Difference between revisions of "InContext Server Installation"
(→Docker-based Installation of InContext Server) |
(→Docker-based Installation of InContext Server) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
Users in the 'docker' group may optionally omit use of sudo. |
Users in the 'docker' group may optionally omit use of sudo. |
||
| − | = Docker-based Installation of InContext Server = |
+ | == Docker-based Installation of InContext Server == |
For a new, simplified deployment process, the InContext Server can be installed using Docker. This section outlines the Docker-based installation process. |
For a new, simplified deployment process, the InContext Server can be installed using Docker. This section outlines the Docker-based installation process. |
||
<B>Please note this section is currently a WORK IN PROGRESS so it may not be fully accurate</B> |
<B>Please note this section is currently a WORK IN PROGRESS so it may not be fully accurate</B> |
||
| − | == Pre-Requisites == |
+ | === Pre-Requisites === |
| − | === Create sudo user if needed on the VM === |
+ | ==== Create sudo user if needed on the VM ==== |
A user, such as centos or ec2-user, with sudo privileges is required as the user under which to install InContext Server |
A user, such as centos or ec2-user, with sudo privileges is required as the user under which to install InContext Server |
||
| − | === This is a Docker installation === |
+ | ==== This is a Docker installation ==== |
This requires Linux and a Docker installation. |
This requires Linux and a Docker installation. |
||
The details on the installation of Docker itself on the Linux vm can be found [[ Command_Center_Installation#Docker_Install|here ]] |
The details on the installation of Docker itself on the Linux vm can be found [[ Command_Center_Installation#Docker_Install|here ]] |
||
Most of the containers will be managed by Docker. However, volumes will be mounted on the Linux virtual machine and a database configuration file will reside on the VM |
Most of the containers will be managed by Docker. However, volumes will be mounted on the Linux virtual machine and a database configuration file will reside on the VM |
||
| − | === Installation Files === |
+ | ==== Installation Files ==== |
The installation files for InContext are located in the same place as the ones for Command Center. |
The installation files for InContext are located in the same place as the ones for Command Center. |
||
Clone the public repo in the home directory of your sudo user. The public repo can be found at the [[https://github.com/Lingoport/CommandCenterConfig|Public Repo]] |
Clone the public repo in the home directory of your sudo user. The public repo can be found at the [[https://github.com/Lingoport/CommandCenterConfig|Public Repo]] |
||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
The other items in the file should not be required to be modified. |
The other items in the file should not be required to be modified. |
||
| − | == Installation Process == |
+ | === Installation Process === |
Modify the `install.conf` file with your specific configurations, including Docker Hub credentials (account with read access to the InContext Image will be shared by Lingoport), MySQL root password (to be created with an associated MySQL 8 container), and desired server port. |
Modify the `install.conf` file with your specific configurations, including Docker Hub credentials (account with read access to the InContext Image will be shared by Lingoport), MySQL root password (to be created with an associated MySQL 8 container), and desired server port. |
||
Revision as of 20:56, 12 April 2024
Contents
Checking InContext Server Installation
The typical G11n system can be installed using either the Lingoport Stack Installer or a Docker-based method. Depending on the installation method used, the process to check if the InContext Server is installed will differ.
Checking Installation for Systems Installed with Lingoport Stack Installer
If your system was installed using the Lingoport Stack Installer, check the installation with:
$sudo systemctl status incontext-server
Output should indicate if the service is active. If the service is not found, it needs to be installed manually.
Checking Installation for Docker-based Systems
For systems intending to use the Docker-based installation, check if the Docker container for the InContext Server is running with:
$ sudo docker ps | grep incontext-server
If there's no output, the container is not running, indicating the InContext Server needs to be set up or there is an issue that needs to be addressed. Users in the 'docker' group may optionally omit use of sudo.
Docker-based Installation of InContext Server
For a new, simplified deployment process, the InContext Server can be installed using Docker. This section outlines the Docker-based installation process.
Please note this section is currently a WORK IN PROGRESS so it may not be fully accurate
Pre-Requisites
Create sudo user if needed on the VM
A user, such as centos or ec2-user, with sudo privileges is required as the user under which to install InContext Server
This is a Docker installation
This requires Linux and a Docker installation. The details on the installation of Docker itself on the Linux vm can be found here Most of the containers will be managed by Docker. However, volumes will be mounted on the Linux virtual machine and a database configuration file will reside on the VM
Installation Files
The installation files for InContext are located in the same place as the ones for Command Center. Clone the public repo in the home directory of your sudo user. The public repo can be found at the [Repo]
Once cloned create a new directory in the home directory called IncontextInstall (It can be named anything you wish)
Copy the contents from CommandCenterConfig/Incontext/ to the new directory
Go into the directory (cd) and make all of the shell scripts executable
cd ~/IncontextInstall chmod +x ./*.sh
Open the install.conf with your editor as there are a couple of items in the file that will need to be modified
Set the home_directory to the home directory of the current user
Set the incontext_image_version to the current version of InContext-Server. If unsure what the version is, it can be found Here
Optionally change the serverPort if desired or leave it at the default
Set the database_root_password to a password that you want to use for the root user on the database. Note this should be a good password so something from a random generator is a good idea of significant length.
The other items in the file should not be required to be modified.
Installation Process
Modify the `install.conf` file with your specific configurations, including Docker Hub credentials (account with read access to the InContext Image will be shared by Lingoport), MySQL root password (to be created with an associated MySQL 8 container), and desired server port.
Execute the `InstallIncontext.sh` script with sudo privileges.
$ sudo ./InstallIncontext.sh
This script will:
- Create necessary Docker network and volumes
- Pull the Lingoport InContext Server image from Docker Hub
- Start the InContext Server and MySQL containers with appropriate configurations
You may be prompted if there is missing info in the install.conf. Ensure you follow any prompts provided by the script for a successful installation.
The script will download all the Docker images that are required and perform the docker based installation.
Once installed it will also start the InContext Server
To confirm that Incontext is running use the below Docker command
sudo docker container ls
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
d29515f5f979 lingoport/incontext_pro:1.5.0_2 "catalina.sh run" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 0.0.0.0:8085->8080/tcp, :::8085->8080/tcp angry_tu
4d323af14731 mysql:8.0 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 2 minutes ago Up 2 minutes 3306/tcp, 33060/tcp incontextDatabase
The output will show both the running Incontext server as well as the MySQL db that is used by Incontext
At this point, the base system should be up and running.
Verify the installation by checking the Docker container status and accessing the InContext Server through the web browser.
Go to User Guide to log in for the first time and perform the base configuration.
Manual Installation
For systems not utilizing Docker or needing a specific setup, manual installation is also available.
InContext Server Installation Requirements
- Java 11
- MySQL 8
- Tomcat 9.0.x
Installation Steps - Docker
1. Download and unzip the `IncontextServer-<version>.zip` file. 2. Modify `install.conf` with necessary details. 3. Execute `./install.sh` with sudo privileges.
Installation Steps - Non-Docker
1. Download and unzip the IncontextServer-<version>.zip file from our SFTP site.
2. Change directory: cd incontext-server
3. Modify install.conf to set the values required by the install. Any information left blank will be prompted by the install script.
MYSQL_ROOT_PASS- this is the password that was used or created by the Stack Installer or Stack Updater.INCONTEXT_MYSQL_USER / INCONTEXT_MYSQL_PASS- this is a new MySQL username and password.INSTALL_TOMCAT_HERE='/usr/local/tomcat'- Unless there is reason to change the location, leave it at the default.
4. Run the install script (note you must have sudo privileges): ./install.sh. If it is successful, one should see:
Incontext Server successfully installed.
InContext Server Files
There are three files that comprise the InContext Server. The Lingoport InContext Server automated installation process will put these files in the appropriate location.
- incontext-server.war
- incontext-server.sh
- IncontextServerConfig.groovy
Installation Steps - Non-Docker
−
The incontext-server.war is the server itself and must be placed under the tomcat/webapps directory.
−
The incontext-server.sh file is a script for starting/stopping the InContext Server and must be configured and placed in the tomcat directory.
− The IncontextServerConfig.groovy file is the configuration file for the InContext Server and must be configured and placed in the tomcat directory.
−
Running the InContext Server - Non-Docker
To start the InContext Server:
$sudo systemctl start incontext-server
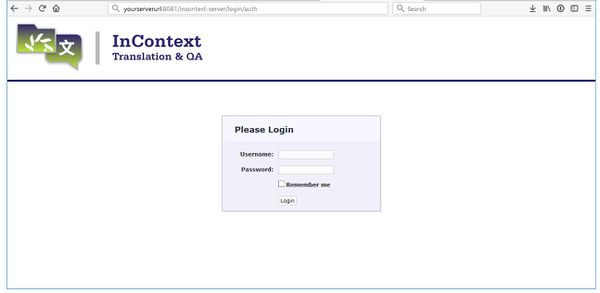
Then browse to: http://yourserverurl:8081/incontext-server
To stop the InContext Server:
$sudo systemctl stop incontext-server
To check the status of the InContext Server:
$sudo systemctl status incontext-server
Next Steps
Whether installed via Docker or manually, the next steps involve configuring and using the InContext Server for your localization needs. For more details on post-installation setup and usage, refer to the InContext Server Users Guide.
InContext Capture Installation provides additional resources for setting up InContext for Translation.
For information on how to proceed after installation, please see the: InContext Server Users Guide