Difference between revisions of "Components Diagram"
(→Translation Systems) |
(→Translation Systems) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
== Translation Systems == |
== Translation Systems == |
||
| − | LRM connects seamlessly to translation systems. Out of the box, Lingotek and FTP are available. WorldServer can be added. Other systems may require some custom work to add |
+ | LRM connects seamlessly to translation systems. Out of the box, Lingotek and FTP are available. WorldServer can be added. Other tranlation systems may require some custom work to add to the framework without changes to the core installation. |
A translation system is typically set for an entire group of projects and can be specified for individual projects as well, using the <code>config_l10n_vendor.xml</code> file located either in the group or the project <code>config</code> directory: |
A translation system is typically set for an entire group of projects and can be specified for individual projects as well, using the <code>config_l10n_vendor.xml</code> file located either in the group or the project <code>config</code> directory: |
||
Revision as of 00:18, 14 October 2015
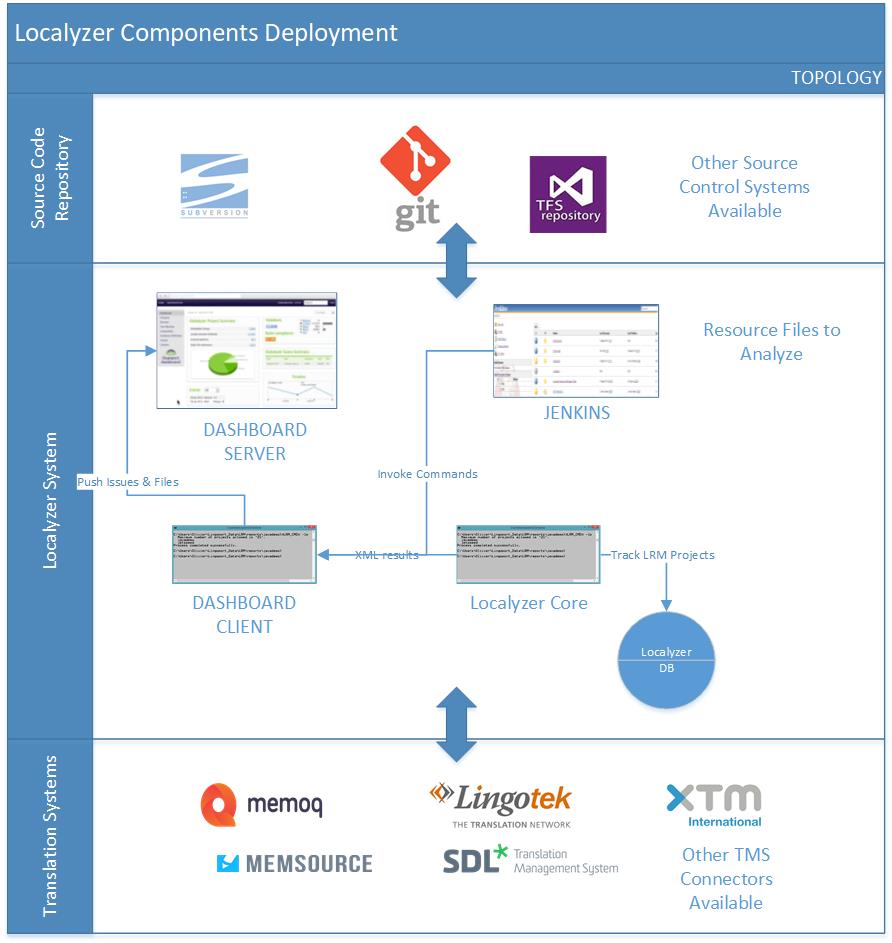
The following diagram describes a typical deployment for LRM. The LRM system must have access to the projects' repositories and the translation endpoints.
Contents
Repositories
Two repository types, SVN and Git, are supported out of the box. Many more can be added to the framework depending on the requirements, provided the repository types support command line calls. To configure the repository for a project once the LRM system has been installed and configured, please refer to this section: Project Configuration File.
The config_vcs.properties file defines the project repository configuration.
LRM System
LRM
LRM is composed of a number of jar files and configuration files. To install and configure LRM, please refer to the LRM Installation FAQ.
Jenkins
Jenkins orchestrates the different tasks and automates a number of LRM tasks by calling scripts. To install and configure Jenkins, please refer to these sections:
Dashboard
The Dashboard is composed of two parts, the Dashboard server and the Dashboard client. They can be set up on different systems if necessary.
Dashboard Server
The Dashboard server is a Web application and must be network accessible to the stakeholders, for instance development teams and management, localization managers, QA, and/or translators. It shows the status of the project.
Dashboard Client
The Dashboard client uses the results of LRM to push data to the Dashboard server.
Translation Systems
LRM connects seamlessly to translation systems. Out of the box, Lingotek and FTP are available. WorldServer can be added. Other tranlation systems may require some custom work to add to the framework without changes to the core installation.
A translation system is typically set for an entire group of projects and can be specified for individual projects as well, using the config_l10n_vendor.xml file located either in the group or the project config directory:
Lingotek
Lingotek provides a SaaS translation management system. To configure a project to send files back to forth to Lingotek, please refer to this section: http://wiki.lingoport.com/index.php5?title=Group_Configuration_Files#config_l10n_vendor.xml
FTP
A file transfer protocol (FTP) endpoint for outgoing files and one for incoming files can be configured. The files sent and received must conform to a naming and a structure convention. To configure a project to send files back and forth to FTP, please refer to this section: http://wiki.lingoport.com/index.php5?title=Group_Configuration_Files#config_l10n_vendor.xml