Difference between revisions of "Resource Files"
(→Unique Extensions) |
(→Unique Extensions) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
<li><b>[[LRM_strings_Support#strings_parser_type|''strings'']]</b> parser</li> |
<li><b>[[LRM_strings_Support#strings_parser_type|''strings'']]</b> parser</li> |
||
<li><b>[[LRM_text_Support|''text'']]</b> parser</li> |
<li><b>[[LRM_text_Support|''text'']]</b> parser</li> |
||
| − | <li><b>[[LRM_XML_Support|xml]]</b> parser</li> |
+ | <li><b>[[LRM_XML_Support|''xml'']]</b> parser</li> |
| − | <li><b>[[LRM_yaml_Support|yaml]]</b> parser</li> |
+ | <li><b>[[LRM_yaml_Support|''yaml'']]</b> parser</li> |
</ul> |
</ul> |
||
Revision as of 21:39, 17 June 2019
What resource file types are supported by LRM?
Standard LRM extensions
- .htm and .html files using the html parser
- .json (Mostly JavaScript, and other programming languages) using the json parser
- .msg (C, C++, ...) using the msg parser
- .po files using the po parser
- .properties files (Java-type resources) using properties parser
- .resx files (used in the .Net world) using xml parser and the ResxParser.xml format definition
- .rc (Delphi, ...) using the rc parser
- .rjs (for JavaScript) using the js parser
- .rxml using the xml parser and the RxmlParser.xml format definition)
- .strings (Mobile iOS) using the strings parser
- strings.xml (Android) using the xml parser and the AndroidParser.xml format definition
- .txt files using the text parser
- .yaml, .yml using the yaml parser
Unique Extensions
Any file extension can be handled by LRM as long as the corresponding parser type is defined. The file must be able to be parsed correctly by the defined parser type or an error will occur.
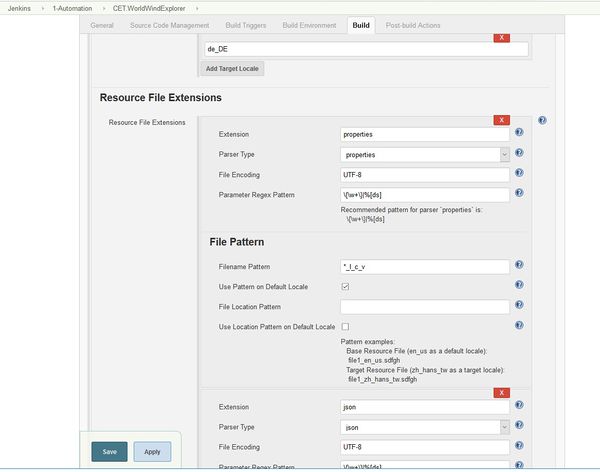
Above is an example configuring a Jenkins LRM project. The Extension is 'properties' and the Parser Type is 'properties' so LRM will recognize the file myfile_en_US.properties as a resource file. If the filename is myfile_en_US.prop, that would not be recognized as a properties resource file. Changing the Extension to 'prop' would allow myfile_en_US.prop to be recognized as a properties parser type file.
The parser types are: