Difference between revisions of "Command Center Installation"
(→Verify Installation) |
(→Requirements) |
||
| (115 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
Before installing or updating Command Center, please verify this section is complete. |
Before installing or updating Command Center, please verify this section is complete. |
||
| − | == |
+ | == Introduction == |
| + | |||
| + | === Basic Deployment Diagram === |
||
| + | |||
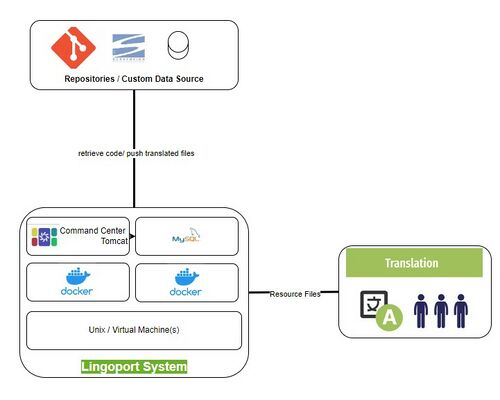
| + | The Lingoport system clones repository either for Globalyzer or Localyzer, or both. Access to the VM with Docker is necessary in order to install the Lingoport products. That may be internal to the customer or on a system hosted and managed by Lingoport. |
||
| + | |||
| + | Furthermore, for Localyzer projects, resource files (files that need translation, not code) is sent to the LSP or the TMS. |
||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Docker Deployed Command Center.jpg|500px|center]] |
||
| + | |||
| + | * Repositories may be inside or outside a customer's network |
||
| + | * '''Lingoport Command Center System''' may be inside or outside a customer's network |
||
| + | * Translation system, LSP may be inside or outside a customer's network. |
||
| + | |||
| + | This leads to a number of configurations, all supported by Lingoport, with security enforced either by Lingoport or by the customer in terms of IT, Firewall, access, etc. |
||
=== IT === |
=== IT === |
||
| + | When '''Lingoport hosts''' Command Center access to the repositories and to the LSP/TMS will need to be granted. Lingoport will then be in charge of security which IP addresses have access to what part of the application or the API entry points. |
||
| − | When installing Command Center on premises, the customer '''IT''' group is very important to the successful deployment of the Lingoport applications when installing the suite on site. In particular, the IT group that sets up the Linux system must understand the usage model for the system. |
||
| + | |||
| + | When installing Command Center '''on premises''', the customer '''IT''' group is very important to the successful deployment of the Lingoport applications when installing the suite on site. In particular, the IT group that sets up the Linux system must understand the usage model for the system. |
||
Lingoport requires a meeting with the parties responsible for setting up and maintaining the host system <b>before</b> installation can properly begin. The hope is that once the system is setup for installation, minimal IT interaction is necessary. |
Lingoport requires a meeting with the parties responsible for setting up and maintaining the host system <b>before</b> installation can properly begin. The hope is that once the system is setup for installation, minimal IT interaction is necessary. |
||
| Line 11: | Line 27: | ||
Preparations must be made with the '''IT''' team to ensure that all '''prerequisites''' are met before installation. For new installations, this is the recommended method to use to verify that all the various actors work together well. |
Preparations must be made with the '''IT''' team to ensure that all '''prerequisites''' are met before installation. For new installations, this is the recommended method to use to verify that all the various actors work together well. |
||
| − | === |
+ | === Requirements === |
Before installing Command Center, the following needs to be configured: |
Before installing Command Center, the following needs to be configured: |
||
* Hardware |
* Hardware |
||
| Line 19: | Line 35: | ||
* Https |
* Https |
||
| + | The next sections on this page address each one of these points and more. |
||
| − | === Diagram === |
||
| − | |||
| − | [[File:Docker Deployment Diagram.png|500px|center]] |
||
| − | |||
==Hardware & Software Requirements== |
==Hardware & Software Requirements== |
||
| Line 34: | Line 47: | ||
{| border="1" class="wikitable" style="width=50%" |
{| border="1" class="wikitable" style="width=50%" |
||
! Element |
! Element |
||
| + | ! Required |
||
| − | ! Minimum |
||
| − | ! Recommended |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! CPU |
! CPU |
||
| − | | 2 |
+ | | 2 (4 better) |
|- |
|- |
||
! Memory |
! Memory |
||
| − | | |
+ | | 32 GB |
| − | | 16 GB |
||
|- |
|- |
||
! Disk |
! Disk |
||
| − | | 160 GB |
||
| 500 GB |
| 500 GB |
||
|} |
|} |
||
| Line 52: | Line 62: | ||
===Software requirements=== |
===Software requirements=== |
||
| − | The current versions of these software products can be found at: [[Introduction#Current_versions_of_Lingoport_products_and_supporting_applications | Current versions of Lingoport products and supporting applications]] |
||
| + | Since this is a Docker installation, most of the containers will be managed by Docker. However, volumes will be mounted on the Linux virtual machine and a database configuration file will reside on the VM: This requires Linux and a Docker installation. |
||
| − | {| border="1" class="wikitable" style="width=50%" |
||
| − | ! Software |
||
| − | ! Recommended |
||
| − | |- |
||
| − | ! Operating System |
||
| − | | Linux, CentOS (7) or RedHat (8) |
||
| − | |} |
||
| + | === Support Browsers and Versions === |
||
| − | Since this is a Docker installation, most of the containers will be managed by Docker. However, volumes will be mounted on the Linux VM and a database configuration file will reside on the VM: This requires Linux. |
||
| + | The following browsers are supported: |
||
| + | * Chrome: 117+ |
||
| + | * Edge: 117+ |
||
| + | * Firefox: 71+ |
||
==Access and Ports / Firewall== |
==Access and Ports / Firewall== |
||
| + | |||
Command Center may need to be accessible by Lingoport and customer personnel to configure jobs, check the console if any problem arise, run jobs if necessary. Command Center needs to be accessible by many customer actors, including development teams, management, and QA, Lingoport, Translation Vendors. |
Command Center may need to be accessible by Lingoport and customer personnel to configure jobs, check the console if any problem arise, run jobs if necessary. Command Center needs to be accessible by many customer actors, including development teams, management, and QA, Lingoport, Translation Vendors. |
||
| + | === Ports === |
||
| − | Please see [[Deployment_Scenarios#External_Access_and_Ports |External Access and Ports]] for all the details. |
||
| + | ===== Internal to company network ===== |
||
| − | ==HTTPS== |
||
| − | HTTPS configuration is often achieved via a reverse proxy hosted on the Linux system. Instructions to do so using Apache are as follows for CentOS / RHEL: |
||
| + | {| border="1" class="wikitable" style="text-align:left; width=50%;" |
||
| − | 1. Install apache and mod_ssl (https support for apache) |
||
| + | !Services!!Ports!!Inbound (session)!!Outbound (session)!!Notes |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |SSH (for system config/maintenance)|| 22 || Y || N || System configuration and maintenance |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Command Center || 8083 (HTTP) and/or 443 (HTTPS) || Y || N || Default 8083 (configurable at install time) HTTPS requires reverse proxy Ex: Apache and Installation of SSL certificate. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |[[Terms_and_Definitions#translationvendor|Translation Vendor]] interactions: FTP/FTPS/SFTP (MemoQ, etc.) || 21 (FTP) or 443 (FTPS) or 22 (SFTP - recommended) || (FTP/S only) || Y || FTP/FTPS also require data ports (> 1024). Recommend SFTP if possible. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |[[Terms_and_Definitions#translationvendor|Translation Vendor]] interactions: Trados Enterprise, XTM and Memsource || 80 (HTTP) optional. 443 (HTTPS) required. || (Some cases) || Y || May need to be external if XTM/Memsource not installed on premise. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |SMTP/SMTPS || 25 or 465 or 587 || N || Y || Depends on corporate mail setup. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Globalyzer Server (Optional) || 80 or 443 || N || Y || Only needed when Globalyzer Server is on premises |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Repository Access || 22 (SSH) 443 (HTTPS/S3) 3690 (SVN) 7990 (Bitbucket) 7999 (Bitbucket) 8080 (TFS) || N || Y || VCS systems can vary, check with particular port(s) being used (Could be external/internal/both) |
||
| + | |} |
||
| + | ==== External access ==== |
||
| − | <code>sudo yum install httpd</code> |
||
| + | {| border="1" class="wikitable" style="text-align:left; width=50%;" |
||
| − | <code>sudo yum install mod_ssl</code> |
||
| + | !Services!!Ports!!Inbound!!Outbound!!Notes |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Lingoport SSH access || 22 || Y || N || Optional. Recommended for ease of upgrades and maintenance. |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |RHEL/CentOS/Ubuntu Packages || 80 (Debian) 443 (RHEL) || N || Y || Operating system packages access (Most likely external, but could be managed internally as well) |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Globalyzer Server || 80 and 443 || N || Y || Access to Globalyzer Server in Lingoport Cloud for rule sets (Unless using on-premises Globalyzer Server) |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |hub.docker.com || 80 and 443 || N || Y || Command Center Image location |
||
| + | |- |
||
| + | |Repository Access || 22 (SSH) 443 (HTTPS/S3) 3690 (SVN) 7990 (Bitbucket) 7999 (Bitbucket) 8080 (TFS) || N || Y || VCS systems can vary, check with particular port(s) being used (Could be external/internal/both) |
||
| + | |} |
||
| + | ==HTTPS== |
||
| − | 2. Configure SELinux to allow apache network connections |
||
| + | HTTPS is recommended but not necessary for the Command Center installation. HTTPS may already be set up or your IT may have a standard on how to set up HTTPS. If that's the case, go the next section. |
||
| − | <code>sudo setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect true</code> |
||
| + | Otherwise, follow this link for a suggested HTTPS configuration: |
||
| − | 3. Add http (not s) config file with the following content (edit as appropriate): |
||
| + | * [[ HTTPS configuration | HTTPS Configuration ]] |
||
| + | == Email Sender == |
||
| − | <code>/etc/httpd/conf.d/lingoport-apps.conf</code> |
||
| + | Email notifications are sent to a project configured recipients . See [[ Projects_page#Create_a_new_project | Create a new project ]] after this installation. |
||
| + | For those notifications to be sent, the following will be configured in the settings. |
||
| + | The following information will then be needed: |
||
| − | <pre> |
||
| + | * Host URL ''(like smpt.gmail.com for instance)'' |
||
| − | <VirtualHost *:80> |
||
| + | * Authorization method ''(SMTP, SMTPS, etc.)'' |
||
| + | * Sender email address ''(localyzer@customerdomain.com for instance)'' |
||
| + | * Sender password |
||
| + | == Docker Install== |
||
| − | # ServerName SERVER_URL_REPLACE_ME # example: myserver.lingoport.io |
||
| + | Docker is a platform that allows you to easily develop, test, and deploy applications as containers. This section will walk you through the process of installing Docker on a Linux system. |
||
| + | The supported versions of Linux are: |
||
| − | AllowEncodedSlashes NoDecode |
||
| − | ProxyPreserveHost On |
||
| − | ProxyRequests Off |
||
| + | * [[Installing Docker on RedHat Enterprise Linux 8 |RedHat Enterprise Linux 8]] |
||
| − | # Default command center config - hosted on port 8083 under url path '/command-center/' |
||
| + | * [[Installing Docker on CentOS 7 |CentOS 7]] (EOL June 2024) |
||
| − | ProxyPass /command-center/ http://localhost:8083/command-center/ nocanon |
||
| + | * [[Installing Docker on RedHat Enterprise Linux 7|RedHat Enterprise Linux 7]] (EOL June 2024) |
||
| − | ProxyPassReverse /command-center/ http://localhost:8083/command-center/ |
||
| + | * [[Oracle Linux 8]] |
||
| + | * [[Installing Docker on Ubuntu 20.04|Ubuntu 20.04]] |
||
| + | * [[Installing_Docker_on_Amazon_Linux_2|Amazon Linux 2]] |
||
| + | Other versions of Linux may work correctly, but these are the versions and processes that have been verified. |
||
| − | # Default fallback config, redirect to port 8083 for urls without '/command-center/' as the starting path. |
||
| − | # Adjust this if a different fallback mechanism is preferred. |
||
| − | ProxyPass / http://localhost:8083/ |
||
| − | ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:8083/ |
||
| + | == Credentials == |
||
| − | # Force HTTPS only (Requires ssl config enabled) |
||
| − | #Header edit Location ^http://(.*)$ https://$1 |
||
| − | #RewriteEngine on |
||
| − | #RewriteCond %{SERVER_NAME} =SERVER_URL_REPLACE_ME |
||
| − | #RewriteRule ^ https://%{SERVER_NAME}%{REQUEST_URI} [END,NE,R=permanent] |
||
| − | </VirtualHost> |
||
| + | When deploying Command Center, the configuration determines if the user management is done by Command Center itself, via an LDAP, or via SSO (using SAML). |
||
| − | </pre> |
||
| + | === Command Center User Database === |
||
| + | One administration user is configured when Command Center is installed. Contact support (at) lingoport (dot) com in order to get an administration user and password. That user can then create Command Center users. It is strongly recommended to change the first administration password and keep it safe. |
||
| − | 4. Restart apache to apply the settings |
||
| + | === LDAP === |
||
| − | <code>sudo systemctl restart httpd</code> |
||
| + | * LDAP Connection |
||
| − | 5. Acquire a certificate. Please follow your organization's instructions to do so. You should have a private key, and acquire both a certificate and a certificate chain. Some orgs may provide the certificate in the same file as the chain. Please request .pem style certificates, or convert the certificates to .pem. |
||
| + | * Management |
||
| + | === SSO === |
||
| − | 6. Place the certificate and private key on a secure location on your system. Standard location is <code>/etc/pki/tls/</code>, with the certificate under <code>/etc/pki/tls/certs/</code> and the associated private key under </code>/etc/pki/tls/private/</code> |
||
| + | * SSO Connection |
||
| − | 7. Add apache config to utilize the certificate: |
||
| + | * Management |
||
| + | = New Command Center Installation = |
||
| − | <code>/etc/httpd/conf.d/lingoport-apps-ssl.conf</code> |
||
| + | ==sudo user== |
||
| − | <pre> |
||
| + | A user, such as <code>centos</code> or <code>ec2-user</code>, with <code>sudo</code> privileges is required as the user under which to install Command Center. |
||
| − | <IfModule mod_ssl.c> |
||
| + | * Note: This should not be the legacy <code>jenkins</code> user. |
||
| − | <VirtualHost *:443> |
||
| − | ServerName SERVER_URL_REPLACE_ME # example: myserver.lingoport.io |
||
| − | DocumentRoot /var/www/html |
||
| + | ==Create the database conf file== |
||
| − | AllowEncodedSlashes NoDecode |
||
| + | Use the sudo user home for Docker, such as /home/centos for CentOS systems and /home/ec2-user for RedHat virtual systems. |
||
| − | ProxyPreserveHost On |
||
| − | ProxyRequests Off |
||
| + | The mysql and conf.d folders may need to be created as well. |
||
| − | # Default command center config - hosted on port 8083 under url path '/command-center/' |
||
| + | |||
| − | ProxyPass /command-center/ http://localhost:8083/command-center/ nocanon |
||
| + | vi /home/<user>/mysql/conf.d/mysql.cnf |
||
| − | ProxyPassReverse /command-center/ http://localhost:8083/command-center/ |
||
| − | |||
| − | # Default fallback config, redirect to port 8083 for urls without '/command-center/' as the starting path. |
||
| − | # Adjust this if a different fallback mechanism is preferred. |
||
| − | ProxyPass / http://localhost:8083/ |
||
| − | ProxyPassReverse / http://localhost:8083/ |
||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | # SSL Settings. These may be placed in other config files instead, but are left here for convenience. |
||
| − | SSLEngine on |
||
| − | |||
| − | # BEGIN Possible security settings - based on LetsEncrypt recommendations as of Feb 2023. |
||
| − | # --- |
||
| − | # Please adjust to your own organization's guidelines! |
||
| − | SSLHonorCipherOrder off |
||
| − | SSLProtocol all -SSLv2 -SSLv3 -TLSv1 -TLSv1.1 |
||
| − | SSLCipherSuite ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-ECDSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:ECDHE-RSA-CHACHA20-POLY1305:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 |
||
| − | |||
| − | SSLOptions +StrictRequire |
||
| − | |||
| − | # Add vhost name to log entries: |
||
| − | LogFormat "%h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b \"%{Referer}i\" \"%{User-agent}i\"" vhost_combined |
||
| − | LogFormat "%v %h %l %u %t \"%r\" %>s %b" vhost_common |
||
| − | # --- |
||
| − | # END Possible security settings |
||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | # Reference the certificates: |
||
| − | SSLCertificateFile /etc/pki/tls/certs/<yourserver.yourorg.com>.pem |
||
| − | SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/pki/tls/private/<yourserversprivatekey>.pem |
||
| − | |||
| − | # Not necessary if the certificate file includes a chain as well. See [[apache doc|https://httpd.apache.org/docs/2.4/mod/mod_ssl.html#sslcertificatefile]] |
||
| − | SSLCertificateChainFile /etc/letsencrypt/live/dockerdev1.lingoport.io/chain.pem |
||
| − | |||
| − | </VirtualHost> |
||
| − | </IfModule> |
||
| − | |||
| − | </pre> |
||
| − | |||
| − | 8. Optionally enforce a redirect to https by uncommenting and filling out the following section in <code>/etc/httpd/conf.d/lingoport-apps.conf</code> |
||
| − | |||
| − | Before: |
||
<pre> |
<pre> |
||
| + | [client] |
||
| − | # Force HTTPS only (Requires ssl config enabled) |
||
| + | default-character-set = utf8mb4 |
||
| − | #Header edit Location ^http://(.*)$ https://$1 |
||
| + | [mysql] |
||
| − | #RewriteEngine on |
||
| + | default-character-set = utf8mb4 |
||
| − | #RewriteCond %{SERVER_NAME} =SERVER_URL_REPLACE_ME |
||
| − | #RewriteRule ^ https://%{SERVER_NAME}%{REQUEST_URI} [END,NE,R=permanent] |
||
</pre> |
</pre> |
||
| + | == Configuration == |
||
| − | After: |
||
| + | Get the installation and update scripts and the install.conf file from the main branch of this public repository: |
||
| + | * https://github.com/Lingoport/CommandCenterConfig |
||
| − | <pre> |
||
| − | # Force HTTPS only (Requires ssl config enabled) |
||
| − | Header edit Location ^http://(.*)$ https://$1 |
||
| − | RewriteEngine on |
||
| − | RewriteCond %{SERVER_NAME} =example.somecorp.com |
||
| − | RewriteRule ^ https://%{SERVER_NAME}%{REQUEST_URI} [END,NE,R=permanent] |
||
| − | </pre> |
||
| + | You should have files such as: |
||
| + | install.conf |
||
| − | 9. Restart apache to apply the settings |
||
| + | BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh |
||
| + | InstallCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | UninstallCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | UpdateCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | If you need to install SSO version, the relevant files are: |
||
| + | install.conf |
||
| − | <code>sudo systemctl restart httpd</code> |
||
| + | BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh |
||
| + | InstallSSOCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | UninstallCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | UpdateSSOCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | saml_configuration.conf |
||
| + | Copy the above files under your home directory, ''for instance'' <code><user>/commandCenterInstall</code> where <user> may be <code>/home/centos</code> or <code>/home/ec2-user</code>. |
||
| − | == Docker Pre-Requisite== |
||
| − | Docker is a platform that allows you to easily develop, test, and deploy applications as containers. This section will walk you through the process of installing Docker on a Linux system. |
||
| + | ===Set up install.conf === |
||
| − | On the system (most likely a VM) dedicated to Command Center, make sure you have the latest version of docker up and running. The following steps may help. |
||
| + | Unless directed otherwise, change the top part of the <code>install.conf</code> file. |
||
| − | A user with '''sudo''' privileges is required to run most commands. |
||
| + | Set up <code>saml_configuration.conf</code> if you are going to use SAML |
||
| − | ====Uninstall old docker versions==== |
||
| + | The initial version number will be provided for the first installation. |
||
| − | This is an optional step in case your docker version is out of date: |
||
| + | For updates, <code>command_center_image_version</code> will be the only parameter to change in the <code>install.conf</code> file. |
||
| − | sudo yum remove docker \ |
||
| − | docker-client \ |
||
| − | docker-client-latest \ |
||
| − | docker-common \ |
||
| − | docker-latest \ |
||
| − | docker-latest-logrotate \ |
||
| − | docker-logrotate \ |
||
| − | docker-engine |
||
| + | <pre> |
||
| − | ====Install docker using the repository==== |
||
| + | # Provide the Command Center version |
||
| + | # For *Regular* Updates, this should be the only parameter to change |
||
| + | command_center_image_version=113 |
||
| + | Make sure to keep a copy of that file in case you overwrite it when updating from the https://github.com/Lingoport/CommandCenterConfig Git repository |
||
| − | sudo yum install -y yum-utils |
||
| − | sudo yum-config-manager \ |
||
| − | --add-repo \ |
||
| − | https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo |
||
| − | |||
| − | sudo yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-plugin |
||
| + | # |
||
| − | ====Start Docker.==== |
||
| + | # After Install, Updates should not need to change anything below |
||
| − | Start docker using the following command: |
||
| + | # ---------------------------------------------------------------- |
||
| + | # The Server URL: '"https://yourserver/command-center"' |
||
| − | $ sudo systemctl start docker |
||
| + | serverURL='"https://SERVER_DNS_HERE/command-center"' |
||
| + | # Provide the home directory, lingoport/commandcenter/Lingoport_Data |
||
| − | Enable the Docker service to start automatically on system boot by running the following command: |
||
| + | # folder will be created |
||
| + | home_directory=/home/centos |
||
| + | # Provide the Command Center server port |
||
| − | $ sudo systemctl enable docker |
||
| + | serverPort=8083 |
||
| + | </pre> |
||
| − | ====Verify that Docker Engine is installed correctly ==== |
||
| − | Run the hello-world image. |
||
| + | ==Run InstallCommandCenter.sh== |
||
| − | $ sudo docker run hello-world |
||
| + | chmod +x *.sh |
||
| − | This command will run a test container and display a message indicating that the installation is working properly. |
||
| + | sudo ./InstallCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | If you are using sso version installer, run |
||
| − | == Credentials == |
||
| + | chmod +x *.sh |
||
| − | When deploying Command Center, the configuration determines if the user management is done by Command Center itself, via an LDAP, or via SSO (using SAML). |
||
| + | sudo ./InstallSSOCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | To check the running container status |
||
| − | === Command Center User Database === |
||
| + | sudo docker ps |
||
| − | One administration user is configured. Contact support (at) lingoport (dot) com in order to get an administration user and password. That user can then create Command Center users. It is strongly recommended to change the first administration password and keep it safe. |
||
| − | === |
+ | === Re-install Command Center === |
| + | If you need to re-run the '''InstallCommandCenter.sh'''h, make sure to run '''UninstallCommandCenter.sh''' first to clean your environment. |
||
| − | * LDAP Connection |
||
| + | * Uninstall Command Center |
||
| − | * Management |
||
| + | sudo ./UninstallCommandCenter.sh |
||
| − | === SSO === |
||
| − | * SSO Connection |
||
| − | * Management |
||
| + | * Verify that Command Center and the database is no longer in the list |
||
| + | sudo docker ps |
||
| + | * Remove the image to download and install again |
||
| − | = New Command Center Installation = |
||
| + | sudo docker image ls |
||
| − | ==Create the database conf file== |
||
| + | sudo docker image rm --force <command center image ID> |
||
| − | If you are using a CentOS system: |
||
| + | * Start the install again |
||
| − | Uses the ''centos'' user, with ''sudo'' privileges, as default user for docker |
||
| + | sudo ./InstallCommandCenter.sh |
||
| − | * /home/centos/mysql/conf.d/mysql.cnf |
||
| − | [client] |
||
| − | default-character-set = utf8mb4 |
||
| − | [mysql] |
||
| − | default-character-set = utf8mb4 |
||
| + | Note: Docker image version is not the Command Center version, check latest docker image version at https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/lingoport/command-center_dev/general |
||
| − | If you are using a RedHat system: |
||
| + | You should see at least an MySQL and a Command Center container running. |
||
| − | * /home/ec2-user/mysql/conf.d/mysql.cnf |
||
| + | == Note: Database backup == |
||
| − | [client] |
||
| + | To backup the database, run the following script: |
||
| − | default-character-set = utf8mb4 |
||
| − | [mysql] |
||
| − | default-character-set = utf8mb4 |
||
| + | chmod +x *.sh |
||
| − | == Configuration == |
||
| + | sudo ./BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh |
||
| + | The database backup sql file will be under '''$home_directory/commandcenter/backup''' folder, named '''commandcenter_backup_$current_date.sql''' |
||
| − | Request the ''CommandCenterInstall.zip'' file from your customer success engineer. The zip file contains four files: |
||
| + | Right after installation, the backup is not necessary. However, as you configure and on-board projects, you may want to set up a backup strategy. |
||
| + | To backup the database periodically, schedule to run BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh on a regular basis, for instance with a Cron service. |
||
| + | == Verify Installation == |
||
| − | install.conf |
||
| + | Log in to the URL based on the command-center-config.sh settings, so something like: |
||
| − | InstallCommandCenter.sh |
||
| − | UninstallCommandCenter.sh |
||
| − | UpdateCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | <nowiki>https://commandcenter.mycompany.io/command-center</nowiki> |
||
| − | Copy the above files under your home directory,''for instance'' /home/centos/commandcenterinstall or /home/ec2-user/commandcenterinstall. |
||
| − | ===Set up install.conf === |
||
| + | You should now be able to install the licenses and create projects. |
||
| − | Fill in your home directory, DB password, serverURL and port number, your Docker Hub username and token. The initial version number will be provided for the first installation. For updates, this will be the only parameter to change in the <code>install.conf</code> file. |
||
| + | The Command Center will initially have one Administrator user '''CCAdmin''' with the password '''please.reset.me'''. |
||
| − | <pre> |
||
| − | #!/bin/bash |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | # Provide your home directory, lingoport/commandcenter/Lingoport_Data folder will be created |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | home_directory=/home/centos |
||
| + | If the installation is unsuccessful for any reason, do not try to re-install. Instead, uninstall, make any needed changes, and re-install to avoid conflicts. |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | # Provide the MYSQL root password you want to create for the MySQL database container |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | database_root_password= |
||
| + | sudo ./UninstallCommandCenter.sh |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | # Provide your Docker Hub username |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | docker_username= |
||
| + | = Command Center Update = |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | # Provide your Docker Hub account token |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | docker_account_token= |
||
| + | == Get latest scripts == |
||
| − | # |
||
| + | Make sure to make a copy of the '''install.conf''' file used previously in case it's overwritten by the git pull / git clone below. |
||
| − | # The Server URL: '"https://yourserver/command-center"' |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | serverURL= |
||
| + | Make sure to update the installation and update scripts and the install.conf file from the main branch of this public repository: |
||
| − | # |
||
| + | * https://github.com/Lingoport/CommandCenterConfig |
||
| − | # Provide the Command Center server port |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | serverPort= |
||
| + | Note: You may need to <code>chmod -x</code> the scripts under DockerScripts before git pull. |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | # Command Center version |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | command_center_image_version= |
||
| + | == Backup the database == |
||
| − | # DO NOT CHANGE THE PARAMETERS BELOW |
||
| + | You don't have to backup the current version of the database before proceeding to the update to the new version of the system, because the Update script will backup your current database automatically before updating. If you want to do the backup manually, you can use the BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh script |
||
| + | chmod +x *.sh |
||
| − | # |
||
| + | sudo ./BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh |
||
| − | # Provide the Docker network name you want to create |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | database_network=mysqlnetscommand |
||
| + | The database backup sql file will be under $home_directory/commandcenter/backup folder, named commandcenter_backup_$current_date.sql |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | # The company name on your Localyzer license |
||
| − | # |
||
| − | company_name= |
||
| + | To backup the database periodically, schedule to run <code>BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh</code>, for instance with cron services. |
||
| + | === Note: Restoring the database === |
||
| − | # lingoport/command-center_dev or lingoport/command-center |
||
| − | docker_image=lingoport/command-center |
||
| − | </pre> |
||
| + | If later, at some point, the database needs to be restored, the following shows how to do so: |
||
| − | ==Run InstallCommandCenter.sh== |
||
| − | chmod +x |
+ | chmod +x *.sh |
| − | sudo ./ |
+ | sudo ./RestoreCommandCenterDatabase.sh YYYY-MM-DD |
| + | Check your database backup sql file under '''$home_directory/commandcenter/backup''' folder, they are named '''commandcenter_backup_$current_date.s'''ql, for example, if you backup the database on 2023 September 20th, you will see a commandcenter_backup_2023-09-20.sql file, and you can use below command to restore it |
||
| − | To check the running container status |
||
| + | sudo ./RestoreCommandCenterDatabase.sh 2023-09-20 |
||
| − | sudo docker ps |
||
| + | == Return to the previous version == |
||
| − | If you need to re-run the InstallCommandCenter.sh, make sure to run UninstallCommandCenter.sh first to clean your environment. |
||
| + | 1. Stop the current active Command Center container |
||
| − | Note: Docker image version is not the Command Center version, check latest docker image version at https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/lingoport/command-center_dev/general |
||
| − | You |
+ | You can use "docker ps" to see all active containers, and use "docker stop CONTAINER ID" to stop your current Command Center container |
| + | 2. Restart your previous Command Center server version |
||
| − | == Verify Installation == |
||
| − | Log in to the URL based on the command-center-config.sh settings, so something like: |
||
| + | You can use "docker ps -a" to see all exited containers, and use "docker start CONTAINER ID" to restart your previous version Command Center container |
||
| − | https://commandcenter.mycompany.io/ |
||
| + | 3. Restore the database to match your previous Command Center server version |
||
| + | sudo ./RestoreCommandCenterDatabase.sh YYYY-MM-DD |
||
| − | You should now be able to install the licenses and create projects. |
||
| − | The Command Center will initially have one Administrator user '''CCAdmin''' with the password '''please.reset.me'''. |
||
| − | |||
| − | = Command Center Update = |
||
==Update install.conf == |
==Update install.conf == |
||
| Line 395: | Line 355: | ||
See full [[Command_Center_Installation#Configuration | Configuration ]] above. |
See full [[Command_Center_Installation#Configuration | Configuration ]] above. |
||
| − | + | ==Run UpdateCommandCenter.sh== |
|
chmod +x UpdateCommandCenter.sh |
chmod +x UpdateCommandCenter.sh |
||
sudo ./UpdateCommandCenter.sh |
sudo ./UpdateCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | |||
| + | If you are using SSO version installer, run UpdateSSOCommandCenter.sh instead of UpdateCommandCenter.sh |
||
To check the running container status |
To check the running container status |
||
sudo docker ps |
sudo docker ps |
||
| + | |||
| + | The database backup sql file is in $home_directory/commandcenter/ folder, named commandcenter_backup_$current_date.sql |
||
= Start and Stop System = |
= Start and Stop System = |
||
| Line 435: | Line 399: | ||
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES |
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES |
||
3d9da7a80e0a '''lingoport/command-center''':80 "catalina.sh run" 3 days ago Up 6 hours 0.0.0.0:8081->8080/tcp, :::8081->8080/tcp pedantic_aryabhata |
3d9da7a80e0a '''lingoport/command-center''':80 "catalina.sh run" 3 days ago Up 6 hours 0.0.0.0:8081->8080/tcp, :::8081->8080/tcp pedantic_aryabhata |
||
| − | 683c55907c06 '''mysql''': |
+ | 683c55907c06 '''mysql''':8.0 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 3 days ago Up 6 hours 3306/tcp, 33060/tcp quizzical_newton |
Check with IT that the DNS for that system is correct. |
Check with IT that the DNS for that system is correct. |
||
| Line 442: | Line 406: | ||
Ask IT to check the https and the server URL / DNS. |
Ask IT to check the https and the server URL / DNS. |
||
| + | |||
| + | == To check files on disk == |
||
| + | To troubleshoot, it may be necessary to check files handled by Docker, such as looking for reports under Lingoport_Data. In that case, first use the Docker PS command to get the container ID of the Command Center application. |
||
| + | |||
| + | sudo docker container ls -a |
||
| + | CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES |
||
| + | '''3d9da7a80e0a''' '''lingoport/command-center''':80 "catalina.sh run" 3 days ago Up 6 hours 0.0.0.0:8081->8080/tcp, :::8081->8080/tcp pedantic_aryabhata |
||
| + | |||
| + | With the container ID, execute the following command to run bash with access to those files: |
||
| + | |||
| + | sudo docker exec -it '''3d9da7a80e0a''' bash |
||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == How to backup and restore a system == |
||
| + | |||
| + | If you have a system that you want to install a new version of Command Center, but keep the current configuration, here are the steps to do that. |
||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Backup the Command Center databases''' |
||
| + | |||
| + | sudo ./BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh |
||
| + | |||
| + | This will create two files <code><home>/commandcenter/backup/commandcenter_backup_YYYY-MM-DD.sql</code> and <code><home>/commandcenter/backup/LRM_backup_YYYY-MM-DD.sql</code> Where YYYY-MM-DD is the current date. |
||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Stop the currently running Command Center container and its associated MySQL container''' |
||
| + | |||
| + | sudo docker ps |
||
| + | sudo docker stop <Command Center Container ID> <MySQL Container ID> |
||
| + | sudo docker ps |
||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Modify the install.conf file for the correct version of Command Center to install''' |
||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Install Command Center''' |
||
| + | |||
| + | sudo ./InstallCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | |||
| + | If there is an error about the container in use, remove the container that is identified and attempt the install again. |
||
| + | |||
| + | sudo docker rm <container> |
||
| + | sudo ./InstallCommandCenter.sh |
||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Verify that Command Center comes up in the browser. Login with the CCAdmin user. There should be no projects or configuration set up''' |
||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Restore from the database''' |
||
| + | |||
| + | sudo ./RestoreCommandCenterDatabase.sh YYYY-MM-DD |
||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Verify that Command Center is populated with the correct information''' |
||
= Next Steps = |
= Next Steps = |
||
| − | Command Center is now ready to be used. Proceed to the URL configured in the installation and follow the [[Command_Center_User_Guide | User Guide's]] steps. |
+ | Command Center is now ready to be used. Proceed to the URL configured in the installation and follow the [[Command_Center_User_Guide | User's Guide's]] steps. |
Latest revision as of 21:42, 30 September 2024
Contents
Pre-Requisites
Before installing or updating Command Center, please verify this section is complete.
Introduction
Basic Deployment Diagram
The Lingoport system clones repository either for Globalyzer or Localyzer, or both. Access to the VM with Docker is necessary in order to install the Lingoport products. That may be internal to the customer or on a system hosted and managed by Lingoport.
Furthermore, for Localyzer projects, resource files (files that need translation, not code) is sent to the LSP or the TMS.
- Repositories may be inside or outside a customer's network
- Lingoport Command Center System may be inside or outside a customer's network
- Translation system, LSP may be inside or outside a customer's network.
This leads to a number of configurations, all supported by Lingoport, with security enforced either by Lingoport or by the customer in terms of IT, Firewall, access, etc.
IT
When Lingoport hosts Command Center access to the repositories and to the LSP/TMS will need to be granted. Lingoport will then be in charge of security which IP addresses have access to what part of the application or the API entry points.
When installing Command Center on premises, the customer IT group is very important to the successful deployment of the Lingoport applications when installing the suite on site. In particular, the IT group that sets up the Linux system must understand the usage model for the system. Lingoport requires a meeting with the parties responsible for setting up and maintaining the host system before installation can properly begin. The hope is that once the system is setup for installation, minimal IT interaction is necessary.
Preparations must be made with the IT team to ensure that all prerequisites are met before installation. For new installations, this is the recommended method to use to verify that all the various actors work together well.
Requirements
Before installing Command Center, the following needs to be configured:
- Hardware
- Linux
- Docker
- Firewall
- Https
The next sections on this page address each one of these points and more.
Hardware & Software Requirements
The following sections describe the hardware and software requirements for Command Center.
Please note that the Globalyzer Server installation is in a different section.
Hardware Requirements
| Element | Required |
|---|---|
| CPU | 2 (4 better) |
| Memory | 32 GB |
| Disk | 500 GB |
The Globalyzer Server may be hosted by Lingoport, reside on another server, or be installed on the same system. Other Linux and Windows machines may have Globalyzer clients installed.
Software requirements
Since this is a Docker installation, most of the containers will be managed by Docker. However, volumes will be mounted on the Linux virtual machine and a database configuration file will reside on the VM: This requires Linux and a Docker installation.
Support Browsers and Versions
The following browsers are supported:
- Chrome: 117+
- Edge: 117+
- Firefox: 71+
Access and Ports / Firewall
Command Center may need to be accessible by Lingoport and customer personnel to configure jobs, check the console if any problem arise, run jobs if necessary. Command Center needs to be accessible by many customer actors, including development teams, management, and QA, Lingoport, Translation Vendors.
Ports
Internal to company network
| Services | Ports | Inbound (session) | Outbound (session) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSH (for system config/maintenance) | 22 | Y | N | System configuration and maintenance |
| Command Center | 8083 (HTTP) and/or 443 (HTTPS) | Y | N | Default 8083 (configurable at install time) HTTPS requires reverse proxy Ex: Apache and Installation of SSL certificate. |
| Translation Vendor interactions: FTP/FTPS/SFTP (MemoQ, etc.) | 21 (FTP) or 443 (FTPS) or 22 (SFTP - recommended) | (FTP/S only) | Y | FTP/FTPS also require data ports (> 1024). Recommend SFTP if possible. |
| Translation Vendor interactions: Trados Enterprise, XTM and Memsource | 80 (HTTP) optional. 443 (HTTPS) required. | (Some cases) | Y | May need to be external if XTM/Memsource not installed on premise. |
| SMTP/SMTPS | 25 or 465 or 587 | N | Y | Depends on corporate mail setup. |
| Globalyzer Server (Optional) | 80 or 443 | N | Y | Only needed when Globalyzer Server is on premises |
| Repository Access | 22 (SSH) 443 (HTTPS/S3) 3690 (SVN) 7990 (Bitbucket) 7999 (Bitbucket) 8080 (TFS) | N | Y | VCS systems can vary, check with particular port(s) being used (Could be external/internal/both) |
External access
| Services | Ports | Inbound | Outbound | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lingoport SSH access | 22 | Y | N | Optional. Recommended for ease of upgrades and maintenance. |
| RHEL/CentOS/Ubuntu Packages | 80 (Debian) 443 (RHEL) | N | Y | Operating system packages access (Most likely external, but could be managed internally as well) |
| Globalyzer Server | 80 and 443 | N | Y | Access to Globalyzer Server in Lingoport Cloud for rule sets (Unless using on-premises Globalyzer Server) |
| hub.docker.com | 80 and 443 | N | Y | Command Center Image location |
| Repository Access | 22 (SSH) 443 (HTTPS/S3) 3690 (SVN) 7990 (Bitbucket) 7999 (Bitbucket) 8080 (TFS) | N | Y | VCS systems can vary, check with particular port(s) being used (Could be external/internal/both) |
HTTPS
HTTPS is recommended but not necessary for the Command Center installation. HTTPS may already be set up or your IT may have a standard on how to set up HTTPS. If that's the case, go the next section.
Otherwise, follow this link for a suggested HTTPS configuration:
Email Sender
Email notifications are sent to a project configured recipients . See Create a new project after this installation. For those notifications to be sent, the following will be configured in the settings.
The following information will then be needed:
- Host URL (like smpt.gmail.com for instance)
- Authorization method (SMTP, SMTPS, etc.)
- Sender email address (localyzer@customerdomain.com for instance)
- Sender password
Docker Install
Docker is a platform that allows you to easily develop, test, and deploy applications as containers. This section will walk you through the process of installing Docker on a Linux system.
The supported versions of Linux are:
- RedHat Enterprise Linux 8
- CentOS 7 (EOL June 2024)
- RedHat Enterprise Linux 7 (EOL June 2024)
- Oracle Linux 8
- Ubuntu 20.04
- Amazon Linux 2
Other versions of Linux may work correctly, but these are the versions and processes that have been verified.
Credentials
When deploying Command Center, the configuration determines if the user management is done by Command Center itself, via an LDAP, or via SSO (using SAML).
Command Center User Database
One administration user is configured when Command Center is installed. Contact support (at) lingoport (dot) com in order to get an administration user and password. That user can then create Command Center users. It is strongly recommended to change the first administration password and keep it safe.
LDAP
- LDAP Connection
- Management
SSO
- SSO Connection
- Management
New Command Center Installation
sudo user
A user, such as centos or ec2-user, with sudo privileges is required as the user under which to install Command Center.
- Note: This should not be the legacy
jenkinsuser.
Create the database conf file
Use the sudo user home for Docker, such as /home/centos for CentOS systems and /home/ec2-user for RedHat virtual systems.
The mysql and conf.d folders may need to be created as well.
vi /home/<user>/mysql/conf.d/mysql.cnf
[client] default-character-set = utf8mb4 [mysql] default-character-set = utf8mb4
Configuration
Get the installation and update scripts and the install.conf file from the main branch of this public repository:
You should have files such as:
install.conf BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh InstallCommandCenter.sh UninstallCommandCenter.sh UpdateCommandCenter.sh
If you need to install SSO version, the relevant files are:
install.conf BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh InstallSSOCommandCenter.sh UninstallCommandCenter.sh UpdateSSOCommandCenter.sh saml_configuration.conf
Copy the above files under your home directory, for instance <user>/commandCenterInstall where <user> may be /home/centos or /home/ec2-user.
Set up install.conf
Unless directed otherwise, change the top part of the install.conf file.
Set up saml_configuration.conf if you are going to use SAML
The initial version number will be provided for the first installation.
For updates, command_center_image_version will be the only parameter to change in the install.conf file.
# Provide the Command Center version # For *Regular* Updates, this should be the only parameter to change command_center_image_version=113 Make sure to keep a copy of that file in case you overwrite it when updating from the https://github.com/Lingoport/CommandCenterConfig Git repository # # After Install, Updates should not need to change anything below # ---------------------------------------------------------------- # The Server URL: '"https://yourserver/command-center"' serverURL='"https://SERVER_DNS_HERE/command-center"' # Provide the home directory, lingoport/commandcenter/Lingoport_Data # folder will be created home_directory=/home/centos # Provide the Command Center server port serverPort=8083
Run InstallCommandCenter.sh
chmod +x *.sh
sudo ./InstallCommandCenter.sh
If you are using sso version installer, run
chmod +x *.sh
sudo ./InstallSSOCommandCenter.sh
To check the running container status
sudo docker ps
Re-install Command Center
If you need to re-run the InstallCommandCenter.shh, make sure to run UninstallCommandCenter.sh first to clean your environment.
- Uninstall Command Center
sudo ./UninstallCommandCenter.sh
- Verify that Command Center and the database is no longer in the list
sudo docker ps
- Remove the image to download and install again
sudo docker image ls sudo docker image rm --force <command center image ID>
- Start the install again
sudo ./InstallCommandCenter.sh
Note: Docker image version is not the Command Center version, check latest docker image version at https://hub.docker.com/repository/docker/lingoport/command-center_dev/general
You should see at least an MySQL and a Command Center container running.
Note: Database backup
To backup the database, run the following script:
chmod +x *.sh
sudo ./BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh
The database backup sql file will be under $home_directory/commandcenter/backup folder, named commandcenter_backup_$current_date.sql
Right after installation, the backup is not necessary. However, as you configure and on-board projects, you may want to set up a backup strategy. To backup the database periodically, schedule to run BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh on a regular basis, for instance with a Cron service.
Verify Installation
Log in to the URL based on the command-center-config.sh settings, so something like:
https://commandcenter.mycompany.io/command-center
You should now be able to install the licenses and create projects.
The Command Center will initially have one Administrator user CCAdmin with the password please.reset.me.
If the installation is unsuccessful for any reason, do not try to re-install. Instead, uninstall, make any needed changes, and re-install to avoid conflicts.
sudo ./UninstallCommandCenter.sh
Command Center Update
Get latest scripts
Make sure to make a copy of the install.conf file used previously in case it's overwritten by the git pull / git clone below.
Make sure to update the installation and update scripts and the install.conf file from the main branch of this public repository:
Note: You may need to chmod -x the scripts under DockerScripts before git pull.
Backup the database
You don't have to backup the current version of the database before proceeding to the update to the new version of the system, because the Update script will backup your current database automatically before updating. If you want to do the backup manually, you can use the BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh script
chmod +x *.sh
sudo ./BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh
The database backup sql file will be under $home_directory/commandcenter/backup folder, named commandcenter_backup_$current_date.sql
To backup the database periodically, schedule to run BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh, for instance with cron services.
Note: Restoring the database
If later, at some point, the database needs to be restored, the following shows how to do so:
chmod +x *.sh
sudo ./RestoreCommandCenterDatabase.sh YYYY-MM-DD
Check your database backup sql file under $home_directory/commandcenter/backup folder, they are named commandcenter_backup_$current_date.sql, for example, if you backup the database on 2023 September 20th, you will see a commandcenter_backup_2023-09-20.sql file, and you can use below command to restore it
sudo ./RestoreCommandCenterDatabase.sh 2023-09-20
Return to the previous version
1. Stop the current active Command Center container
You can use "docker ps" to see all active containers, and use "docker stop CONTAINER ID" to stop your current Command Center container
2. Restart your previous Command Center server version
You can use "docker ps -a" to see all exited containers, and use "docker start CONTAINER ID" to restart your previous version Command Center container
3. Restore the database to match your previous Command Center server version
sudo ./RestoreCommandCenterDatabase.sh YYYY-MM-DD
Update install.conf
Change the version number in the install.conf to get the Command Center image update version.
command_center_image_version=<new version number>
See full Configuration above.
Run UpdateCommandCenter.sh
chmod +x UpdateCommandCenter.sh
sudo ./UpdateCommandCenter.sh
If you are using SSO version installer, run UpdateSSOCommandCenter.sh instead of UpdateCommandCenter.sh
To check the running container status
sudo docker ps
The database backup sql file is in $home_directory/commandcenter/ folder, named commandcenter_backup_$current_date.sql
Start and Stop System
- From Command Center, as an administrator, go to settings and click 'Restart'
- From the VM, use docker commands to stop or start Command Center. For example:
sudo docker ps sudo docker stop <hash> sudo docker ps sudo docker container ls -a | grep command sudo docker start <hash> sudo docker ps
Uninstall
sudo ./UninstallCommandCenter.sh Uninstalling the Command Center Servers ...
sudo docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
FAQ and Troubleshooting
Make sure the Server URL is reachable
Navigate to the server URL set up in install.conf: is the login screen available?
If it is not, first check that the docker container is up and running. Make sure both lingoport/command-center and mysql are running.
sudo docker container ls -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 3d9da7a80e0a lingoport/command-center:80 "catalina.sh run" 3 days ago Up 6 hours 0.0.0.0:8081->8080/tcp, :::8081->8080/tcp pedantic_aryabhata 683c55907c06 mysql:8.0 "docker-entrypoint.s…" 3 days ago Up 6 hours 3306/tcp, 33060/tcp quizzical_newton
Check with IT that the DNS for that system is correct.
Check with IT that the firewall allows for reaching the URL from your system.
Ask IT to check the https and the server URL / DNS.
To check files on disk
To troubleshoot, it may be necessary to check files handled by Docker, such as looking for reports under Lingoport_Data. In that case, first use the Docker PS command to get the container ID of the Command Center application.
sudo docker container ls -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 3d9da7a80e0a lingoport/command-center:80 "catalina.sh run" 3 days ago Up 6 hours 0.0.0.0:8081->8080/tcp, :::8081->8080/tcp pedantic_aryabhata
With the container ID, execute the following command to run bash with access to those files:
sudo docker exec -it 3d9da7a80e0a bash
How to backup and restore a system
If you have a system that you want to install a new version of Command Center, but keep the current configuration, here are the steps to do that.
- Backup the Command Center databases
sudo ./BackupCommandCenterDatabase.sh
This will create two files <home>/commandcenter/backup/commandcenter_backup_YYYY-MM-DD.sql and <home>/commandcenter/backup/LRM_backup_YYYY-MM-DD.sql Where YYYY-MM-DD is the current date.
- Stop the currently running Command Center container and its associated MySQL container
sudo docker ps sudo docker stop <Command Center Container ID> <MySQL Container ID> sudo docker ps
- Modify the install.conf file for the correct version of Command Center to install
- Install Command Center
sudo ./InstallCommandCenter.sh
If there is an error about the container in use, remove the container that is identified and attempt the install again.
sudo docker rm <container> sudo ./InstallCommandCenter.sh
- Verify that Command Center comes up in the browser. Login with the CCAdmin user. There should be no projects or configuration set up
- Restore from the database
sudo ./RestoreCommandCenterDatabase.sh YYYY-MM-DD
- Verify that Command Center is populated with the correct information
Next Steps
Command Center is now ready to be used. Proceed to the URL configured in the installation and follow the User's Guide's steps.