On Boarding a project with both LRM and Globalyzer
Contents
Before On Boarding a project with both LRM and Globalyzer
To on-board a project, a some basic information is needed:
Globalyzer
Code Repository Location
- The code repository location and branch for the project.
- Git locations could look like: https://github.com/group/project ; In addition, the branch for the Git project is needed.
- SVN locations could look like: https://svn.group.com/project/trunk.
- Read and Write Access granted to repository.
Globalyzer Scan Information
- The directories and files to be scanned, as well as what should not be scanned, like code libraries.
- The rulesets to be used to scan the source code.
- A Globalyzer Project file is created with this information and put in the code repository.
LRM
Code Repository Location
- The code repository location and branch for the project.
- Git locations could look like: https://github.com/group/project ; In addition, the branch for the Git project is needed
- SVN locations could look like: https://svn.group.com/project/trunk
- Read and Write Access granted to repository
Users
- The list of translation requesters. Those members to add to Jenkins so they have permission to trigger the Prep Kit job:
username1@company.org, username2@companyname.com - The list of emails to be notified of the LRM actions:
username1@company.org, username2@companyname.com, username3@companyname.comNote: All emails will also be used as Dashboard user identifiers.
Locales
- The locale of the files created by developers and to be translated
- The list of target translation locales
- The pseudo-locale
Resource File types
- Files types (for instance .properties, .resx, etc.)
- Naming convention for the base file: for instance <filename>_en.properties or <filename>.properties
- Translated file naming convention: for instance <filename>_fr_FR.properties
- The files or directories which follow the above convention but should NOT be translated. For instance **/config*.properties
Localization Vendor
- Who is the translation management system and how are the resource files going to be transferred to them?
- Lingoport supports Local vendors, FTP and SFTP, and WorldServer and Lingotek and also other vendors.
On Boarding the LRM Automation Job
Jenkins
Create the Jenkins job
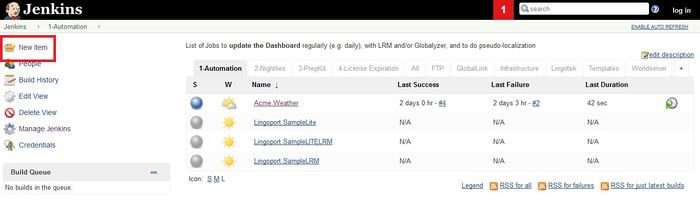
To begin the on-boarding process, go to Jenkins, and select the 1-Automation Tab, and New Item
- Make a copy of
Lingoport.SampleLRM - Set the name of the new job to <groupname>.<projectname>
- Make sure Add to current view is checked and select OK
Configure the Jenkins job
General
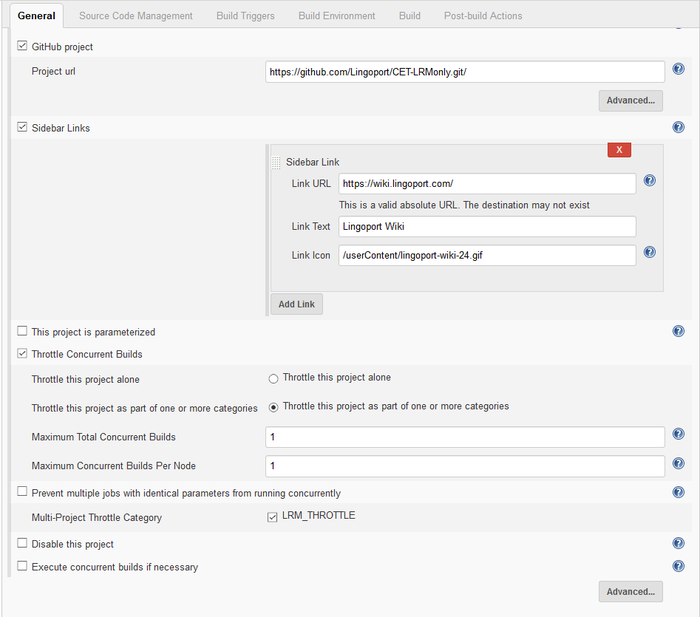
- General section: Select the GitHub project and fill in the Project url
- Throttle Current Builds should be checked.
- LRM Throttle should be checked.
Source Code Management
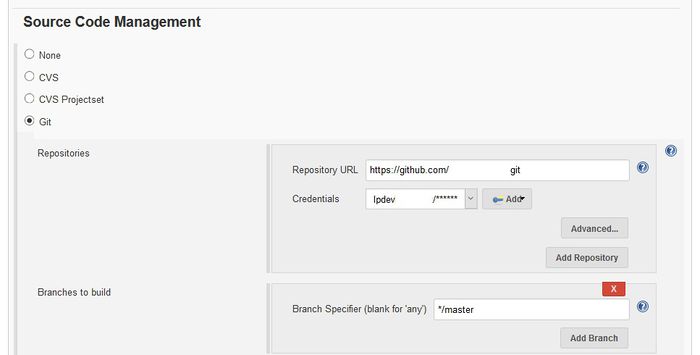
Source Code Management section: Set up the Repository, Credentials, and Branch
Build Triggers
These are left unchecked by default, but the Build Periodically can be set to build on a repeating basis.
Build Environment
Leave these unchecked.
Build
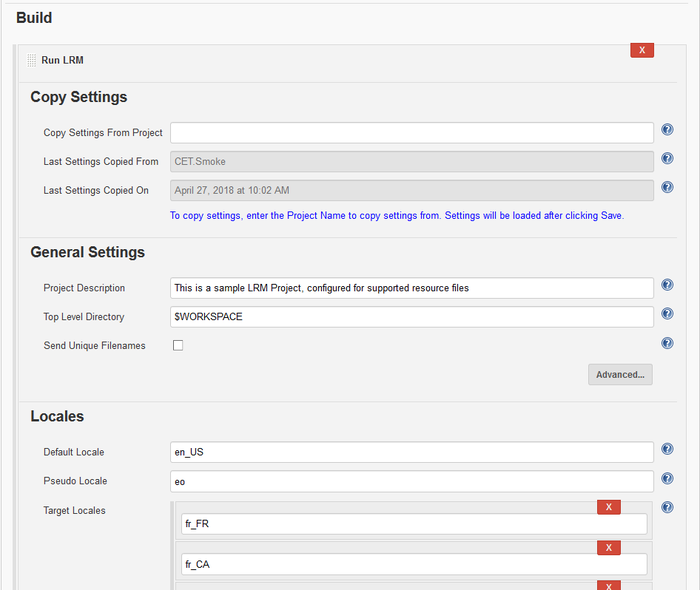
- The Top Level Directory is defaulted to look at the whole repository. If the resource files are located under a resources directory, this can be changed to
$WORKSPACE/resources. - Locales are defaulted to common values. Remove and add locales to get the appropriate translation languages. Pseudo locale defaults to 'eo'.
- Copy Settings: Use this if you have a project already set up with a similar configuration. This can save configuration time. If there is no other project, just leave it unfilled.
- Set the Send Unique File Names to 1 if you want the prep kit files to have unique file names. The default is not to send unique file names. If you have multiple file names that have the same name you may want to change the flag to 1. For more information see LRM Unique File Names
- Advanced: Detect Errors: It is unlikely you need to change the default settings.
- Missed Translation Error: (Default: Unchecked) If you check this box, when a string is returned back from translation with the same text as the original one, an error will be raised. Be cautious with this check: Population for instance is the same word in English and in French.
- Parameter Mismatch Error: (Default: Checked) Keep this check if you'd like to make sure that when a parameter(s) is (are) sent in a text, say "Hello {userName}", the same parameter(s) is (are) sent back untranslated. If the French translation is "Bonjour {nom d'utilisateur}", the 'userName' variable cannot be replaced at run time in the application.
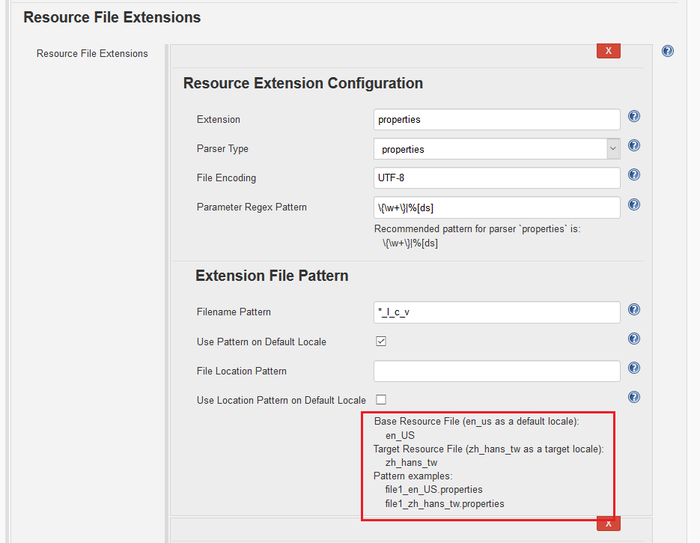
- You can have more than one file extension. For example, you may have .json file and .properties files in the same repository. For each file extension, fill in or modify the following fields:
- Extension: the resource file extension, for instance properties (without the '.'), json, resx, etc.
- Filename Pattern:
- The
*(star) character represents the filename without the extension or the locales; lrepresents the locale's language, for instance 'fr' for Frenchcrepresents the locale's country, for instance 'FR' for Francevrepresents the locale's variant. That's less frequent. is the variant.
- The
- A few examples may help:
*_l_c_v: If a target locale is fr_FR and messages_en.properties needs to be translated, the French file will be message_fr_FR.properties*.l-c-v: If a target locale is fr_FR and messages.resx needs to be translated, the French file will be messages.fr-FR.resx*-l-c-v: If a target locale is fr_FR and messages-en.json needs to be translated, the French file will be messages-fr-FR.json
- The sample at the bottom shows what the system is going to look for resource files. Verify that the resource files look like the example, otherwise errors could occur.
- For the other entries, leave them defaulted unless told to change them.
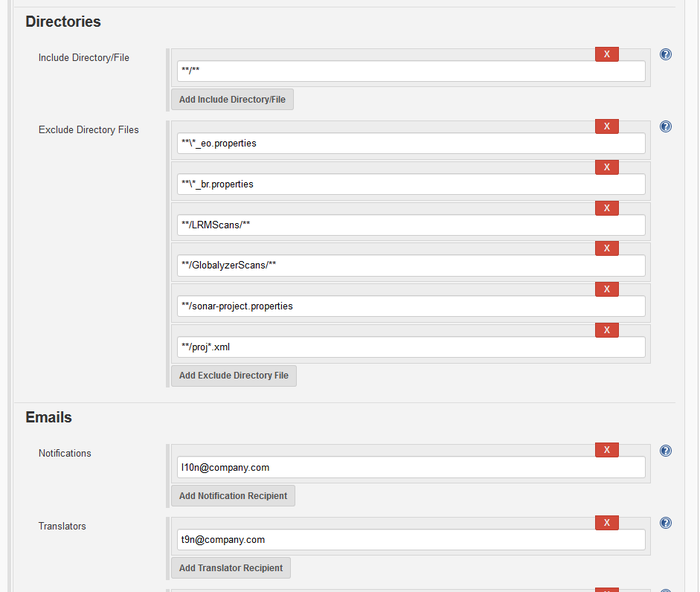
- Directories: Which directories and files to include and which ones to exclude as resource files.
- Emails: Who will be receiving emails for which notification
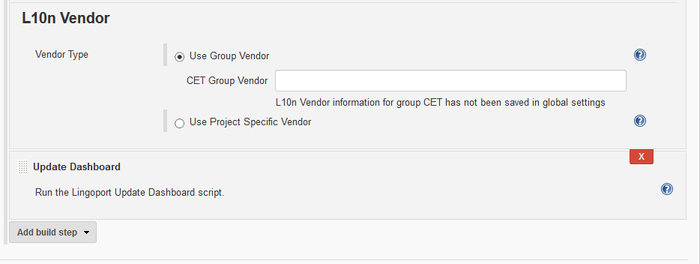
- The L10n Vendor can be configured in Jenkins, Manage Jenkins or in the project. Also a project can have a different value than other projects in the same group.
Post Build Actions
- Nothing needs to be modified in this section
Select the Save button. Enable the project and Build Now. The Jenkins project should run and push the results to the Lingoport Dashboard.
For more information, see Project Configuration Files
Verifying the Automation Job
The Jenkins job should complete successfully and populate the Lingoport Dashboard.
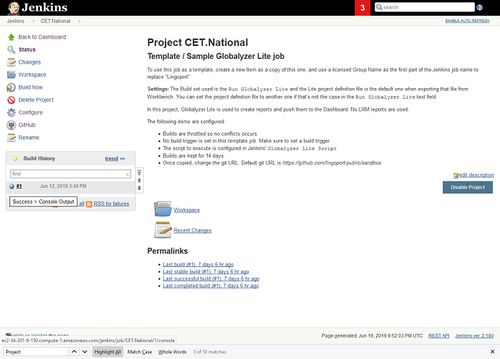
To check if it completed successfully, select the project and look at the Build History
The indicator should look like a blue ball. If it is a red ball, select it to go to Console Output and look for errors.
If the indicator is blue, then login to the Lingoport Dashboard and verify that the project is on the Dashboard. When you hover over the Next Send Translation Content, a list of files to be translated will come up. Verify that they are the correct files to be translated.
If there are problems at this point, please contact support@lingoport.com for assistance.