Difference between revisions of "About Localyzer"
(→Sequencing: What does the Resource Manager send when resource files are modified?) |
|||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
'''Absolutely'''. Lingoport Resource Manager helps automate tasks. It also shows the status of the state of translation within the source code itself. It helps different software development cultures, in particular those applying Agile processes, by facilitating the tracking, sending, and receiving of resource kits. Non Agile processes do still benefit from the Resource Manager. |
'''Absolutely'''. Lingoport Resource Manager helps automate tasks. It also shows the status of the state of translation within the source code itself. It helps different software development cultures, in particular those applying Agile processes, by facilitating the tracking, sending, and receiving of resource kits. Non Agile processes do still benefit from the Resource Manager. |
||
| − | == |
+ | ==What does the Resource Manager send when resource files are modified? == |
| − | LRM projects can be on-boarded as either '''full file''' or '''changes only'''. LRM defaults to changes only for most resource |
+ | LRM projects can be on-boarded as either '''full file''' or '''changes only'''. LRM defaults to 'changes only' for most resource file types, but this can be modified in the <code>config_lrm_info.properties</code> configuration file. |
* '''Full file''': when some strings in a file need to be sent for translation, the entire file is sent |
* '''Full file''': when some strings in a file need to be sent for translation, the entire file is sent |
||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
In LRM parlance, the set of files sent to be translated is called a '''prep kit'''. Each prep kit has a '''kit number''' associated with it. |
In LRM parlance, the set of files sent to be translated is called a '''prep kit'''. Each prep kit has a '''kit number''' associated with it. |
||
| + | ==What about sequencing - when translations are returned in a different order?== |
||
If <code>messages.properties, errors.properties, and resources.properties</code> were sent for translation in kit 17 with a total of 243 strings to be translated in French, LRM is expecting back from the French translation the same 243 translated strings (based on their keys) from <code>messages.properties, errors.properties, and resources.properties</code>, as sent in kit 17. This may be different than the same files in kit 23, or what files currently reside in the repository for that project. |
If <code>messages.properties, errors.properties, and resources.properties</code> were sent for translation in kit 17 with a total of 243 strings to be translated in French, LRM is expecting back from the French translation the same 243 translated strings (based on their keys) from <code>messages.properties, errors.properties, and resources.properties</code>, as sent in kit 17. This may be different than the same files in kit 23, or what files currently reside in the repository for that project. |
||
Revision as of 20:26, 25 April 2019
Contents
- 1 Lingoport Resource Manager Overview
- 2 What Does the Lingoport Resource Manager Do?
- 3 What are the Major Benefits of LRM?
- 4 What Resource File Types are Supported?
- 5 Does the Resource Manager Compete with Translation Products?
- 6 Does the Resource Manager Help with Agile Processes?
- 7 What does the Resource Manager send when resource files are modified?
- 8 What about sequencing - when translations are returned in a different order?
Lingoport Resource Manager Overview
Lingoport Resource Manager (LRM) is a software product that bridges the gap between software development and the localization processes. It is geared toward project development organizations tackling globalization of their software so they can target international markets. The Lingoport Dashboard consumes LRM's reports to show translation status in a user-friendly display.
- Hand over resource files to translation.
- Process translated files received from translation.
On the project and globalization management side, the Lingoport Dashboard provides an up-to-date status of the resources and their translation by locale. A number of views are presented, with drill-down to the specific issues detected by the Lingoport Resource Manager.
The Dashboard permission settings allows a granular presentation of the Lingoport Resource Manager project so management, development, and/or the translation vendor can all benefit from the status.
What Does the Lingoport Resource Manager Do?
- The Lingoport Resource Manager provides a translation status for resource files.
- LRM facilitates and helps automate passing resource files from the development environment to the translation vendor and back.
- It validates and packages the resources to be sent for translation in a prep kit.
- When the corresponding prep kit is received from the localization vendor for a locale, LRM validates the translated files and adds the translated files to the source code repository.
- LRM notifies registered recipients on certain actions, such as sending files to be translated or receiving files from translation.
The overall process is managed using Jenkins and jobs developed by Lingoport to automate the process.
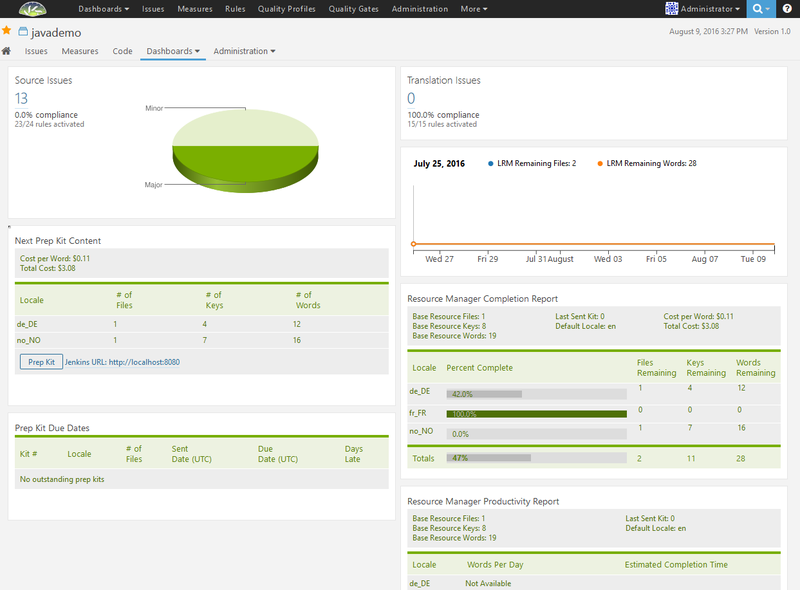
This image illustrates the Lingoport Resource Manager (LRM) Dashboard.
- Under Next Prep Kit Content, two locales (de_DE and no_NO - German and Norwegian) each have 1 file to be translated. There are 4 keys to be translated for German and 7 keys to be translated for Norwegian.
- Under Prep Kit Due Dates, it shows that there are no outstanding prep kits to come back from the translation management system.
- The Resource Manager Completion Report says that there is 1 Base Resource Files and it had 8 keys for a total of 19 words. The Default Locale is en (English).
- This project involves three locales: de_DE (German), fr_FR (French) and no_NO (Norwegian). German is 42% completed with 4 keys left to be translated. French is 100% translated and Norwegian is not translated at all.
- The Resource Manager Productivity Report summarizes the Words Per Day for each locale and estimates the Completion Time.
What are the Major Benefits of LRM?
This list captures some of the major benefits of the Lingoport Resource Manager (LRM):
- LRM integrates seamlessly, sending files from repositories to translation and back.
- LRM automates iterative, non-value-added file management tasks.
- LRM automates validation checking for common errors.
- LRM processes reduce human error.
- LRM provides an intuitive, real-time dashboard status overview for all stakeholders.
- LRM supports ease of deployment and operation.
- LRM bridges the gap between development and localization.
- LRM speeds localized resource turnaround time.
- LRM reduces human resource opportunity cost.
- LRM supports industry-standard development environments.
- LRM enhances Agile localization.
What Resource File Types are Supported?
See Supported Resource Bundles for an up to date list of supported resource file types.
Does the Resource Manager Compete with Translation Products?
No. Lingoport Resource Manager assists development organizations with automating error prone tasks, as well as managing and tracking resources for global readiness. The Resource Manager is not a translation tool nor is it a content management system (CMS).
Does the Resource Manager Help with Agile Processes?
Absolutely. Lingoport Resource Manager helps automate tasks. It also shows the status of the state of translation within the source code itself. It helps different software development cultures, in particular those applying Agile processes, by facilitating the tracking, sending, and receiving of resource kits. Non Agile processes do still benefit from the Resource Manager.
What does the Resource Manager send when resource files are modified?
LRM projects can be on-boarded as either full file or changes only. LRM defaults to 'changes only' for most resource file types, but this can be modified in the config_lrm_info.properties configuration file.
- Full file: when some strings in a file need to be sent for translation, the entire file is sent
- Changes only: When some strings in a file need to be sent for translation, only the part of the file with those strings is sent.
In LRM parlance, the set of files sent to be translated is called a prep kit. Each prep kit has a kit number associated with it.
What about sequencing - when translations are returned in a different order?
If messages.properties, errors.properties, and resources.properties were sent for translation in kit 17 with a total of 243 strings to be translated in French, LRM is expecting back from the French translation the same 243 translated strings (based on their keys) from messages.properties, errors.properties, and resources.properties, as sent in kit 17. This may be different than the same files in kit 23, or what files currently reside in the repository for that project.
When files are modified, the delta (either full file or changes only) from the previous kit number is sent. LRM handles the order in which the translations are returned. For instance, if LRM sends kits 101, 102, and 103 before any is returned, and 102 is returned in French before 101, 103 is returned in Russian, then 101 is returned in French, then 103, etc., LRM handles those sequencing. If 103 is returned before 102 in Japanese, 103 translations will be kept even if 102 contains the same strings.
Example
Suppose you have a Acme_en_US.properties file that is a combination of keys and values from several files and looks like:
# SOURCE_FILE C:/Users/janedoe/Desktop/mySource/javascript/example-source-javascript/Matrix.js
MATR_VIEWING_45=Viewing rows {0} to {1} of {2}
# SOURCE_FILE C:/Users/janedoe/Desktop/mySource/javascript/example-source-javascript/search3.js
SEAR_ALGORIT_50=algorithm
SEAR_AGGREGA_51=aggregated
SEAR_RECIPIE_52=recipient
SEAR_GREAT_53=great
SEAR_MONITOR_54=monitors
SEAR_LAUNCHE_55=launches
SEAR_PANES_56=panes
SEAR_LEVERAG_57=leverage
SEAR_SIGNIFI_58=significant
SEAR_ZONES_59=zones
SEAR_NUMERIC_60=numeric
SEAR_DAILY_61=daily
SEAR_LICK_62=lick
SEAR_OPTIONA_63=optionally
SEAR_MARK_64=mark
SEAR_UNABLE_65=unable
SEAR_CASES_66=cases
SEAR_DEVIATI_67=deviation
# SOURCE_FILE C:/Users/janedoe/Desktop/mySource/javascript/example-source-javascript/strings.js
STRI_HEREISA_46=here is a string
# SOURCE_FILE C:/Users/janedoe/Desktop/mySource/javascript/strings/CommonItemLibrary.js
COMM_PLEASES_47=Please select a valid departure date.
COMM_PLEASES_48=Please select a valid check in date.
COMM_PLEASES_49=Please select a valid check out date.
# SOURCE_FILE C:/Users/janedoe/Desktop/mySource/javascript/strings/travelPreferences.asp
TRAV_YOUHAVE_44=You have already added the maximum number of allowable hotels.
# SOURCE_FILE C:/Users/janedoe/Desktop/mySource/javascript/strings/travelPreferences.asp
TRAV_YOUHAVE_44=You have already added the maximum number of allowable hotels.
The prep kit will be sent to translation with all the keys and values and #Acme_1_5 - FULL-FILE to indicate that this is the first prep kit and it will translate everything. When this prep kit is imported, the project will be 100% translated for all locales.
If the following lines:
SEAR_DAILY_61=daily SEAR_LICK_62=lick SEAR_OPTIONA_63=optionally
are changed to:
SEAR_DAILY_61=one change SEAR_LICK_62=two modification SEAR_OPTIONA_63=three fix
The first prep kit has been sent and imported. The second prep kit will have the changes to the 1 file, 3 keys and 6 words. The file sent to be translated will look like:
#Acme_2_5 - CHANGES-ONLY SEAR_DAILY_61=one change SEAR_LICK_62=two modification SEAR_OPTIONA_63=three fix
If more keys are changed,
SEAR_OPTIONA_63=four changes SEAR_MARK_64=five for good SEAR_UNABLE_65=six half
Note that key SEAR_OPTIONA_63 has been changed in both prep kits. Create another prep kit (this one is #3), the prep kit sent will look like:
#Acme_3_5 - CHANGES-ONLY SEAR_OPTIONA_63=four changes SEAR_MARK_64=five for good SEAR_UNABLE_65=six half
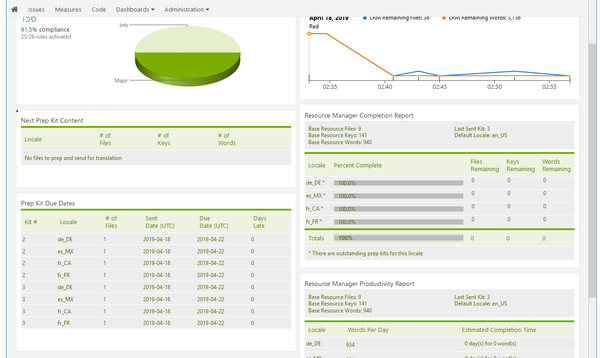
The Dashboard looks like:
The project has been 100% translated and two more prep kits are outstanding with changes.
If prep kit #3 is imported, the imported .properties files look like:
... SEAR_NUMERIC_60=numeric SEAR_DAILY_61=daily SEAR_LICK_62=lick SEAR_OPTIONA_63=four changes SEAR_MARK_64=five for good SEAR_UNABLE_65=six half SEAR_CASES_66=cases ...
If prep kit #2 is then imported, the imported .properties files look like:
... SEAR_NUMERIC_60=numeric SEAR_DAILY_61=one change SEAR_LICK_62=two modification SEAR_OPTIONA_63=four changes SEAR_MARK_64=five for good SEAR_UNABLE_65=six half SEAR_CASES_66=cases ...
Note that since SEAR_OPTIONA was changed for both prep kit #2 and #3, LRM remembered the order and kept the value from prep kit #3, even though the prep kits were imported in the reverse order.