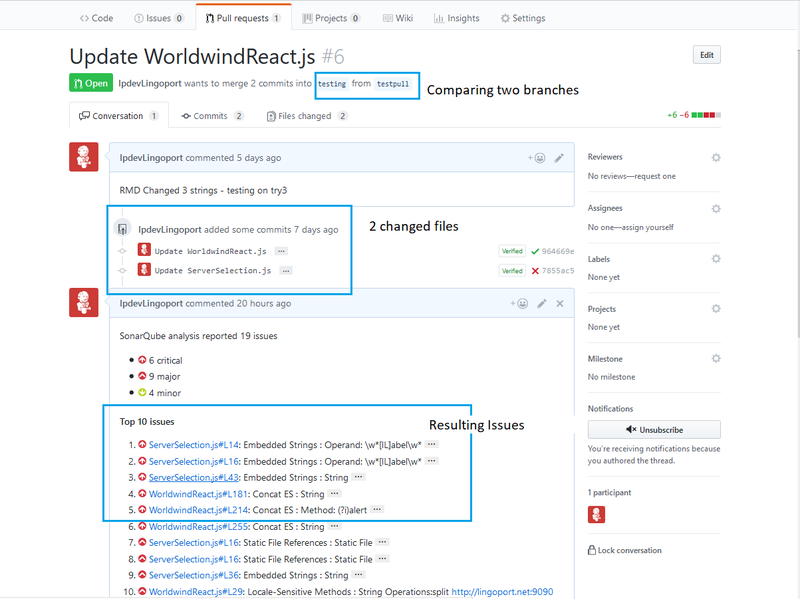
Files can be committed in a Git branch or directly in the Master branch. When committing files in a branch, pull requests let you know what changes you've made to a repository before they are committed to the repository's master branch. Once a pull request is sent, interested parties can review the set of changes, discuss potential modifications, and even push follow-up commits if necessary.
Configuring Pull Requests
Verify the Lingoport Dashboard Plugin
The Pull Requests rely on the Dashboard GitHub plugin. If your system was installed using the Stack Installer, this plugin should have been included
- Go to the Lingoport Dashboard and log in as Administrator.
- Select the Administration tab at the top of the window.
- Select the System pulldown and Update Center
- With Installed selected, search for GitHub. You should find a plugin with the description: "Provide some integration between GitHub and SonarQube"
If you do not find the Plugin installed, select Available, search for 'GitHub' again and Install it.
Set up Nodes on Jenkins
If you are using the Distributed Pull Requests option, the first thing that needs to be done is to set up nodes in Jenkins. If you installed the Node Installer and followed its setup instructions, there should be a master system (where Jenkins and Lingoport Dashboard are hosted) and at least one agent or node system. The master system should be able to ssh into the agents centos user and the jenkins user. If this is not completed, make sure that is done before proceeding further.
If you are not using nodes and agents, skip to the next section.
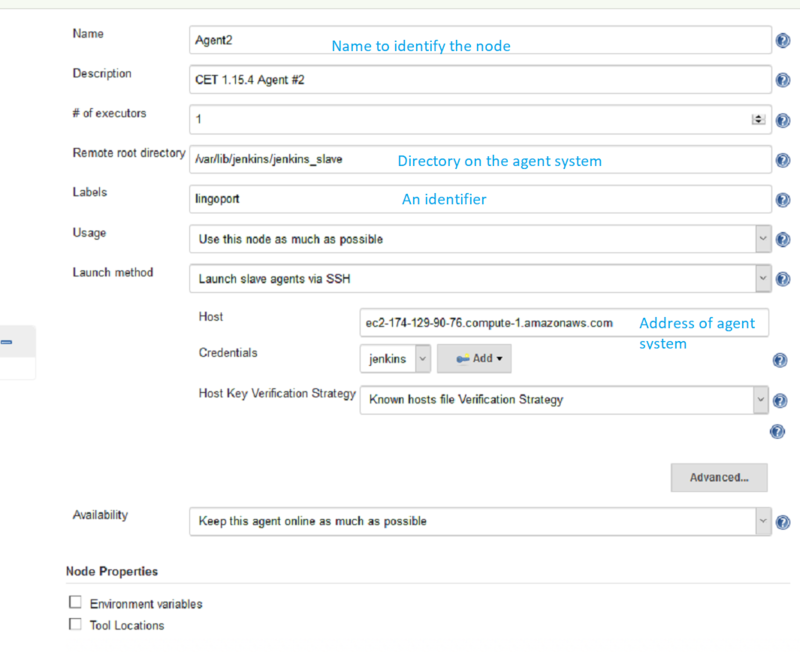
Create Nodes in Jenkins
On the Master system, in Jenkins, select Manage Jenkins → Manage Nodes → New Node
Set up each agent node using this example:
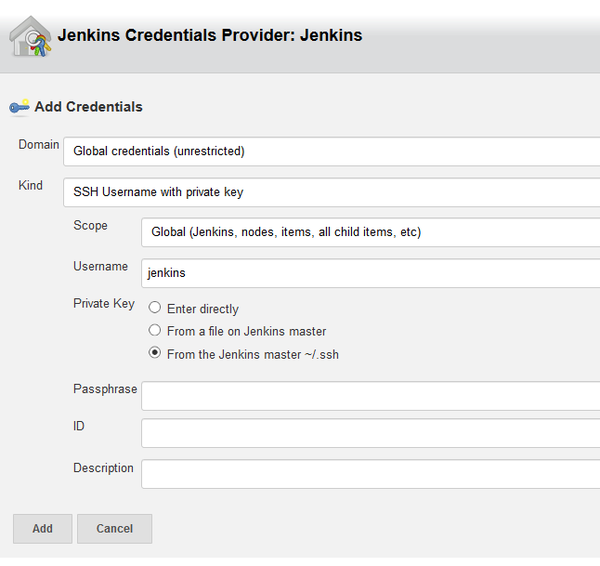
Select Add to create the jenkins ssh credentials
Nothing needs to be done with the master node. Online the new nodes and the console output should look like:
[01/26/18 16:26:19] [SSH] Opening SSH connection to ec2-54-227-210-213.compute-1.amazonaws.com:22. [01/26/18 16:26:19] [SSH] SSH host key matches key in Known Hosts file. Connection will be allowed. [01/26/18 16:26:19] [SSH] Authentication successful. [01/26/18 16:26:19] [SSH] The remote user's environment is: BASH=/usr/bin/bash BASHOPTS=cmdhist:extquote:force_fignore:hostcomplete:interactive_comments:progcomp:promptvars:sourcepath ....
Verify the Agent setup in Jenkins
To verify that the Agent setup is correct, use the Jenkins 'Debug' job.
Under General check Restrict where this project can be run and set it to lingoport.
In the Execute Shell leave only:
whoami pwd sleep 5
Run the job. The console output should show:
Started by user anonymous Building remotely on Agent1 (lingoport) in workspace /var/lib/jenkins/jenkins_slave/workspace/Debug [Debug] $ /bin/sh -xe /tmp/jenkins7953464360000549139.sh + whoami jenkins + pwd /var/lib/jenkins/jenkins_slave/workspace/Debug + sleep 5
Note that it shows that it ran on the Agent using the lingoport label.
Jenkins PullRequest and DistributedPullRequest jobs
There are two Jenkins job templates for Distributed Pull Requests.
- Lingoport.SampleLite-PullRequest
- Lingoport.SampleLite-DistributedPullRequest
The Distributed Pull Request makes use of the Jenkins master/agent system.
- Create a new Jenkins job using the Lingoport.SampleLite-PullRequest or Lingoport.SampleLite-DistributedPullRequest template. This should be modeled on an existing Jenkins project. For example, if you have a Jenkins project called Acme.BigProject and you want to use PullRequests with this project and repository, name the new project Acme.BigProject-PullRequest.