Resource Files
Contents
What resource file types are supported by LRM?
Standard LRM extensions
- .htm and .html files using the html parser
- .json (Mostly JavaScript, and other programming languages) using the json parser
- .msg (C, C++, ...) using the msg parser
- .po files using the po parser
- .properties files (Java-type resources) using properties parser
- .resx files (used in the .Net world) using xml parser and the ResxParser.xml format definition
- .rc (Delphi, ...) using the rc parser
- .rjs (for JavaScript) using the js parser
- .rxml using the xml parser and the RxmlParser.xml format definition)
- .strings (Mobile iOS) using the strings parser
- strings.xml (Android) using the xml parser and the AndroidParser.xml format definition
- .txt files using the text parser
- .yaml, .yml using the yaml parser
Unique Extensions
Any file extension can be handled by LRM as long as the corresponding parser type is defined. The file must be able to be parsed correctly by the defined parser type or an error will occur.
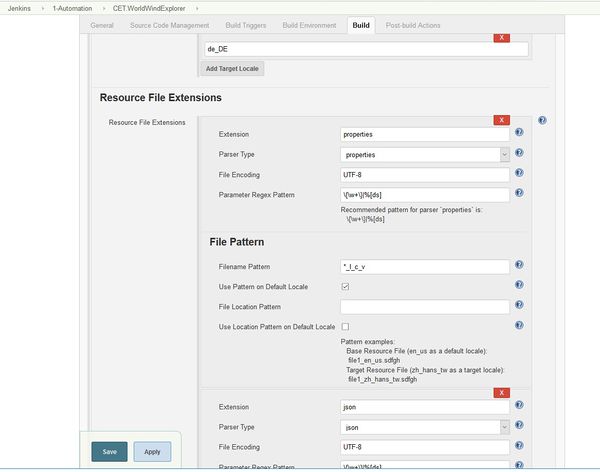
Above is an example configuring a Jenkins LRM project. The Extension is 'properties' and the Parser Type is 'properties' so LRM will recognize the file myfile_en_US.properties as a resource file. If the filename is myfile_en_US.prop, that would not be recognized as a properties resource file. Changing the Extension to 'prop' would allow myfile_en_US.prop to be recognized as a properties parser type file.
The parser types are:
- html parser
- js parser
- json parser
- msg parser
- po parser
- properties parser
- rc parser
- strings parser
- text parser
- xml parser
- yaml parser
How to work with unsupported File Types
LRM supports a number of file types out of the box (See above). However, other file types may represent user facing strings to be translated. In that case, some customization is required to on-board those projects. The bash script transform framework facilitates the customization.
Analyze the file types
If the file types fall into a category not supported by LRM out of the box, the first thing to do is to see what is the closest file types supported by LRM.
Use the transform framework
The transform framework needs three scripts in order to fit in with LRM. The three scripts need to be under the $JENKINS_HOME/lingoport/transform/<nameoftransform>/ directory.
The <nameoftransform> must be indicative of the type of transformation to apply. For instance, it could be loc to handle .loc files (see below). In that case, three scripts will need to be under /var/lib/jenkins/lingoport/transform/loc for a typical installation where the jenkins user is under /var/lib/jenkins.
The three scripts to write are:
- transform_from_repo.sh: How to transform the files from the repository so they fit into an LRM supported file type
- transform_to_repo.sh: How to transform translated/pseudo-localized files in an LRM supported file type into the repository file type
- transform_files_list.sh: How to transform the file names from the LRM supported file naming into the repository file naming
When those scripts are written, the transformation is defined in the config directory of the on-boarded project with the transform.properties. This file contains one properties, 'transform'. For instance, if loc is the directory with those three scripts under $JENKINS_HOME/lingoport/transform/ for a <PROJECT> under a <GROUP>, the file will be:
$JENKINS_HOME/Lingoport_Data/L10nStreamlining/<GROUP>/projects/<PROJECT>/config/transform.properties
transform=loc
Bash Variables
A few Bash variables are available when called from the Lingoport Jenkins jobs that use the transform framework. They are set before calling the transform framework.
- CLIENT_SOURCE_DIR : For an LRM project such as CET.json, the CLIENT_SOURCE_DIR would typically be ~jenkins/jobs/CET.json/workspace. Note: This is not necessarily the WORKSPACE of the running Jenkins job from which the transform is called (Dashboard Update for instance).
- LRM_GROUP_NAME : The name of the LRM Group Name (e.g. 'CET' )
- LRM_PROJECT_NAME : The name of the LRM Project Name (e.g. 'json' )
- TRANSFORM_DIR : The transform scripts directory (e.g. 'loc' )
Example: .loc files
Say the repository contains resource files like the following hmUiMessage.loc file:
;hmUiMessage.loc ;********************************************************************* #include hmUiMain.loc ;********************************************************************* message1 The first message message2 The second message message3 The third message message4 The fourth message
The file may not be in ASCII or UTF-8 format; For instance this file is in UTF-16BE
A supported file format that is close to this one is properties.
transform_from_repo.sh
An example snippet of bash code for this type of file may be something like:
#!/bin/bash
# Find all the files ending in 'loc'
find $CLIENT_SOURCE_DIR -name "*loc" > ~/tmp/input_files.txt
# Transform each .loc file into a .properties file
cat ~/tmp/input_files.txt | while read -r FILEPATH
do
FILENAME=`basename $FILEPATH`
DIRNAME=`dirname $FILEPATH`
file "$FILEPATH"
SUFFIX=".loc"
ROOTNAME=${FILEPATH%$SUFFIX}
TARGET="${ROOTNAME}.properties"
iconv -f UTF-16 -t UTF-8 -c "$FILEPATH" > "$TARGET"
sed -i 's/^#/# #/' "$TARGET"
sed -i 's/^;/# ;/' "$TARGET"
sed -i -e "s/[[:space:]]\+/=/" "$TARGET"
sed -i -e "s/^=$//" "$TARGET"
done
transform_to_repo.sh
An example snippet of bash code for this type of file may be something like:
#!/bin/bash
# Find all the files ending in .properties
find $CLIENT_SOURCE_DIR -name "*.properties" > ~/tmp/input_files.txt
#
# Transform each .properties into a .loc
#
cat ~/tmp/input_files.txt | while read -r FILEPATH
do
FILENAME=`basename $FILEPATH`
DIRNAME=`dirname $FILEPATH`
ls -l "$FILEPATH"
SUFFIX=".properties"
ROOTNAME=${FILEPATH%$SUFFIX}
TARGET="${ROOTNAME}.loc"
cp "$FILEPATH" "$TARGET"
sed -i 's/^#=#/#/' "$TARGET"
sed -i 's/^#=;/;/' "$TARGET"
sed -i -e "s/^#\([[:alnum:]]*\)/;\1/" "$TARGET"
sed -i -e "s/\([[:alnum:]]*\)=/\1\t/" "$TARGET"
iconv -f UTF-8 -t UTF-16 -c "$TARGET" > tmp.tmp
mv tmp.tmp "$TARGET"
done
transform_files_list.sh
An example snippet of bash code for this type of file may be something like:
#!/bin/bash
# Check if there is a parameter
if [ -z "$1" ]
then
echo "Error: Missing the argument like /<path>/pseudo_files.txt"
exit 1
fi
# If the file exists then do something, otherwise exit
if [ -f "$1" ]; then
echo " File to rewrite: $1"
else
echo " $1 not found"
exit 1
fi
# Rename .properties to .loc files inside the list of files passed as a parameter
sed -i 's/\.properties/.loc/' "$1"
Why are there files in my repository that end in _LRMLQA?
These are the LRM instrumented files that were created during the instrument resource files command. See LRM Instrumented Files for more information.
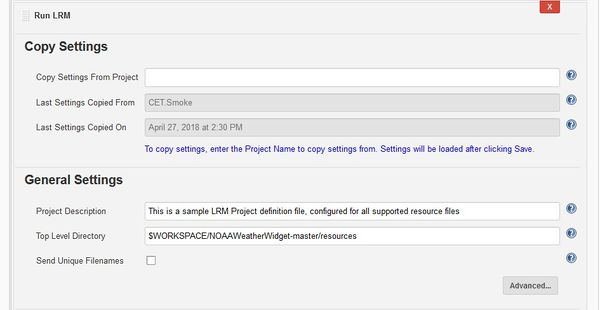
What is Send Unique Filenames?
When configuring an LRM project in Jenkins, under the General Settings, there is a checkbox for Send Unique Filenames.
This is defaulted to be unchecked. Check this box if the files to be translated have the same names, but are in different folders. For example if you have resource files in two directories, but the files themselves are the same names.
../first_en_US/values.json ../second_en_US/values.json
LRM sends only the files to be translated. Checking the Send Unique Filename box ensures that the files get unique names that are tracked and then returned to the correct location upon import.
For this example, if the default is left and it is unchecked, then a prep kit will be created for each file. For this example, two prep kits would be created and sent to be translated.