Difference between revisions of "Pseudo Localization"
(→Corrected Version) |
(→Showing i18n Issues with Pseudo-localization) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
In the example below, the pseudo-locale is 'esperanto' and the English strings have been pseudo-localized. Some issues can be identified when the application is running using the pseudo-locale: |
In the example below, the pseudo-locale is 'esperanto' and the English strings have been pseudo-localized. Some issues can be identified when the application is running using the pseudo-locale: |
||
| − | [[File:Pseudo-Localization Example Issues.jpg|center| |
+ | [[File:Pseudo-Localization Example Issues.jpg|center|700px]] |
* <span style="color:red">1 : Truncation</span>: The end characters have been truncated, indicating a likely UI issues around the space set for the text. The UI may need to be refactored to accommodate for longer text in languages such as German. |
* <span style="color:red">1 : Truncation</span>: The end characters have been truncated, indicating a likely UI issues around the space set for the text. The UI may need to be refactored to accommodate for longer text in languages such as German. |
||
Revision as of 16:34, 9 April 2024
Contents
What is Pseudo-Localization?
Pseudo-localization is an effective way to test the localization-readiness of an application. By pseudo-localizing the resource files, an application can be tested for internationalization without waiting for localization.
Creating pseudo-localized resource files help test for
- embedded strings,
- text that was externalized but should not be,
- text expansion issues,
- character-encoding problems,
- text concatenation issues, and
- UI boundary issues can be identified.
An application typically retrieves strings based on a locale, such as French. A pseudo-locale is like a normal locale, but the strings are not translated, they simply show differently.
Showing i18n Issues with Pseudo-localization
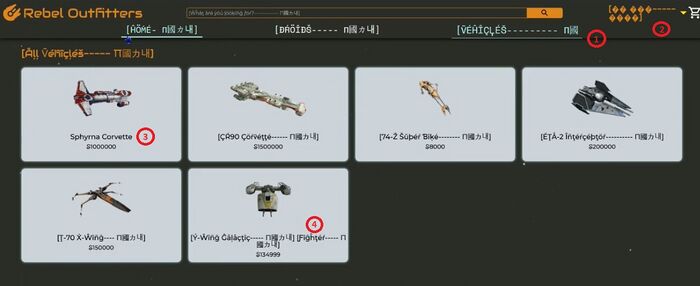
In the example below, the pseudo-locale is 'esperanto' and the English strings have been pseudo-localized. Some issues can be identified when the application is running using the pseudo-locale:
- 1 : Truncation: The end characters have been truncated, indicating a likely UI issues around the space set for the text. The UI may need to be refactored to accommodate for longer text in languages such as German.
- 2 : Mojibake: When the pseudo-localized text is showing as mojibake, such as �, this likely indicates a character encoding or a font issue. The application does not support non ASCII characters or non Latin-1 characters.
- 3 : Embedded String / Hard Code String: If the text shows in the original source locale, here English, as opposed to being pseudo-localized, it indicates a likely hard coded string which has not been externalized into a resource file. That string cannot be sent to translation and will show in the interface as the original source string. This is a common internationalization issue.
- 4: Concatenation: The pseudo-localization shows that two strings have been put together to make up Y-Wing Galactic Fighter, since the end character shows up after Galactic Fighter and a start character shows up before Fighter.
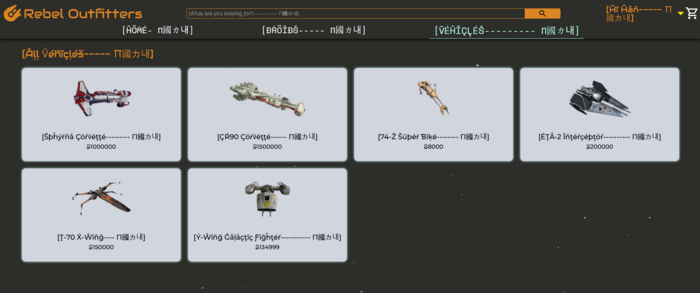
Corrected Version
If the i18n issues above were corrected, running the application using the pseudo-locale would look like the following:
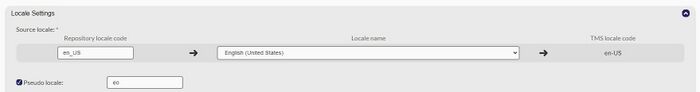
Configuration
Localyzer makes pseudo-localization quite simple: For the resource files in a repository to be pseudo-localized, edit the Locales by clicking the pseudo-locale checkbox and enter the locale to be used as shown below with eo (esperanto):