Difference between revisions of "About InContext QA"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[File: InContextQA.png |700px]] |
[[File: InContextQA.png |700px]] |
||
| − | InContext QA allows a user to select a mis-translation, suggest a new value, and submit the change to LRM. |
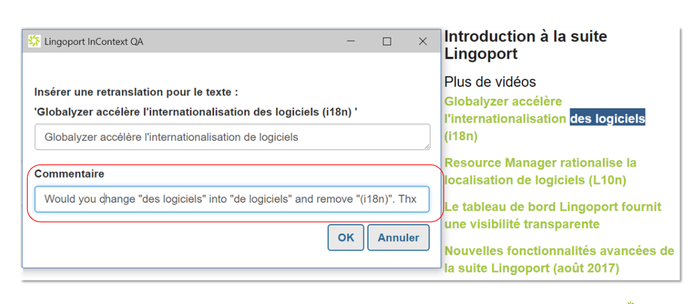
+ | InContext QA allows a user to select a mis-translation, suggest a new value, and submit the change to LRM. In the example above, a reveiwer found that the French translation was incorrect. The string was highlighted and a new string was suggested and a comment given. |
= High Level Goals = |
= High Level Goals = |
||
Revision as of 20:58, 28 March 2019
InContext QA allows a user to select a mis-translation, suggest a new value, and submit the change to LRM. In the example above, a reveiwer found that the French translation was incorrect. The string was highlighted and a new string was suggested and a comment given.
High Level Goals
The Lingoport InContext QA goals are:
- Facilitate the translation review process of internationalized applications
- Provide a simple way to review and edit translations of an application’s string resources in Chrome
The following is not a goal of Lingoport InContext QA:
- Lingoport InContext QA does not replace how translation is done: It is not a translation management system (TMS) and not pretending to be one.
Benefits
- Strings to review are in context. They are on a live Web app so reviewers can see strings in the context they are presented.
- There is no software developer involvement, freeing up developers from the localization process.
- Easy, direct interaction from reviewer to localization group.
- Automatic updates
- Light, minimal learning curve for reviewers.
- Non-intrusive, no changes to the code and web apps can be deployed while being reviewed.
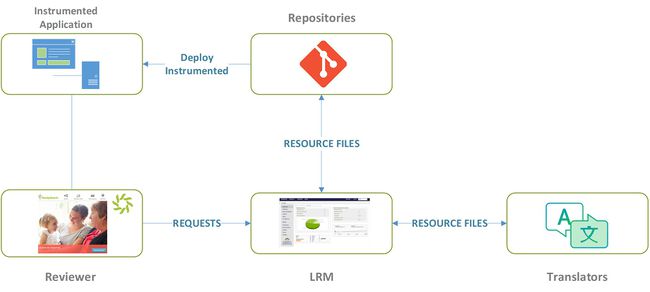
System Overview
For an on-boarded repository, the happy path looks like:
- Resource files are analyzed by Lingoport Resource Manager (LRM) and displayed in the Dashboard
- Resource files which need to be translated are sent to the Translation Group
- Translated resource files are received by LRM and pushed to the repo
- Translated resource files are instrumented
- The application with instrumented resource files are deployed to a Linguistic QA server
- The reviewers navigate to the deployed instrumented application
- The reviewers submit suggestions which are captured by LRM
- LRM handles the retranslation requests and deals with the book keeping, the automation, the metrics, etc.