Deployment and Security
Typical Deployment of the Lingoport Suite and Ports
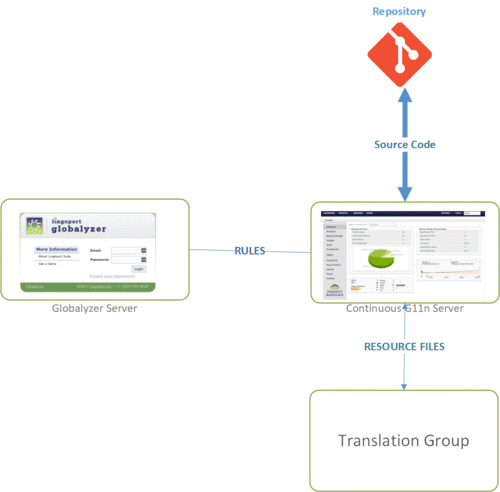
Setting up the Suite on a Customer's system can be done in many ways, as shown in the different deployment scenarios. The following is meant to show the necessary access to the system.
- The code repository needs to be able to work with the Continuous Globalization Server. This is done through the Jenkins jobs and Lingobot.
- The Continuous Globalization Server needs to be able to access the Globalyzer rulesets that are located either on our hosted server or on a local server.
- The Continuous Globalization Server needs to be able to send and receive resource files with the Translation Management System.
- The resource files are also stored in the code repository.
- Additionally, there are administrative needs for Continuous Globalization Server to be able to access Jenkins plugins, SMTP email, and SSH access.
Ports
- Jenkins is accessed via
- port 80 or 443
- port 8080 if installed prior to May 2018
- Lingoport Dashboard is accessed via
- port 80 or 443
- port 9000 if installed prior to May 2018
- The Translation Vendor may be accessed by different means, for instance
- port 21 for FTP or
- port 22 for SFTP.
- Other ports for different vendors
- Access for the Lingoport (or internal) installation team is typically done over SSH / via PuTTY.
- Alternately, it may be done through GoToMeeting/Webex screensharing between a Lingoport engineer and a customer engineer. This process may be significantly slower.
- The system must be able to access https://www.globalyzer.com.
Other aspects
- Jenkins installation requires access to the Jenkins update site, http://updates.jenkins-ci.org
- Dashboard may require access to the SonarQube update site, http://update.sonarsource.org
- Notifications are sent using an SMTP account: The system must allow access to an SMTP server (e.g. smtp.gmail.com for Google)