Command Center Installation
Contents
Pre-Requisites
Before installing or updating Command Center, please verify this section is complete.
Intro
IT
When installing Command Center on premises, the customer IT group is very important to the successful deployment of the Lingoport applications when installing the suite on site. In particular, the IT group that sets up the Linux system must understand the usage model for the system. Lingoport requires a meeting with the parties responsible for setting up and maintaining the host system before installation can properly begin. The hope is that once the system is setup for installation, minimal IT interaction is necessary.
Preparations must be made with the IT team to ensure that all prerequisites are met before installation. For new installations, this is the recommended method to use to verify that all the various actors work together well.
Basics
Before installing Command Center, the following needs to be configured:
- Hardware
- Linux
- Docker
- Firewall
- Https
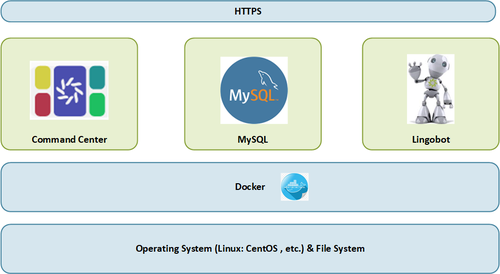
Diagram
Hardware & Software Requirements
The following sections describe the hardware and software requirements for Command Center.
Please note that the Globalyzer Server installation is in a different section.
Hardware Requirements
| Element | Minimum | Recommended |
|---|---|---|
| CPU | 2 | 4 |
| Memory | 16 GB | 16 GB |
| Disk | 160 GB | 500 GB |
The Globalyzer Server may be hosted by Lingoport, reside on another server, or be installed on the same system. Other Linux and Windows machines may have Globalyzer clients installed.
Software requirements
The current versions of these software products can be found at: Current versions of Lingoport products and supporting applications
| Software | Recommended |
|---|---|
| Operating System | Linux, CentOS (7) or RedHat (8) |
Since this is a Docker installation, most of the containers will be managed by Docker. However, volumes will be mounted on the Linux VM and a database configuration file will reside on the VM: This requires Linux.
Access and Ports / Firewall
Command Center may need to be accessible by Lingoport and customer personnel to configure jobs, check the console if any problem arise, run jobs if necessary. Command Center needs to be accessible by many customer actors, including development teams, management, and QA, Lingoport, Translation Vendors.
Please see External Access and Ports for all the details.
HTTPS
HTTPS configuration is often achieved via a reverse proxy hosted on the Linux system. Instructions to do so using Apache are as follows for CentOS / RHEL:
1. Install apache and mod_ssl (https support for apache)
sudo yum install httpd
sudo yum install mod_ssl
2. Configure SELinux to allow apache network connections
sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect true
3. Add http (not s) config file with the following content (edit as appropriate):
/etc/httpd/conf.d/lingoport-apps.conf
<VirtualHost *:80>
# ServerName SERVER_URL_REPLACE_ME # example: myserver.lingoport.io
AllowEncodedSlashes NoDecode
ProxyPreserveHost On
ProxyRequests Off
# Default command center config - hosted on port 8083 under url path '/command-center/'
ProxyPass /command-center/ http://localhost:8083/command-center/ nocanon
ProxyPassReverse /command-center/ http://localhost:8083/command-center/
# Default fallback config, redirect to port 8083 for urls without '/command-center/' as the starting path.
# Adjust this if a different fallback mechanism is preferred.
ProxyPass / http://localhost:8083/
ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:8083/
# Force HTTPS only (Requires ssl config enabled)
#Header edit Location ^http://(.*)$ https://$1
#RewriteEngine on
#RewriteCond %{SERVER_NAME} =SERVER_URL_REPLACE_ME
#RewriteRule ^ https://%{SERVER_NAME}%{REQUEST_URI} [END,NE,R=permanent]
</VirtualHost>
4. Restart apache to apply the settings
sudo systemctl restart httpd
5. Acquire a certificate. Please follow your organization's instructions to do so. You should have a private key, and acquire both a certificate and a certificate chain. Some orgs may provide the certificate in the same file as the chain. Please request .pem style certificates, or convert the certificates to .pem.
6. Place the certificate and private key on a secure location on your system. Standard location is /etc/pki/tls/, with the certificate under /etc/pki/tls/certs/ and the associated private key under /etc/pki/tls/private/
7. Add apache config to utilize the certificate:
/etc/httpd/conf.d/lingoport-apps-ssl.conf
<IfModule mod_ssl.c>
<VirtualHost *:443>
ServerName SERVER_URL_REPLACE_ME # example: myserver.lingoport.io
DocumentRoot /var/www/html
AllowEncodedSlashes NoDecode
ProxyPreserveHost On
ProxyRequests Off
# Default command center config - hosted on port 8083 under url path '/command-center/'
ProxyPass /command-center/ http://localhost:8083/command-center/ nocanon
ProxyPassReverse /command-center/ http://localhost:8083/command-center/
# Default fallback config, redirect to port 8083 for urls without '/command-center/' as the starting path.
# Adjust this if a different fallback mechanism is preferred.
ProxyPass / http://localhost:8083/
ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:8083/
# SSL Settings. These may be placed in other config files instead, but are left here for convenience.
SSLEngine on
# BEGIN Possible security settings - based on LetsEncrypt recommendations as of Feb 2023.
# ---
# Please adjust to your own organization's guidelines!
SSLHonorCipherOrder off
SSLProtocol all -SSLv2 -SSLv3 -TLSv1 -TLSv1.1
SSLCipherSuite ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
SSLOptions +StrictRequire
# Add vhost name to log entries:
LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-agent}i\"" vhost_combined
LogFormat "%v %h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" vhost_common
# ---
# END Possible security settings
# Reference the certificates:
SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/<yourserver.yourorg.com>.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/<yourserversprivatekey>.pem
# Not necessary if the certificate file includes a chain as well. See [[apache doc|https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/mod_ssl.html#sslcertificatefile]]
SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/dockerdev1.lingoport.io/chain.pem
</VirtualHost>
</IfModule>
8. Optionally enforce a redirect to https by uncommenting and filling out the following section in /etc/httpd/conf.d/lingoport-apps.conf
Before:
# Force HTTPS only (Requires ssl config enabled)
#Header edit Location ^http://(.*)$ https://$1
#RewriteEngine on
#RewriteCond %{SERVER_NAME} =SERVER_URL_REPLACE_ME
#RewriteRule ^ https://%{SERVER_NAME}%{REQUEST_URI} [END,NE,R=permanent]
After:
# Force HTTPS only (Requires ssl config enabled)
Header edit Location ^http://(.*)$ https://$1
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{SERVER_NAME} =example.somecorp.com
RewriteRule ^ https://%{SERVER_NAME}%{REQUEST_URI} [END,NE,R=permanent]
9. Restart apache to apply the settings
sudo systemctl restart httpd
Docker Pre-Requisite
Docker is a platform that allows you to easily develop, test, and deploy applications as containers. This section will walk you through the process of installing Docker on a Linux system.
On the system (most likely a VM) dedicated to Command Center, make sure you have the latest version of docker up and running. The following steps may help.
A user with sudo privileges is required to run most commands.
Uninstall old docker versions
This is an optional step in case your docker version is out of date:
sudo yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
Install docker using the repository
sudo yum install -y yum-utils
sudo yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin
Start Docker.
Start docker using the following command:
$ sudo systemctl start docker
Enable the Docker service to start automatically on system boot by running the following command:
$ sudo systemctl enable docker
Verify that Docker Engine is installed correctly
Run the hello-world image.
$ sudo docker run hello-world
This command will run a test container and display a message indicating that the installation is working properly.
Credentials
When deploying Command Center, the configuration determines if the user management is done by Command Center itself, via an LDAP, or via SSO (using SAML).
Command Center User Database
One administration user is configured. Contact support (at) lingoport (dot) com in order to get an administration user and password. That user can then create Command Center users. It is strongly recommended to change the first administration password and keep it safe.
LDAP
- LDAP Connection
- Management
SSO
- SSO Connection
- Management
New Command Center Installation
Create the database conf file
If you are using a CentOS system:
Uses the centos user, with sudo privileges, as default user for docker
- /home/centos/mysql/conf.d/mysql.cnf
[client] default-character-set = utf8mb4 [mysql] default-character-set = utf8mb4
If you are using a RedHat system:
- /home/ec2-user/mysql/conf.d/mysql.cnf
[client] default-character-set = utf8mb4 [mysql] default-character-set = utf8mb4
Configuration
Request the CommandCenterInstall.zip file from your customer success engineer. The zip file contains four files:
install.conf InstallCommandCenter.sh UninstallCommandCenter.sh UpdateCommandCenter.sh
Copy the above files to your home directory (/home/centos or /home/ec2-user)
Set up install.conf
You need to provide your serverURL, your Docker Hub username and token, and MYSQL root password you want to use. Also make sure the version is the one that is wanted.
#!/bin/bash # # Provide the Docker network name you want to create # database_network=mysqlnetscommand # # Provide the MYSQL root password you want to create for the MySQL database container # database_root_password=mySQL!c0mma9d # # Provide your Docker Hub username # docker_username=xxxlingoport # # Provide your Docker Hub account token # docker_account_token=dckr_xxx_bMjvwehHwO7svVHuIExj3i346eM # # Provide the Command Center version # command_center_image_version=69 # # The Server URL: '"http://yourserver:8081/command-center"' # serverURL='"http://<yourserver>:8081/command-center"' # # The company name on your Localyzer license # company_name=Lingoport
Put the current version in here (version 80?) - RMD
Run InstallCommandCenter.sh
chmod +x InstallCommandCenter.sh
sudo ./InstallCommandCenter.sh
To check the running container status
sudo docker ps
If you need to re-run the InstallCommandCenter.sh, make sure to run UninstallCommandCenter.sh first to clean your environment.
Note: Docker image version is not the Command Center version, check latest docker image version at https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/lingoport/command-center_dev/general
You should see at least an MySQL and a Command Center container running.
Verify Installation
Log in to the URL based on the command-center-config.sh settings, so something like:
[TEMPORARY-TO BE REWRITTEN ] (not http!)
https://commandcenter.mycompany.io/ or https://lingoport.mycompany.io/command-center or http://server.mycompany.io:8081/command-center
You should now be able to install the licenses and create projects.
The Command Center will initially have one Administrator user CCAdmin with the password please.reset.me.
Command Center Update
Update install.conf
Change the version number in the install.conf to get the Command Center image update version.
command_center_image_version=69
See full Configuration above.
Run UpdateCommandCenter.sh
chmod +x UpdateCommandCenter.sh
sudo ./UpdateCommandCenter.sh
To check the running container status
sudo docker ps
Start and Stop System
- From Command Center, as an administrator, go to settings and click 'Restart'
- From the VM, use docker commands to stop or start Command Center. For example:
sudo docker ps sudo docker stop <hash> sudo docker ps sudo docker container ls -a | grep command sudo docker start <hash> sudo docker ps
Uninstall
sudo ./UninstallCommandCenter.sh Uninstalling the Command Center Servers ...
sudo docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
FAQ and Troubleshooting
Put some basic docker commands in to check that things are running. How to check a file on the system. RMD
Next Steps
Command Center is now ready to be used. Proceed to the URL configured in the installation and follow the User Guide steps.