Difference between revisions of "Command Center Installation"
(→Docker) |
(→Start Docker.) |
||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
====Start Docker.==== |
====Start Docker.==== |
||
| + | Start docker using the following command: |
||
$ sudo systemctl start docker |
$ sudo systemctl start docker |
||
| + | |||
| + | Enable the Docker service to start automatically on system boot by running the following command: |
||
| + | |||
| + | $ sudo systemctl enable docker |
||
====Verify that Docker Engine is installed correctly ==== |
====Verify that Docker Engine is installed correctly ==== |
||
Revision as of 17:12, 17 January 2023
Contents
- 1 Pre-Requisites
- 1.1 Intro
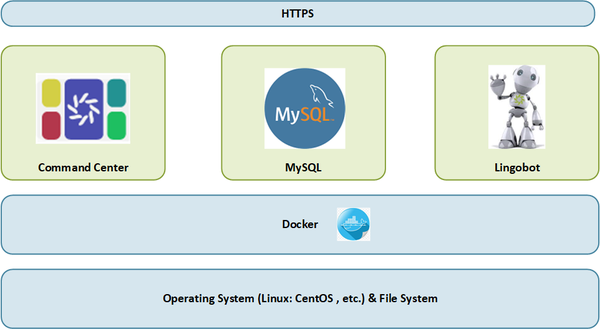
- 1.2 Diagram
- 1.3 Hardware
- 1.4 Docker
- 1.4.1 Uninstall old docker versions
- 1.4.2 Install docker using the repository
- 1.4.3 Start Docker.
- 1.4.4 Verify that Docker Engine is installed correctly
- 1.4.5 Copy install/update/uninstall and install.conf file to your home directory (/home/centos)
- 1.4.6 Set up install.conf
- 1.4.7 Run InstallCommmandCenter.sh
- 1.5 Firewall
- 1.6 Credentials
- 1.7 Installation Files
- 2 Installation
Pre-Requisites
Before installing or updating Command Center, please verify this section is complete.
Intro
Diagram
Hardware
Docker
Docker is a platform that allows you to easily develop, test, and deploy applications as containers. This section will walk you through the process of installing Docker on a Linux system.
On the system (most likely a VM) dedicated to Command Center, make sure you have the latest version of docker up and running. The following steps may help.
A user with sudo privileges is required to run most commands.
Uninstall old docker versions
This is an optional step in case your docker version is out of date:
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
Install docker using the repository
sudo yum install -y yum-utils
sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
Start Docker.
Start docker using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl start docker
Enable the Docker service to start automatically on system boot by running the following command:
$ sudo systemctl enable docker
Verify that Docker Engine is installed correctly
Run the hello-world image.
$ sudo docker run hello-world
Copy install/update/uninstall and install.conf file to your home directory (/home/centos)
You can find files at https://github.com/Lingoport/Command-Center/tree/liliDev/docker
install.conf InstallCommmandCenter.sh UninstallCommmandCenter.sh UpdateCommmandCenter.sh
Set up install.conf
You need to provide your serverURL, your Docker Hub username and token, and MYSQL root password you want to use
Run InstallCommmandCenter.sh
To check the running container status
docker ps
Note: Docker image version is not the Command Center version, check latest docker image version at https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/lingoport/command-center_dev/general
Firewall
Credentials
(internal, LDAP, SSO)
Installation Files
Please contact support (at) lingoport (dot) com in order to get files which will be used for the installation or the update of your Command Center instance:
command-center-config.sh: for your specific configurationInstallCommandCenter.sh: for new installations: This will drop any data in the database and start cleanlyUpdateCommandCenter.sh: for updates to an existing system
Installation
Create the database conf file
The following is provided for a CentOS system:
Uses the centos user as default user for docker
/home/centos/mysql/conf.d/mysql.cnf
[client] default-character-set = utf8mb4
[mysql] default-character-set = utf8mb4
Install Command Center
New Installation
Configure the settings
In the command-center-config.sh, set the following variables. Make sure to keep the 'export' statements as those will be used to create the environment variables for the install script below.
Run the docker installer
Run the InstallCommandCenter.sh under home directory
To verify the installation went well, check the docker processes.
sudo docker ps
You should see at least an MySQL and a Command Center container running.
Log in to the URL based on the command-center-config.sh settings, so something like:
https://commandcenter.mycompany.io/
You should now be able to install the licenses and create projects.
Update
Licenses
Start and Stop System
Verify Installation
Installation / Update (Docker)